|
Castle Rings, Wiltshire
Castle Rings is a univallate hill fort in the parish of Donhead St Mary in Wiltshire in England.Wiltshire and Swindon History Centre 2011. The fort is a Scheduled Ancient Monument, with a list entry identification number of 1005698.Historic England. Castle Rings has been dated to the Iron Age and is situated at an altitude of upon Upper Greensand sandstone beds. The main bulk of the fort enclosure lies within the boundaries of Donhead St Mary parish but some of the outlying earthworks are situated in the neighbouring Sedgehill and Semley parish. In the mid-1980s a metal detectorist unearthed a hoard of stater coins of the Durotriges tribe within the hill fort. Lady Theodora Grosvenor described the fort in her 1867 book ''Motcombe, Past and Present'': Physical characteristics The rampart of the fort stands high with a deep ditch; the ditch is set between double earth banks. The ditch averages wide and varies in depth to a maximum of . The inner rampart has an average wid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entrance To Castle Rings Fort - Geograph
Entrance generally refers to the place of entering like a gate, door, or road or the permission to do so. Entrance may also refer to: * ''Entrance'' (album), a 1970 album by Edgar Winter * Entrance (display manager), a login manager for the X window manager * Entrance (liturgical), a kind of liturgical procession in the Eastern Orthodox tradition * Entrance (musician), born Guy Blakeslee * ''Entrance'' (film), a 2011 film * The Entrance, New South Wales, a suburb in Central Coast, New South Wales, Australia * "Entrance" (Dimmu Borgir song), from the 1997 album ''Enthrone Darkness Triumphant'' * Entry (cards), a card that wins a trick to which another player made the lead, as in the card game contract bridge * N-Trance, a British electronic music group formed in 1990 * University and college admissions * Entrance Hall * Entryway See also *Enter (other) *Entry (other) Entry may refer to: *Entry, West Virginia, an unincorporated community in the United States * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treasure Trove
A treasure trove is an amount of money or coin, gold, silver, plate, or bullion found hidden underground or in places such as cellars or attics, where the treasure seems old enough for it to be presumed that the true owner is dead and the heirs undiscoverable. An archaeological find of treasure trove is known as a hoard. The legal definition of what constitutes treasure trove and its treatment under law vary considerably from country to country, and from era to era. The term is also often used metaphorically. Collections of articles published as a book are often titled ''Treasure Trove'', as in ''A Treasure Trove of Science''. This was especially fashionable for titles of children's books in the early- and mid-20th century. Terminology ''Treasure trove'', sometimes rendered ''treasure-trove'', literally means "treasure that has been found". The English term ''treasure trove'' was derived from ''tresor trové'', the Anglo-French equivalent of the Latin legal term ''thesaurus i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheduled Monuments In Wiltshire
This is a list of scheduled monuments in Wiltshire. In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a "nationally important" archaeological site or historic building that has been given protection against unauthorised change by being placed on a list (or "schedule") by the Secretary of State for Culture, Media and Sport; English Heritage takes the leading role in identifying such sites. Scheduled monuments are defined in the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Areas Act 1979 and the National Heritage Act 1983. There are about 20,000 scheduled monument entries on the list, which is maintained by English Heritage; more than one site can be included in a single entry. While a scheduled monument can also be recognised as a listed building In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hill Forts In Wiltshire
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. It often has a distinct summit. Terminology The distinction between a hill and a mountain is unclear and largely subjective, but a hill is universally considered to be not as tall, or as steep as a mountain. Geographers historically regarded mountains as hills greater than above sea level, which formed the basis of the plot of the 1995 film ''The Englishman who Went up a Hill but Came down a Mountain''. In contrast, hillwalkers have tended to regard mountains as peaks above sea level. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' also suggests a limit of and Whittow states "Some authorities regard eminences above as mountains, those below being referred to as hills." Today, a mountain is usually defined in the UK and Ireland as any summit at least high, while the official UK government's definition of a mountain is a summit of or higher. Some definitions include a topographical prominence requirement, typically o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society For The Promotion Of Roman Studies
The Society for the Promotion of Roman Studies (The Roman Society) was founded in 1910 as the sister society to the Society for the Promotion of Hellenic Studies. The Society is the leading organisation in the United Kingdom for those interested in the study of Rome and the Roman Empire. Its scope covers Roman history, archaeology, literature and art. History of the society The society was founded at a public meeting in 1910, chaired by Frederic Kenyon, Director of the British Museum, and sponsored by Percy Gardner, George Macmillan, John Penoyre, Francis Haverfield, J. S. Reid, A. H. Smith, G. F. Hill , and G. H. Hallam. The Society's Memorandum and Articles of Association described its major aims as "...to promote Roman studies by creating a library, publishing a journal, and supporting the British School at Rome." The first issue of the ''Journal of Roman Studies'' was published in 1911. Early contributors included Francis Haverfield, Eugénie Strong, Albert Van Buren, Eliz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Numismatic Society
The British Numismatic Society (BNS) is an organisation for promoting and realization of the study of British coins and medals. It was founded in 1903. Publications Its principal publication is the ''British Numismatic Journal'', (published from 1903) commonly abbreviated to "BNJ" in academic references. Back issues of BNJ are free to read online, apart from the most recent three years' editions. The BNS publishes the separate books (especially catalogues of coins) and some serial publications. Library The BNS has the library combined and integrated with the library of the Royal Numismatic Society and located at the Warburg Institute. Membership Becoming a member of the British Numismatic Society is open to all for a £15 fee that covers the first two years of membership. Members have access to the Society's literature on coins and receive a copy of its annual journal. Awards *Sanford Saltus Gold Medal *Blunt Prize *North Book Prize See also *BNTA *Coins of the pound sterlin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle Rings, Donhead St Mary 03
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble. This is distinct from a palace, which is not fortified; from a fortress, which was not always a residence for royalty or nobility; from a ''pleasance'' which was a walled-in residence for nobility, but not adequately fortified; and from a fortified settlement, which was a public defence – though there are many similarities among these types of construction. Use of the term has varied over time and has also been applied to structures such as hill forts and 19th-20th century homes built to resemble castles. Over the approximately 900 years when genuine castles were built, they took on a great many forms with many different features, although some, such as curtain walls, arrowslits, and portcullises, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romano-British Culture
The Romano-British culture arose in Britain under the Roman Empire following the Roman conquest in AD 43 and the creation of the province of Britannia. It arose as a fusion of the imported Roman culture with that of the indigenous Britons, a people of Celtic language and custom. Scholars such as Christopher Snyder believe that during the 5th and 6th centuries – approximately from 410 when the Roman legions withdrew, to 597 when St Augustine of Canterbury arrived – southern Britain preserved an active sub-Roman culture that survived the attacks from the Anglo-Saxons and even used a vernacular Latin when writing. Arrival of the Romans Roman troops, mainly from nearby provinces, invaded in AD 43, in what is now part of England, during the reign of Emperor Claudius. Over the next few years the province of Britannia was formed, eventually including the whole of what later became England and Wales and parts of Scotland.Kinder, H. & Hilgemann W. ''The Penguin Atlas of World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
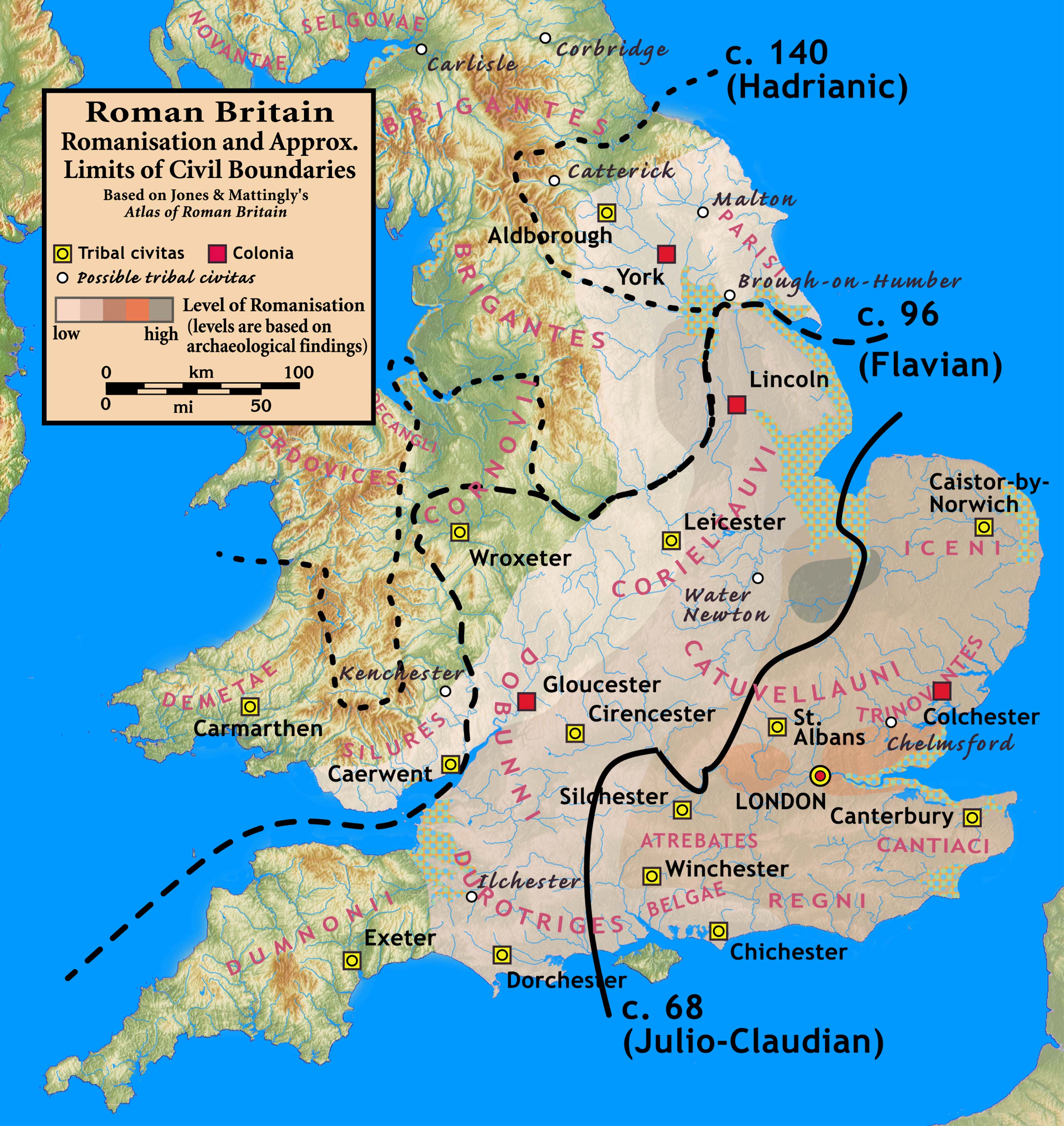
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered was raised to the status of a Roman province. Julius Caesar invaded Britain in 55 and 54 BC as part of his Gallic Wars. According to Caesar, the Britons had been overrun or culturally assimilated by other Celtic tribes during the British Iron Age and had been aiding Caesar's enemies. He received tribute, installed the friendly king Mandubracius over the Trinovantes, and returned to Gaul. Planned invasions under Augustus were called off in 34, 27, and 25 BC. In 40 AD, Caligula assembled 200,000 men at the Channel on the continent, only to have them gather seashells ('' musculi'') according to Suetonius, perhaps as a symbolic gesture to proclaim Caligula's victory over the sea. Three years later, Claudius directed four legi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potter's Wheel
In pottery, a potter's wheel is a machine used in the shaping (known as throwing) of clay into round ceramic ware. The wheel may also be used during the process of trimming excess clay from leather-hard dried ware that is stiff but malleable, and for applying incised decoration or rings of colour. Use of the potter's wheel became widespread throughout the Old World but was unknown in the Pre-Columbian New World, where pottery was handmade by methods that included coiling and beating. A potter's wheel may occasionally be referred to as a "potter's lathe". However, that term is better used for another kind of machine that is used for a different shaping process, turning, similar to that used for shaping of metal and wooden articles. The pottery wheel is an important component to create arts and craft products. The techniques of jiggering and jolleying can be seen as extensions of the potter's wheel: in jiggering, a shaped tool is slowly brought down onto the plastic clay body t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salisbury And South Wiltshire Museum
The Salisbury Museum (previously The Salisbury and South Wiltshire Museum) is a museum in Salisbury, Wiltshire, England. It houses one of the best collections relating to Stonehenge and local archaeology. The museum is housed in The King's House, Salisbury, The King's House, a Grade I listed building, where King James I of England was entertained in 1610 and 1613. Set in the surroundings of the Cathedral Close, the museum faces the west front of Salisbury Cathedral. Previously at 40-42 St Ann Street, where it had been founded in 1860 by Dr Richard Fowler (physician), Richard Fowler, FRS, it transferred to its current site in 1981. The original three-storey building, with mullioned and transom (architectural), transomed windows, ornate plaster ceilings and a fine baluster, oak-balustraded staircase, houses the main temporary exhibition gallery with the ceramics gallery above. The arms of James I's eldest son, Henry Frederick, Prince of Wales, can be seen in a window in the Wedgw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Monuments And Archaeological Areas Act 1979
The Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Areas Act 1979 or AMAAA was a law passed by the UK government, the latest in a series of Ancient Monument Acts legislating to protect the archaeological heritage of England & Wales and Scotland. Northern Ireland has its own legislation. Section 61(12) defines sites that warrant protection due to their being of national importance as 'ancient monuments'. These can be either scheduled monuments or "any other monument which in the opinion of the Secretary of State is of public interest by reason of the historic, architectural, traditional, artistic or archaeological interest attaching to it". If an ancient monument is scheduled then it gains additional legal protection. A monument is defined as: Damage to a scheduled monument is a criminal offence and any works taking place within one require scheduled monument consent from the Secretary of State. The Act also provides for taking ancient monuments into the care of the Secretary of Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |