|
Castle Carlton
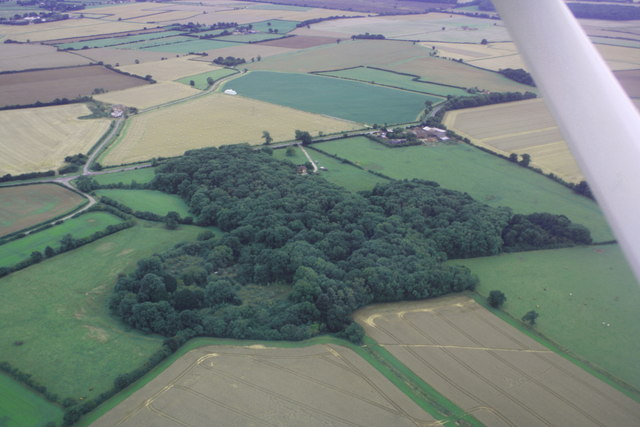
Castle Carlton is a hamlet and former civil parish, now in the parish of Reston, in the East Lindsey district of Lincolnshire, England. It is approximately south of Louth, and just north of the A157 road. In 1931 the parish had a population of 23. On 1 April 1936 the parish was abolished and merged with South Reston. At Castle Carlton, there is a wide moat surrounding a mound on which stood a twelfth-century motte and bailey castle, most likely wooden, founded by Justiciar Hugh Bardolph, who is said to have slain a monster. The village had established itself as a commercial centre by the thirteenth century, reputedly after Hugh Bardolph developed it as a "new town", and it was sometimes known as Market Carlton. Today, it is considered a deserted medieval village, or DMV. The church was dedicated to the Holy Cross and was a small Perpendicular building. It was demolished in 1902. References External links"Castle Carlton" Castlefacts.info. Retrieved 9 April 2013"Castle Car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toft Village
In England and Scotland, a toft village is a settlement comprising small and relatively closely packed farms (tofts) with the surrounding land owned and farmed by those who live in the village's buildings. Late Old English ''toft'', with Old English declension (plural) ''toftas'' > tofts. ''Toft'' as a placename element is usually dated to the Viking Age by place-name historians. Placenames ending in ''-toft'' are usually of Old Norse derivation, ''topt'' meaning "site of a house".''English Etymology'', T. F. Hoad, Oxford University Press 1993. Examples are Langtoft, Habertoft, Huttoft, Knaptoft, Lowestoft, Newtoft, Scraptoft, Sibbertoft, Stowlangtoft, Wibtoft, Yelvertoft and various places simply called Toft in the former Danelaw. This typical Old Norse element allows estimation of the extension of Scandinavian settlements in the Middle Ages such as in Schleswig-Holstein (''-toft'' : Langstoft, Havetoft, Koltoft, Goltoft, Kaltoft...), Normandy (''-tot'' : Lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Reston
South Reston is a village in the East Lindsey district of Lincolnshire, England. It is situated on the A157 road south-east from the town of Louth. The civil parish of South Reston was enlarged by the abolition of the parish of Castle Carlton in 1936. Today both villages form part of Reston civil parish . South Reston parish church was dedicated to Saint Edith; it was declared redundant by the Diocese of Lincoln in 1980, and demolished in 1982. The 15th-century octagonal font remains in the churchyard, as a sundial, and is Grade II listed. The Hall is a Grade II listed brick farmhouse dating from the 17th century. South Reston school was built in 1858 and survived long enough to celebrate its centenary. There is also a Methodist church and a public house A pub (short for public house) is a kind of drinking establishment which is licensed to serve alcoholic drinks for consumption on the premises. The term ''public house'' first appeared in the United Kingdom i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villages In Lincolnshire
A village is a clustered human settlement or Residential community, community, larger than a hamlet (place), hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Though villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture, and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a Church (building), church. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genuki
GENUKI is a genealogy web portal, run as a charitable trust. It "provides a virtual reference library of genealogical information of particular relevance to the UK and Ireland". It gives access to a large collection of information, with the emphasis on primary sources, or means to access them, rather than on existing genealogical research. Name The name derives from "GENealogy of the UK and Ireland", although its coverage is wider than this. From the GENUKI website: Structure The website has a well defined structure at four levels. * The first level is information that is common to all "the United Kingdom and Ireland". * The next level has information for each of England (see example) Ireland, Scotland, Wales, the Channel Islands and the Isle of Man. * The third level has information on each pre-1974 county of England and Wales, each of the pre-1975 counties of Scotland, each of the 32 counties of Ireland and each island of the Channel Islands (e.g. Cheshire, County Kerry an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perpendicular Gothic
Perpendicular Gothic (also Perpendicular, Rectilinear, or Third Pointed) architecture was the third and final style of English Gothic architecture developed in the Kingdom of England during the Late Middle Ages, typified by large windows, four-centred arches, straight vertical and horizontal lines in the tracery, and regular arch-topped rectangular panelling. Perpendicular was the prevailing style of Late Gothic architecture in England from the 14th century to the 17th century. Perpendicular was unique to the country: no equivalent arose in Continental Europe or elsewhere in the British Isles. Of all the Gothic architectural styles, Perpendicular was the first to experience a second wave of popularity from the 18th century on in Gothic Revival architecture. The pointed arches used in Perpendicular were often four-centred arches, allowing them to be rather wider and flatter than in other Gothic styles. Perpendicular tracery is characterized by mullions that rise verticall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deserted Medieval Village
In the United Kingdom, a deserted medieval village (DMV) is a former settlement which was abandoned during the Middle Ages, typically leaving no trace apart from earthworks or cropmarks. If there are fewer than three inhabited houses the convention is to regard the site as deserted; if there are more than three houses, it is regarded as a shrunken medieval village. There are estimated to be more than 3,000 DMVs in England alone. Other deserted settlements Not all sites are medieval: villages reduced in size or disappeared over a long period, from as early as Anglo-Saxon times to as late as the 1960s, due to numerous different causes. Reasons for desertion Over the centuries, settlements have been deserted as a result of natural events, such as rivers changing course or silting up, flooding (especially during the wet 13th and 14th centuries) as well as coastal and estuarine erosion or being overwhelmed by windblown sand. Many were thought to have been abandoned due to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justiciar
Justiciar is the English form of the medieval Latin term ''justiciarius'' or ''justitiarius'' ("man of justice", i.e. judge). During the Middle Ages in England, the Chief Justiciar (later known simply as the Justiciar) was roughly equivalent to a modern Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, as the monarch's chief minister. Similar positions existed in continental Europe, particularly in Norman Italy and in the Carolingian Empire. A similar office was formed in Scotland, although there were usually two or three – the Justiciar of Scotia, the Justiciar of Lothian and, in the 13th century, the Justiciar of Galloway. These offices later evolved into a national one called Lord Justice-General. The modern title is Lord President of the Court of Session. The Justiciar of Ireland was an office established during the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland and was a key tool in its colonisation. Following the conquest of the Principality of Wales in the 13th century, the areas that becam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlton Castle
Castle Hill is the name given to the once substantial motte and bailey, perhaps double bailey, apparently associated with the then new town of Castle Carlton in the county of Lincolnshire, some 7 miles south-east of Louth Louth may refer to: Australia *Hundred of Louth, a cadastral unit in South Australia * Louth, New South Wales, a town *Louth Bay, a bay in South Australia **Louth Bay, South Australia, a town and locality Canada * Louth, Ontario Ireland * County ..., between the villages of North and South Reston (). It was founded in the 12th century by Hugh Bardolf. References *Fry, Plantagenet Somerset, ''The David & Charles Book of Castles'', David & Charles, 1980. Castles in Lincolnshire {{England-castle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motte And Bailey
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively easy to build with unskilled labour, but still militarily formidable, these castles were built across northern Europe from the 10th century onwards, spreading from Normandy and Anjou in France, into the Holy Roman Empire in the 11th century. The Normans introduced the design into England and Wales. Motte-and-bailey castles were adopted in Scotland, Ireland, the Low Countries and Denmark in the 12th and 13th centuries. Windsor Castle, in England, is an example of a motte-and-bailey castle. By the end of the 13th century, the design was largely superseded by alternative forms of fortification, but the earthworks remain a prominent feature in many countries. Architecture Structures A motte-and-bailey castle was made up of two structures: a mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Vision Of Britain Through Time
The Great Britain Historical GIS (or GBHGIS) is a Spatial Database, spatially enabled database that documents and visualises the changing human geography of the British Isles, although is primarily focussed on the subdivisions of the United Kingdom mainly over the 200 years since the first Census Act 1800, census in 1801. The project is currently based at the University of Portsmouth, and is the provider of the website ''A Vision of Britain through Time''. NB: A "GIS" is a geographic information system, which combines map information with statistical analysis, statistical data to produce a visual picture of the iterations or popularity of a particular set of statistics, overlaid on a map of the geographic area of interest. Original GB Historical GIS (1994–99) The first version of the GB Historical GIS was developed at Queen Mary, University of London between 1994 and 1999, although it was originally conceived simply as a mapping extension to the existing Labour Markets Database ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croft (land)
A croft is a fenced or enclosed area of land, usually small and arable, and usually, but not always, with a crofter's dwelling thereon. A crofter is one who has tenure and use of the land, typically as a tenant farmer, especially in rural areas. Etymology The word ''croft'' is West Germanic in etymology and is now most familiar in Scotland, most crofts being in the Highlands and Islands area. Elsewhere the expression is generally archaic. In Scottish Gaelic, it is rendered (, plural ). Legislation in Scotland The Scottish croft is a small agricultural landholding of a type that has been subject to special legislation applying to the Scottish Highlands since 1886. The legislation was largely a response to the complaints and demands of tenant families who were victims of the Highland Clearances. The modern crofters or tenants appear very little in evidence before the beginning of the 18th century. They were tenants at will underneath the tacksman and wadsetters, but pra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |