|
Casorati–Weierstrass Theorem
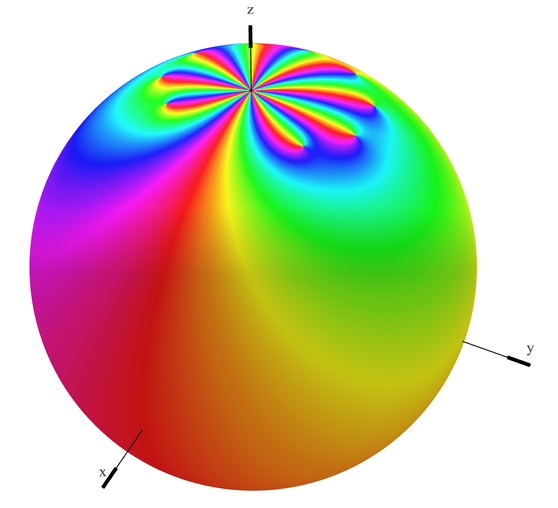
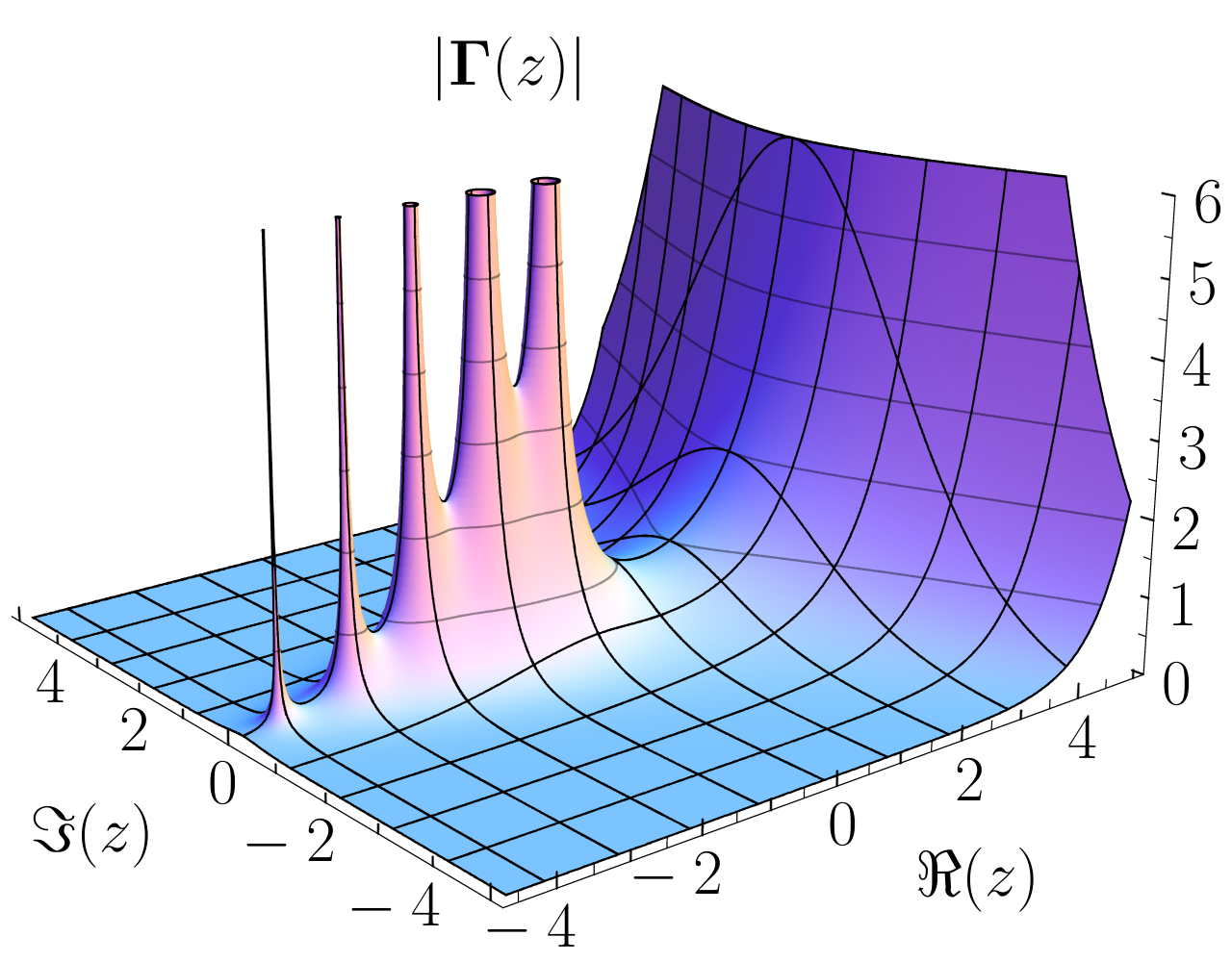
In complex analysis, a branch of mathematics, the Casorati–Weierstrass theorem describes the behaviour of holomorphic functions near their essential singularities. It is named for Karl Theodor Wilhelm Weierstrass and Felice Casorati. In Russian literature it is called Sokhotski's theorem. Formal statement of the theorem Start with some open subset U in the complex plane containing the number z_0, and a function f that is holomorphic on U \setminus \, but has an essential singularity at z_0 . The ''Casorati–Weierstrass theorem'' then states that This can also be stated as follows: Or in still more descriptive terms: The theorem is considerably strengthened by Picard's great theorem, which states, in the notation above, that f assumes ''every'' complex value, with one possible exception, infinitely often on V. In the case that f is an entire function and a = \infty, the theorem says that the values f(z) approach every complex number and \infty, as z tends to infi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Analysis
Complex analysis, traditionally known as the theory of functions of a complex variable, is the branch of mathematical analysis that investigates Function (mathematics), functions of complex numbers. It is helpful in many branches of mathematics, including algebraic geometry, number theory, analytic combinatorics, applied mathematics; as well as in physics, including the branches of hydrodynamics, thermodynamics, and particularly quantum mechanics. By extension, use of complex analysis also has applications in engineering fields such as nuclear engineering, nuclear, aerospace engineering, aerospace, mechanical engineering, mechanical and electrical engineering. As a differentiable function of a complex variable is equal to its Taylor series (that is, it is Analyticity of holomorphic functions, analytic), complex analysis is particularly concerned with analytic functions of a complex variable (that is, holomorphic functions). History Complex analysis is one of the classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taylor Series
In mathematics, the Taylor series or Taylor expansion of a function is an infinite sum of terms that are expressed in terms of the function's derivatives at a single point. For most common functions, the function and the sum of its Taylor series are equal near this point. Taylor series are named after Brook Taylor, who introduced them in 1715. A Taylor series is also called a Maclaurin series, when 0 is the point where the derivatives are considered, after Colin Maclaurin, who made extensive use of this special case of Taylor series in the mid-18th century. The partial sum formed by the first terms of a Taylor series is a polynomial of degree that is called the th Taylor polynomial of the function. Taylor polynomials are approximations of a function, which become generally better as increases. Taylor's theorem gives quantitative estimates on the error introduced by the use of such approximations. If the Taylor series of a function is convergent, its sum is the limit of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur J
Arthur is a common male given name of Brythonic origin. Its popularity derives from it being the name of the legendary hero King Arthur. The etymology is disputed. It may derive from the Celtic ''Artos'' meaning “Bear”. Another theory, more widely believed, is that the name is derived from the Roman clan '' Artorius'' who lived in Roman Britain for centuries. A common spelling variant used in many Slavic, Romance, and Germanic languages is Artur. In Spanish and Italian it is Arturo. Etymology The earliest datable attestation of the name Arthur is in the early 9th century Welsh-Latin text '' Historia Brittonum'', where it refers to a circa 5th to 6th-century Briton general who fought against the invading Saxons, and who later gave rise to the famous King Arthur of medieval legend and literature. A possible earlier mention of the same man is to be found in the epic Welsh poem ''Y Gododdin'' by Aneirin, which some scholars assign to the late 6th century, though this is still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Collingwood
Sir Edward Foyle Collingwood LLD (17 January 1900 – 25 October 1970) was an English mathematician and scientist. He was a member of the Eglingham branch of a prominent Northumbrian family, the son of Col. Cuthbert Collingwood of the Lancashire Fusiliers, whose family seat was at Lilburn Tower, near Wooler, Northumberland. His great grandfather was a brother of Admiral Lord Collingwood. Life Collingwood was born at his family home, Lilburn Tower, near Wooler in Northumberland, the son of Col. Cuthbert George Collingwood and his wife, Dorothy Fawcett. Collingwood was educated at the Royal Naval College, Osborne, on the Isle of Wight and at Dartmouth Royal Naval College and was commissioned into the Royal Navy. By arrangement his first service was aboard the dreadnought battleship HMS ''Collingwood'' but his naval career was cut short during World War I when in 1916 he was invalided out of the Navy following an accidental injury. In 1918 he enrolled to study mathematics at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Removable Singularity
In complex analysis, a removable singularity of a holomorphic function is a point at which the function is undefined, but it is possible to redefine the function at that point in such a way that the resulting function is regular in a neighbourhood of that point. For instance, the (unnormalized) sinc function : \text(z) = \frac has a singularity at . This singularity can be removed by defining \text(0) := 1, which is the limit of as tends to 0. The resulting function is holomorphic. In this case the problem was caused by being given an indeterminate form. Taking a power series expansion for \frac around the singular point shows that : \text(z) = \frac\left(\sum_^ \frac \right) = \sum_^ \frac = 1 - \frac + \frac - \frac + \cdots. Formally, if U \subset \mathbb C is an open subset of the complex plane \mathbb C, a \in U a point of U, and f: U\setminus \ \rightarrow \mathbb C is a holomorphic function, then a is called a removable singularity for f if there exists a holomorph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Removable Singularity
In complex analysis, a removable singularity of a holomorphic function is a point at which the function is undefined, but it is possible to redefine the function at that point in such a way that the resulting function is regular in a neighbourhood of that point. For instance, the (unnormalized) sinc function : \text(z) = \frac has a singularity at . This singularity can be removed by defining \text(0) := 1, which is the limit of as tends to 0. The resulting function is holomorphic. In this case the problem was caused by being given an indeterminate form. Taking a power series expansion for \frac around the singular point shows that : \text(z) = \frac\left(\sum_^ \frac \right) = \sum_^ \frac = 1 - \frac + \frac - \frac + \cdots. Formally, if U \subset \mathbb C is an open subset of the complex plane \mathbb C, a \in U a point of U, and f: U\setminus \ \rightarrow \mathbb C is a holomorphic function, then a is called a removable singularity for f if there exists a holomorph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pole (complex Analysis)
In complex analysis (a branch of mathematics), a pole is a certain type of singularity of a complex-valued function of a complex variable. In some sense, it is the simplest type of singularity. Technically, a point is a pole of a function if it is a zero of the function and is holomorphic in some neighbourhood of (that is, complex differentiable in a neighbourhood of ). A function is meromorphic in an open set if for every point of there is a neighborhood of in which either or is holomorphic. If is meromorphic in , then a zero of is a pole of , and a pole of is a zero of . This induces a duality between ''zeros'' and ''poles'', that is fundamental for the study of meromorphic functions. For example, if a function is meromorphic on the whole complex plane plus the point at infinity, then the sum of the multiplicities of its poles equals the sum of the multiplicities of its zeros. Definitions A function of a complex variable is holomorphic in an open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zero (complex Analysis)
In complex analysis (a branch of mathematics), a pole is a certain type of singularity of a complex-valued function of a complex variable. In some sense, it is the simplest type of singularity. Technically, a point is a pole of a function if it is a zero of the function and is holomorphic in some neighbourhood of (that is, complex differentiable in a neighbourhood of ). A function is meromorphic in an open set if for every point of there is a neighborhood of in which either or is holomorphic. If is meromorphic in , then a zero of is a pole of , and a pole of is a zero of . This induces a duality between ''zeros'' and ''poles'', that is fundamental for the study of meromorphic functions. For example, if a function is meromorphic on the whole complex plane plus the point at infinity, then the sum of the multiplicities of its poles equals the sum of the multiplicities of its zeros. Definitions A function of a complex variable is holomorphic in an open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meromorphic Function
In the mathematical field of complex analysis, a meromorphic function on an open subset ''D'' of the complex plane is a function that is holomorphic on all of ''D'' ''except'' for a set of isolated points, which are poles of the function. The term comes from the Greek ''meros'' ( μέρος), meaning "part". Every meromorphic function on ''D'' can be expressed as the ratio between two holomorphic functions (with the denominator not constant 0) defined on ''D'': any pole must coincide with a zero of the denominator. Heuristic description Intuitively, a meromorphic function is a ratio of two well-behaved (holomorphic) functions. Such a function will still be well-behaved, except possibly at the points where the denominator of the fraction is zero. If the denominator has a zero at ''z'' and the numerator does not, then the value of the function will approach infinity; if both parts have a zero at ''z'', then one must compare the multiplicity of these zeros. From an algebraic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Plane
In mathematics, the complex plane is the plane formed by the complex numbers, with a Cartesian coordinate system such that the -axis, called the real axis, is formed by the real numbers, and the -axis, called the imaginary axis, is formed by the imaginary numbers. The complex plane allows a geometric interpretation of complex numbers. Under addition, they add like vectors. The multiplication of two complex numbers can be expressed more easily in polar coordinates—the magnitude or ''modulus'' of the product is the product of the two absolute values, or moduli, and the angle or ''argument'' of the product is the sum of the two angles, or arguments. In particular, multiplication by a complex number of modulus 1 acts as a rotation. The complex plane is sometimes known as the Argand plane or Gauss plane. Notational conventions Complex numbers In complex analysis, the complex numbers are customarily represented by the symbol ''z'', which can be separated into its real (''x'') an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Circle
In mathematics, a unit circle is a circle of unit radius—that is, a radius of 1. Frequently, especially in trigonometry, the unit circle is the circle of radius 1 centered at the origin (0, 0) in the Cartesian coordinate system in the Euclidean plane. In topology, it is often denoted as because it is a one-dimensional unit -sphere. If is a point on the unit circle's circumference, then and are the lengths of the legs of a right triangle whose hypotenuse has length 1. Thus, by the Pythagorean theorem, and satisfy the equation x^2 + y^2 = 1. Since for all , and since the reflection of any point on the unit circle about the - or -axis is also on the unit circle, the above equation holds for all points on the unit circle, not only those in the first quadrant. The interior of the unit circle is called the open unit disk, while the interior of the unit circle combined with the unit circle itself is called the closed unit disk. One may also use other notions of "dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Value
In mathematics, the absolute value or modulus of a real number x, is the non-negative value without regard to its sign. Namely, , x, =x if is a positive number, and , x, =-x if x is negative (in which case negating x makes -x positive), and For example, the absolute value of 3 and the absolute value of −3 is The absolute value of a number may be thought of as its distance from zero. Generalisations of the absolute value for real numbers occur in a wide variety of mathematical settings. For example, an absolute value is also defined for the complex numbers, the quaternions, ordered rings, fields and vector spaces. The absolute value is closely related to the notions of magnitude, distance, and norm in various mathematical and physical contexts. Terminology and notation In 1806, Jean-Robert Argand introduced the term ''module'', meaning ''unit of measure'' in French, specifically for the ''complex'' absolute value,Oxford English Dictionary, Draft Revision, June 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |