|
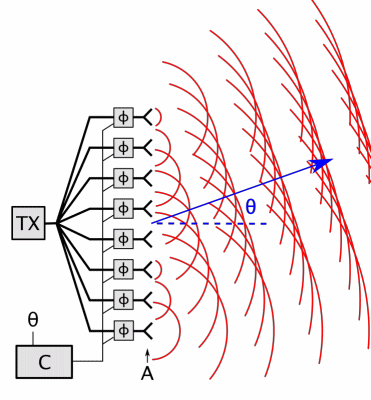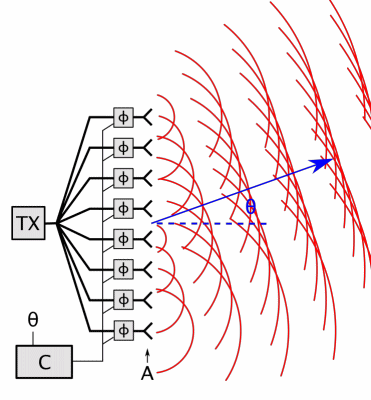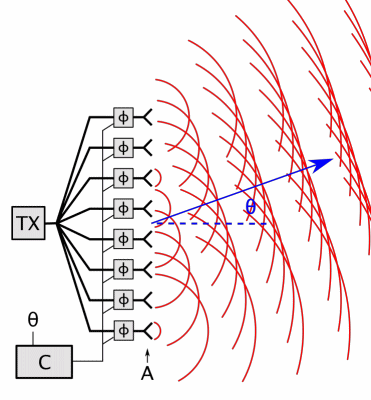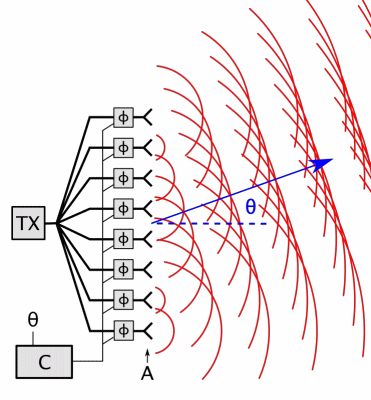
Carrier Interferometry
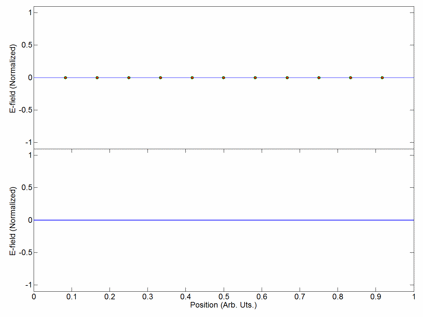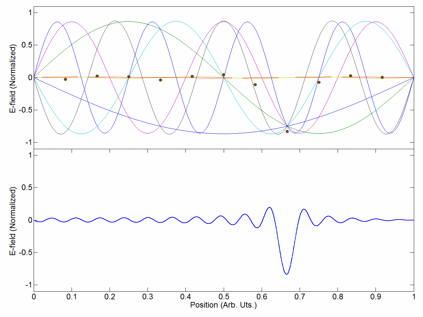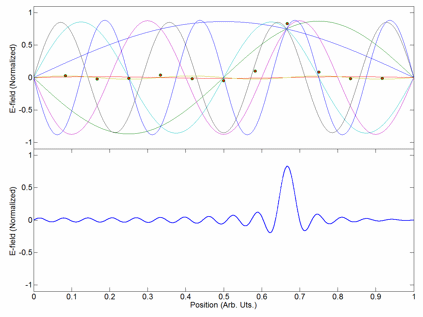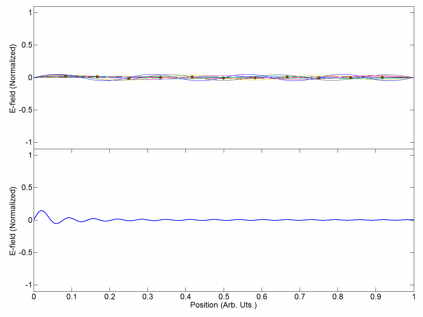
Carrier Interferometry (CI) is a spread spectrum scheme designed to be used in an Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) communication system for multiplexing and multiple access, enabling the system to support multiple users at the same time over the same frequency band. Like MC-CDMA, CI-OFDM spreads each data symbol in the frequency domain. That is, each data symbol is carried over multiple OFDM subcarriers. But unlike MC-CDMA, which uses binary-phase Hadamard codes (code values of 0 or 180 degrees) or binary pseudonoise, CI codes are complex-valued orthogonal codes. In the simplest case, CI code values are coefficients of a discrete Fourier transform (DFT) matrix. Each row or column of the DFT matrix provides an orthogonal CI spreading code which spreads a data symbol. Spreading is achieved by multiplying a vector of data symbols by the DFT matrix to produce a vector of coded data symbols, then each coded data symbol is mapped to an OFDM subcarrier via an input bin o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spread Spectrum
In telecommunication and radio communication, spread-spectrum techniques are methods by which a signal (e.g., an electrical, electromagnetic, or acoustic signal) generated with a particular bandwidth is deliberately spread in the frequency domain, resulting in a signal with a wider bandwidth. These techniques are used for a variety of reasons, including the establishment of secure communications, increasing resistance to natural interference, noise, and jamming, to prevent detection, to limit power flux density (e.g., in satellite downlinks), and to enable multiple-access communications. Telecommunications Spread spectrum generally makes use of a sequential noise-like signal structure to spread the normally narrowband information signal over a relatively wideband (radio) band of frequencies. The receiver correlates the received signals to retrieve the original information signal. Originally there were two motivations: either to resist enemy efforts to jam the communications ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency-shift Keying
Frequency-shift keying (FSK) is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is transmitted through discrete frequency changes of a carrier signal. The technology is used for communication systems such as telemetry, weather balloon radiosondes, caller ID, garage door openers, and low frequency radio transmission in the VLF and ELF bands. The simplest FSK is binary FSK (BFSK). BFSK uses a pair of discrete frequencies to transmit binary (0s and 1s) information. With this scheme, the 1 is called the mark frequency and the 0 is called the space frequency. Modulating and demodulating Reference implementations of FSK modems exist and are documented in detail. The demodulation of a binary FSK signal can be done using the Goertzel algorithm very efficiently, even on low-power microcontrollers. Variations Multiple frequency-shift keying Continuous-phase frequency-shift keying In principle FSK can be implemented by using completely independent free-running oscillat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcarrier Multiplexing
Subcarrier Multiplexing (SCM) is a method for combining (multiplexing) many different communications signals so that they can be transmitted along a single optical fiber. SCM (also known as SCMA, SubCarrier Multiple Access) is used in passive optical network (PON) access infrastructures as a variant of wavelength division multiplexing In fiber-optic communications, wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) is a technology which multiplexes a number of optical carrier signals onto a single optical fiber by using different wavelengths (i.e., colors) of laser light. This techniq ... (WDM). SCM follows a different approach compared to WDM. In WDM an optical carrier is modulated with a baseband signal of typically hundred of Mbit/s. In an SCMA infrastructure, the baseband data is first modulated on a GHz wide subcarrier, that is subsequently modulated on the optical carrier. This way each signal occupies a different portion of the optical spectrum surrounding the centre frequency of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crest Factor
Crest or CREST may refer to: Buildings *The Crest (Huntington, New York), a historic house in Suffolk County, New York *"The Crest", an alternate name for 63 Wall Street, in Manhattan, New York *Crest Castle (Château Du Crest), Jussy, Switzerland *Crest House, a building, now in ruins, at the summit of Mount Evans in Colorado *Crest Theatre, a historic theatre in downtown Sacramento, California *Crest Theatre, formerly Majestic Crest Theatre, Los Angeles, California *Crest Theatre, in Old School Square, Delray Beach, Florida Business or commerce *Crest (toothpaste), a brand of toothpaste *Crest Audio, an American manufacturer of power amplifiers and mixing consoles *Crest Animation Productions, an animation studio in Burbank, California * Crest Animation Studios, an animation studio in India *Crest Books, an imprint of now defunct Fawcett Publications *Crest Hotels, a defunct hotel chain in the UK * Crest Manufacturing Company, producer of the Crestmobile automobile in the 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software-defined Radio
Software-defined radio (SDR) is a radio communication system where components that have been traditionally implemented in analog hardware (e.g. mixers, filters, amplifiers, modulators/demodulators, detectors, etc.) are instead implemented by means of software on a personal computer or embedded system. While the concept of SDR is not new, the rapidly evolving capabilities of digital electronics render practical many processes which were once only theoretically possible. A basic SDR system may consist of a personal computer equipped with a sound card, or other analog-to-digital converter, preceded by some form of RF front end. Significant amounts of signal processing are handed over to the general-purpose processor, rather than being done in special-purpose hardware (electronic circuits). Such a design produces a radio which can receive and transmit widely different radio protocols (sometimes referred to as waveforms) based solely on the software used. Software radios have signif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Antenna System
A distributed antenna system, or DAS, is a network of spatially separated antenna nodes connected to a common source via a transport medium that provides wireless service within a geographic area or structure. DAS antenna elevations are generally at or below the clutter level, and node installations are compact. A distributed antenna system may be deployed indoors (an iDAS) or outdoors (an oDAS). Concept As illustrated in the figure, the idea is to split the transmitted power among several antenna elements, separated in space so as to provide coverage over the same area as a single antenna but with reduced total power and improved reliability. A single antenna radiating at high power (a) is replaced by a group of low-power antennas to cover the same area (b). The idea was described in a paper by Saleh et al. in 1987. These antennas have recently been employed by several service providers in many areas around the United States. DAS is often used in scenarios where alternate tec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Delay Diversity
Cyclic Delay Diversity (CDD) is a diversity scheme used in OFDM-based telecommunication systems, transforming spatial diversity into frequency diversity and thus avoiding intersymbol interference. CDD was introduced in 2001 and can gain frequency diversity at the receiver without changing the SISO receiver structure. The idea of CDD for OFDM had previously also been submitted as a patent application in September 2000. References * Louay M.A. Jalloul and Sam. P. Alex, "Evaluation Methodology and Performance of an IEEE 802.16e System", Presented to the IEEE Communications and Signal Processing Society, Orange County Joint Chapter (ComSig), December 7, 2006. Available at: https://web.archive.org/web/20110414143801/http://chapters.comsoc.org/comsig/meet.html * A. Dammann and S. KaiserPerformance of low complex antenna diversity techniques for mobile OFDM systems In Proceedings 3rd International Workshop on Multi-Carrier Spread-Spectrum & Related Topics (MC-SS 2001), Oberpfaffenhofen, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phased Array
In antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled array of antennas which creates a beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the antennas. In a simple array antenna, the radio frequency current from the transmitter is fed to multiple individual antenna elements with the proper phase relationship so that the radio waves from the separate elements combine ( superpose) to form beams, to increase power radiated in desired directions and suppress radiation in undesired directions. In a phased array, the power from the transmitter is fed to the radiating elements through devices called ''phase shifters'', controlled by a computer system, which can alter the phase or signal delay electronically, thus steering the beam of radio waves to a different direction. Since the size of an antenna array must extend many wavelengths to achieve the high gain needed for narrow bea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIMO
In radio, multiple-input and multiple-output, or MIMO (), is a method for multiplying the capacity of a radio link using multiple transmission and receiving antennas to exploit multipath propagation. MIMO has become an essential element of wireless communication standards including IEEE 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4), IEEE 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5), HSPA+ (3G), WiMAX, and Long Term Evolution (LTE). More recently, MIMO has been applied to power-line communication for three-wire installations as part of the ITU G.hn standard and of the HomePlug AV2 specification. At one time, in wireless the term "MIMO" referred to the use of multiple antennas at the transmitter and the receiver. In modern usage, "MIMO" specifically refers to a class of techniques for sending and receiving more than one data signal simultaneously over the same radio channel by exploiting multipath propagation. Additionally, modern MIMO usage often refers to multiple data signals sent to different receivers (with one or more receiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiber-optic Communication
Fiber-optic communication is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of infrared light through an optical fiber. The light is a form of carrier wave that is modulated to carry information. Fiber is preferred over electrical cabling when high bandwidth, long distance, or immunity to electromagnetic interference is required. This type of communication can transmit voice, video, and telemetry through local area networks or across long distances. Optical fiber is used by many telecommunications companies to transmit telephone signals, internet communication, and cable television signals. Researchers at Bell Labs have reached a record bandwidth–distance product of over kilometers per second using fiber-optic communication. Background First developed in the 1970s, fiber-optics have revolutionized the telecommunications industry and have played a major role in the advent of the Information Age. Because of its advantages over electrical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectral Interferometry
Spectral interferometry (SI) or frequency-domain interferometry is a linear technique used to measure optical pulses, with the condition that a reference pulse that was previously characterized is available. This technique provides information about the intensity and phase of the pulses. SI was first proposed by Claude Froehly and coworkers in the 1970s. A known (acting as the reference) and an unknown pulse arrive at a spectrometer, with a time delay \tau between them, in order to create spectral fringes. A spectrum is produced by the sum of these two pulses and, by measuring said fringes, one can retrieve the unknown pulse. If E_(\omega) and E_(\omega) are the electric fields of the unknown and reference pulse respectively, the time delay can be expressed as a phase factor e^ for the unknown pulses. Then, the combined field is: E_=E_(\omega)+E_(\omega) e^ The average spacing between fringes is inversely proportional to the time delay \tau . Thus, the SI signal is given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mode-locking
Mode locking is a technique in optics by which a laser can be made to produce pulses of light of extremely short duration, on the order of picoseconds (10−12 s) or femtoseconds (10−15 s). A laser operated in this way is sometimes referred to as a femtosecond laser, for example, in modern refractive surgery. The basis of the technique is to induce a fixed phase relationship between the longitudinal modes of the laser's resonant cavity. Constructive interference between these modes can cause the laser light to be produced as a train of pulses. The laser is then said to be "phase-locked" or "mode-locked". Laser cavity modes Although laser light is perhaps the purest form of light, it is not of a single, pure frequency or wavelength. All lasers produce light over some natural bandwidth or range of frequencies. A laser's bandwidth of operation is determined primarily by the gain medium from which the laser is constructed, and the range of frequencies over which a lase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |