|
Carryover (chemical) , in power generation
{{disambig ...
Carryover may refer to: * Carryover effect, in automated analyzer * Carryover basis, in taxation * Carryover cooking * Carryover with steam Carryover with steam, in steam technology, refers to transport of moisture and impurities with steam. The moisture carryover with steam is quantified by the mass flow rate of liquid water per mass flow rate of steam. In boilers producing saturated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carryover Effect
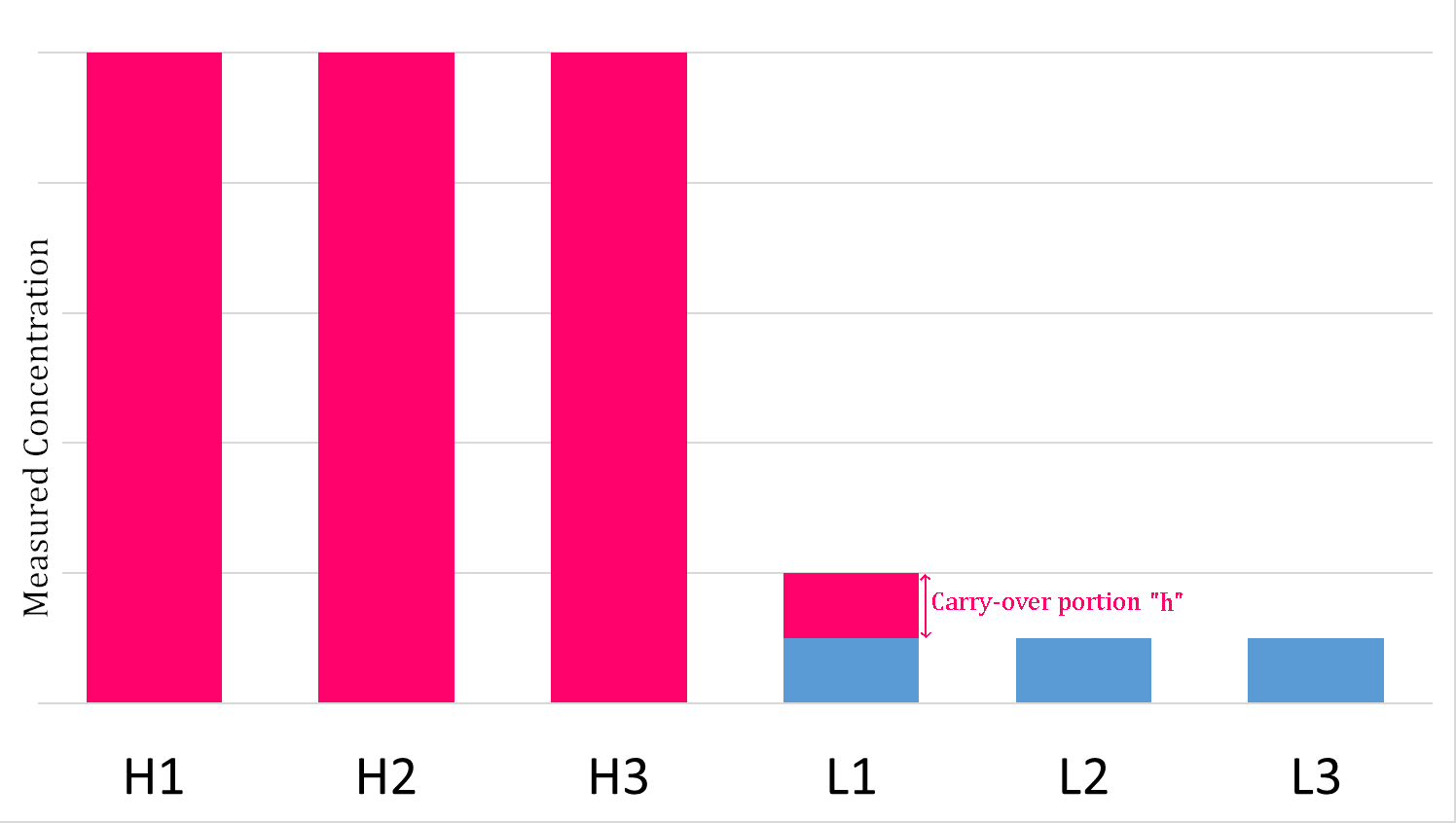
The carryover effect is a term used in clinical chemistry to describe the transfer of unwanted material from one container or mixture to another. It describes the influence of one sample upon the following one. It may be from a specimen, or a reagent, or even the washing medium. The significance of carry over is that even a small amount can lead to erroneous results. Carryover effect in clinical laboratory Carryover experiments are widely used for clinical chemistry and immunochemistry analyzers to evaluate and validate carryover effects. The pipetting and washing systems in an automated analyzer are designed to continuously cycle between the aspiration of patient specimens and cleaning. An obvious concern is a potential for carryover of analyte from one patient specimen into one or more following patient specimens, which can falsely increase or decrease the measured analyte concentration. Specimen carryover is typically addressed by judicious choice of probe material, probe de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carryover Basis
Carryover basis occurs when a property transfer also results in a transfer of the transferor's basis in the property. The transferor's basis in the property "carries over" to the transferee. Tax law of United States of America Carryover basis, also referred to as a ''transferred basis'', applies to inter vivos gifts and transfers in trust. Generally, a taxpayer's basis in property is the cost to acquire the property. However, there is an exception for inter vivos gifts and transfers in trust. For gifts, to calculate a gain, the donee has the same basis in the property as the donor's adjusted basis in the property. The same rule applies for calculating a loss, unless the donor's adjusted basis is greater than the fair market value of the property at the time of the gift. In this case, the loss does not carry over and the basis is the fair market value of the property at the time of the gift. Example In 1998, Mother purchased a lamp for $20. In 2000, Mother gifted the lamp to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carryover Cooking
Carryover cooking (sometimes referred to as resting) is when foods are halted from actively cooking and allowed to equilibrate under their own retained heat. Because foods such as meats are typically measured for cooking temperature near the center of mass, stopping cooking at a given central temperature means that the outer layers of the food will be at higher temperature than that measured. Heat therefore will continue to migrate inwards from the surface, and the food will cook further even after being removed from the source of heat. Carryover cooking is often used as a finishing step in preparation of foods that are roasted or grilled, and should be accounted for in recipes as it can increase the internal temperature of foods by temperatures between 5 and 25 degrees Fahrenheit (3–14°C). The larger and denser the object being heated, the greater the amount of temperature increase due to carryover cooking. Resting, when used as a synonym for carryover cooking, also refers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |