|
Carrier Indians
The Dakelh (pronounced ) or Carrier are the indigenous people of a large portion of the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. The "Carrier" name was derived from an English translation of ''Aghele'', the name from the neighbouring Sekani (Tsek'ehne) ("people of the rocks or mountains", Lht'at'en / Lht'at'enne, ᒡᗧᗥᐣ) for Dakelh people. Sekani people played an important role in the early period of contact between the fur traders and Dakelh people because some Sekani people could speak both Dakelh and Cree and served as interpreters between the fur traders and Dakelh people. They call themselves "Dakelh / Dakelh-ne" (ᑕᗸᒡ, people who “travel upon water”, lit. "people who travel by boat early in the morning", a Synaeresis of uda ukelh and ne), and add the suffixes -xwoten, “people of” or -t’en, “people” to village names or locations to refer to specific groups (e.g., Tl’azt’en, Wet’suwet’en). the Wetʼsuwetʼen (Whutsot'en, ᗘᙢᗥᐣ, "Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dakelh Language
The Dakelh (ᑕᗸᒡ) or Carrier language is a Northern Athabaskan language. It is named after the Dakelh people, a First Nations people of the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada, for whom Carrier has been a common English name derived from French explorers naming of the people. Dakelh people speak two related languages. One, Babine-Witsuwit'en is sometimes referred to as ''Northern Carrier''. The other includes what are sometimes referred to as ''Central Carrier'' and ''Southern Carrier''. Etymology of 'Carrier' The name 'Carrier' is a translation of the Sekani name 'aɣele' "people who carry things around on their backs", due to the fact that the first Europeans to learn of the Carrier, the Northwest Company explorers led by Alexander Mackenzie, first passed through the territory of the Carriers' Sekani neighbours. The received view of the origin of the Sekani name is that it refers to the distinctive Carrier mortuary practice in which a widow carried her husban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dene
The Dene people () are an Aboriginal peoples in Canada, indigenous group of First Nations in Canada, First Nations who inhabit the northern Boreal forest of Canada, boreal and Arctic regions of Canada. The Dene speak Northern Athabaskan languages. ''Dene'' is the common Athabaskan word for "people". The term "Dene" has two usages. More commonly, it is used narrowly to refer to the Athabaskan speakers of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut in Canada, especially including the Chipewyan (Denesuline), Tlicho (''Dogrib''), Yellowknives (T'atsaot'ine), Slavey people, Slavey (Deh Gah Got'ine or Deh Cho), and Sahtu (the Eastern group in Jeff Leer's classification; part of the Northwestern Canada group in Keren Rice's classification). However, it is sometimes also used to refer to all Northern Athabaskan speakers, who are spread in a wide range all across Alaska and northern Canada. The Southern Athabaskan speakers, however, also refer to themselves by similar words: Navajo people, D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
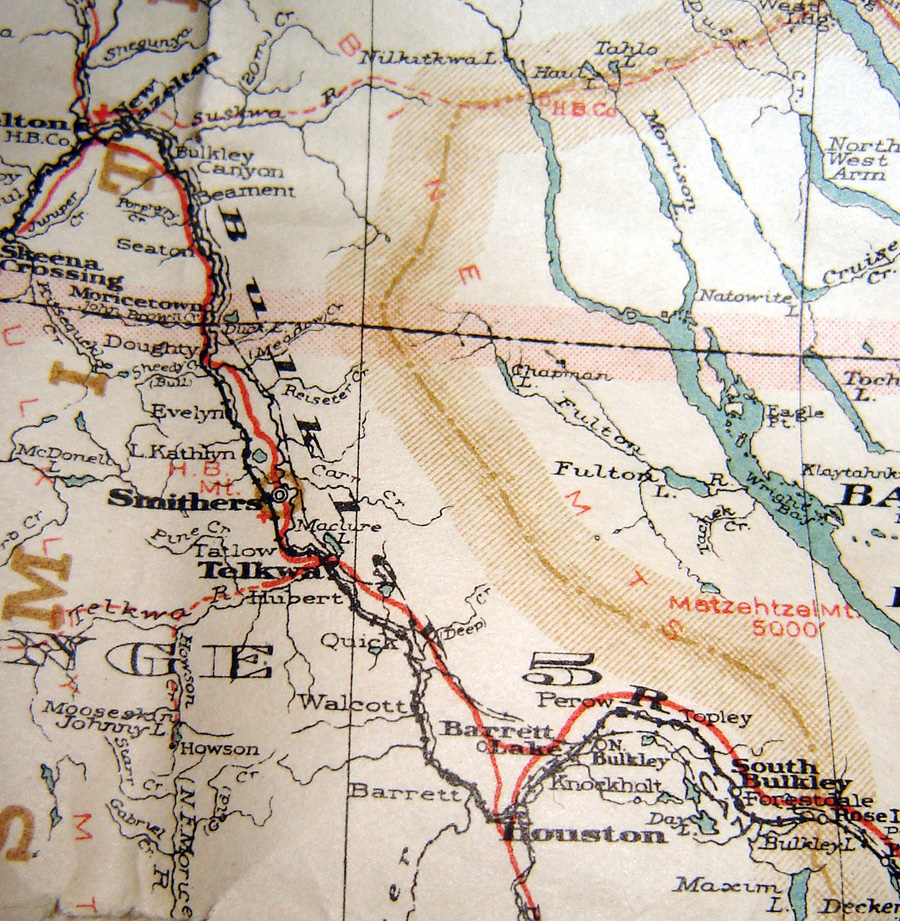
Bulkley Valley
The Bulkley Valley is in the northwest Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. Geography The Bulkley, a stream running through Houston, British Columbia, joins the larger Morice River about to the west. At the confluence, they become not the Morice, but unusually, take the name of the smaller Bulkley. The Bulkley River flows northwestward through the valley that is bounded on the west by the Hudson Bay Mountain range and on the east by the Babine Mountains. The northern boundary of the valley is usually considered the Bulkey's confluence with the Skeena River at Hazelton, although it is sometimes placed further south near Witset. The valley's southern edge is at Bulkley Lake, part way between Houston and Burns Lake. History First Nations The Wet'suwet'en people called the valley home for thousands of years. In the Delgamuukw decision of 1997, the Supreme Court of Canada affirmed that the Wet'suwet'en and neighbouring Gitxsan had Aboriginal title in the area. Surveys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
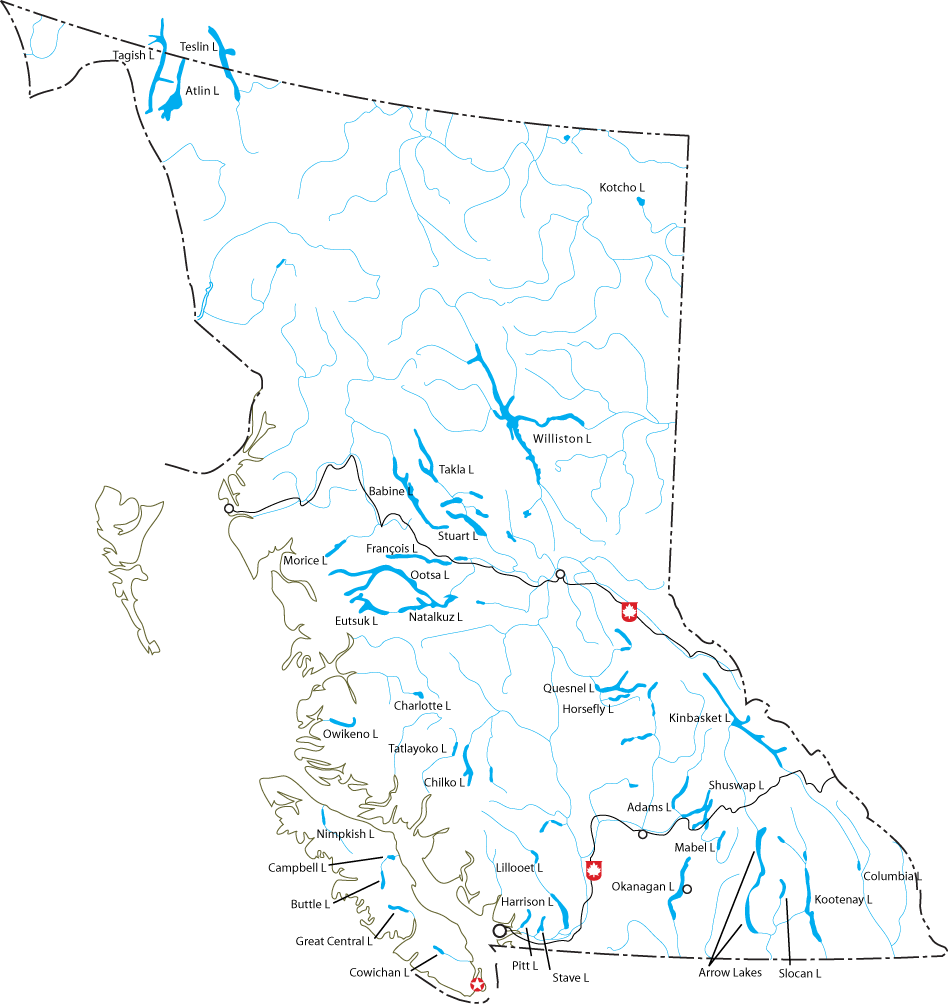
Babine Lake
Babine Lake ( ) or Na-taw-bun-kut ("Long Lake") is the longest natural lake in British Columbia, Canada. Babine Lake is located northeast of the town of Burns Lake in central British Columbia, some west northwest of the city of Prince George. It is long, wide, and has a net area of and a total area of , including islands on the lake which cover . It lies at an elevation of . It drains northwest into the Babine River, an important tributary of the Skeena. There are several provincial parks on Babine Lake: * Babine Lake Marine Provincial Park ** Pendleton Bay site ** Smithers Landing site * Topley Landing Provincial Park * Red Bluff Provincial Park Babine Portage Babine Portage is a campsite located about 12 km north of the Portage Yekooche Reserve along a gravel road, on the west end of Babine Lake. The name originates from the 19th century, when the site was used as an entry point for canoes portaging to the Hudson's Bay Company post. In the past, there were f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fraser Lake, British Columbia
Fraser Lake is a village in northern British Columbia, Canada. It's located on the southwest side of Fraser Lake between Burns Lake and Vanderhoof alongside the Yellowhead Highway. The small community's population is primarily employed by either the forest industry. (Fraser Lake Sawmills, or various logging contractors) The Endako Mines, a large molybdenum mine was a former large employer. The pioneer roots of the area's history date back to the fur trade, with the establishment in 1806 of a fur-trading post by Simon Fraser, at Fort Fraser near the east end of Fraser Lake. The modern day town was established in 1914, during the construction of the Grand Trunk Pacific Railway, and was incorporated as a village in 1966. Fraser Lake is the hometown of Tianda Flegel, winner of The Next Star Season 2. Demographics In the 2021 Census of Population conducted by Statistics Canada, Fraser Lake had a population of 965 living in 444 of its 543 total private dwellings, a change of fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Takla Lake
Takla Lake is the fifth largest natural lake in British Columbia, Canada. It is a deep fjord-like lake with the Swannell Ranges to the east, the Driftwood River flowing into it from the north, and the Middle River draining it. It is the terminus of the early Stuart-Takla sockeye salmon run, and noted for its large rainbow trout, lake trout and Dolly Varden. The peninsula is the home of Mount Blanchet Provincial Park. Also on the peninsula is a herd of collared woodland caribou, and the winter range of grizzly bears. Two special features are Takla Lake Marine Park, and an Ecological Reserve on the peninsula, a stand of very northerly Douglas Fir. Takla Lake is also the origin of both of Canada's national airlines, both Russ Baker and Grant McConachie running bush plane routes out of Takla Lake. It is a popular canoe route from the top end down to Fort St. James Fort St. James is a district municipality and former fur trading post in northern central British Columbia, Can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trembleur Lake
Trembleur Lake is a lake in the Omineca Country of the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada, northwest of Fort St. James between Stuart Lake and the south end of Takla Lake. It is part of the Nechako Lakes. Its name in the Dakelh language The Dakelh (ᑕᗸᒡ) or Carrier language is a Northern Athabaskan language. It is named after the Dakelh people, a First Nations people of the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada, for whom Carrier has been a common English name derive ... is Dzindlat Bun. It has also been known as Cross Lake. Trembleur Lake Provincial Park is on its north shore, above the Middle River. The reserve settlement of Middle River is at that river's mouth into Trembleur Lake. References {{authority control Lakes of British Columbia Omineca Country Range 5 Coast Land District ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nechako Country
The Nechako Country, also referred to as the Nechako District or simply "the Nechako" is one of the historical geographic regions of the Canadian province of British Columbia, located southwest of the city of Prince George and south of Hwy 16 on the inland side of the Hazelton Mountains (an inland subrange of the Coast Mountains), and comprising the basin of the Nechako River and its tributaries. "Nechako" is an anglicization of ''netʃa koh'', its name in the indigenous Carrier language which means "big river". The area is sparsely populated, mostly by members of the Carrier people, and is noted for its many large lakes, including Ootsa Lake Reservoir, which is the source of water for the Kemano Powerhouse on a neighbouring coastal inlet, which is the power supply for the aluminum smelter at Kitimat. To the north of the Nechako Country are the Omineca Country and Bulkley Valley, while to its south is the Chilcotin Country and to the southeast the Cariboo Country. See also * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wells, British Columbia
Wells is a small mining and tourist town in the Cariboo District of central British Columbia, located on BC Highway 26, from Quesnel and before the highway's terminus at Barkerville. It gains much of its revenue and jobs from tourists who pass through on their way to the Bowron Lake Provincial Park and to the historic museum town of Barkerville. History Originally a company town, it was managed by ''Cariboo Gold Quartz Mine''. Fred M. Wells, for whom the town was named, prospected in the area for 10 years before finding the minerals that built the company. At its heyday of the 1930s, Wells sported 4500 people. In 1942 it had a greater population than Quesnel or Prince George. The closure of the gold and other mineral mines in 1967 took its toll on the town and most of the population moved away. Today it has a listed population of just 250 which doubles during the summer months. Between May and September, Wells sees over 100,000 tourists pass through on their way to Bark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barkerville, British Columbia
Barkerville was the main town of the Cariboo Gold Rush in British Columbia, Canada, and is preserved as a historic town. It is located on the north slope of the Cariboo Plateau near the Cariboo Mountains east of Quesnel. BC Highway 26, which follows the route of the Cariboo Wagon Road, the original access to Barkerville, goes through it. History Founding Barkerville is located on the western edge of the Cariboo Mountains in British Columbia. It was named after Billy Barker from Cambridgeshire, England, who was among those who first struck gold at the location in 1861. His claim was the richest and the most famous. Barkerville was built up almost overnight, and was a case of "growth via word of mouth". It grew as fast as the word of Barker's strike spread. His claim would eventually yield 37,500 ounces (1,065 kg/2,350 lb) of gold. Before the construction of the Cariboo Wagon Road, people hauled their own supplies to Barkerville, either on their backs or in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quesnel, British Columbia
Quesnel (Kee-nel in French) is a city located in the Cariboo Regional District of British Columbia, Canada. Located nearly evenly between the cities of Prince George and Williams Lake, it is on the main route to northern British Columbia and the Yukon. Quesnel is located at the confluence of the Fraser River and Quesnel River. Quesnel's metropolitan area has a population of 23,146 making it the largest urban center between Prince George and Kamloops. Quesnel is a sister city to Shiraoi, Japan. Quesnel hosted the 2000 British Columbia Winter Games, a biennial provincial amateur sports competition. To the east of Quesnel is Wells, Barkerville, and Bowron Lake Provincial Park, a popular canoeing destination in the Cariboo Mountains. History Long before the arrival of prospectors during the Cariboo Gold Rush of 1862, the Southern Carrier (Dakelh) people lived off the land around Quesnel, occupying the area from the Bowron Lakes in the east to the upper Blackwater River and Dean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_cropped.jpg)