|
Carrier's Constraint
Carrier's constraint is the observation that air-breathing vertebrates with two lungs that flex their bodies sideways during locomotion find it difficult to move and breathe at the same time, because the sideways flexing expands one lung and compresses the other, shunting stale air from lung to lung instead of expelling it completely to make room for fresh air. It was named by English paleontologist Richard Cowen for David R. Carrier, who wrote his observations on the problem in 1987. Consequences Most lizards move in short bursts, with long pauses for breath. Around the Late Triassic period, animals with Carrier's constraint were preyed on by bipedal species that evolved a more efficient stride. Solutions Workarounds Most snakes have only one lung, so Carrier's constraint does not apply. Monitor lizards increase their stamina by using bones and muscles in the throat and floor of the mouth to "gulp" air via gular pumping. Some other lizards, mainly agamids, use bipedal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eublepharis Macularius 2009 G6
''Eublepharis'' is a genus of terrestrial geckos native to eastern and southwestern Asia. The genus was first described by the British Zoology, zoologist John Edward Gray in 1827. The etymology of their name is 'eu' = good (=true) , 'blephar' = eyelid, and all have fully functional eyelids. Members of this genus are found in eastern and southwestern Asia. These geckos are sturdily built. Their tail is shorter than their snout–vent length, and their body is covered with numerous wart-like bumps. The toes do not have adhesive Lamella (surface anatomy), lamellae or membranes (''Eublepharis'' cannot climb like their other gecko cousins). Like all members of Eublepharidae, they are primarily Nocturnality, nocturnal. Included in this group is the popular pet leopard gecko ''Eublepharis macularius''. Species of the genus ''Eublepharis'' The members of the ''Goniurosaurus kuroiwae'' superspecies were formerly considered members of the genus ''Eublepharis''. References Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agamid
Agamidae is a family containing 582 species in 64 genera of iguanian lizards indigenous to Africa, Asia, Australia, and a few locations in Southern Europe. Many species are commonly called dragons or dragon lizards. Overview Phylogenetically, they may be sister to the Iguanidae, and have similar appearances. Agamids usually have well-developed, strong legs. Their tails cannot be shed and regenerated like those of geckos (and several other families such as skinks), though a certain amount of regeneration is observed in some. Many agamid species are capable of limited change of their colours to regulate their body temperature. In some species, males are more brightly coloured than females, and colours play a part in signaling and reproductive behaviours. Although agamids generally inhabit warm environments, ranging from hot deserts to tropical rainforests, at least one species, the mountain dragon, is found in cooler regions. They are particularly diverse in Australia. This gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Physiology
Evolutionary physiology is the study of the biological evolution of physiological structures and processes; that is, the manner in which the functional characteristics of organisms have responded to natural selection or sexual selection or changed by random genetic drift across multiple generations during the history of a population or species. It is a sub-discipline of both physiology and evolutionary biology. Practitioners in the field come from a variety of backgrounds, including physiology, evolutionary biology, ecology, and genetics. Accordingly, the range of phenotypes studied by evolutionary physiologists is broad, including life history traits, behavior, whole-organism performance, functional morphology, biomechanics, anatomy, classical physiology, endocrinology, biochemistry, and molecular evolution. The field is closely related to comparative physiology, ecophysiology, and environmental physiology, and its findings are a major concern of evolutionary medicine. One def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limerick (poetry)
A limerick ( ) is a form of verse that appeared in England in the early years of the 18th century. In combination with a refrain, it forms a limerick (song), limerick song, a traditional humorous drinking song often with obscene verses. It is written in five-line, predominantly Anapaest, and amphibrach trimeter with a strict rhyme scheme of AABBA, in which the first, second and fifth line rhyme, while the third and fourth lines are shorter and share a different rhyme. It was popularized by Edward Lear in the 19th century, although he did not use the term. From a Folklore, folkloric point of view, the form is essentially transgressive; violation of taboo is part of its function. According to Gershon Legman, who compiled the largest and most scholarly anthology, this folk form is always obscene and the exchange of limericks is almost exclusive to comparatively well-educated men. Women are figuring in limericks almost exclusively as "villains or victims". Legman dismissed the "clea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles, middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors Genetic divergence, diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 Neontology#Extant taxon, extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 Order (biology), orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, Mole (animal), moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the Artiodactyl, even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including Felidae, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight Bird skeleton, skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the common ostrich. There are over 11,000 living species and they are split into 44 Order (biology), orders. More than half are passerine or "perching" birds. Birds have Bird wing, wings whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the Flightless bird, loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemism, endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Utah
The University of Utah (the U, U of U, or simply Utah) is a public university, public research university in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States. It was established in 1850 as the University of Deseret (Book of Mormon), Deseret by the General Assembly of the provisional State of Deseret, making it Utah's oldest institution of higher education. The university received its current name in 1892, four years before Utah attained statehood, and moved to its current location in 1900. It is the flagship university of the Utah System of Higher Education. As of fall 2023, there were 26,827 undergraduate education, undergraduate students and 8,409 postgraduate education, graduate students, for an enrollment total of 35,236, making it the List of colleges and universities in Utah#Public institutions, second-largest public university in Utah. Graduate studies include the S.J. Quinney College of Law and the University of Utah School of Medicine, School of Medicine, Utah's first medical school ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodilia
Crocodilia () is an order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorph pseudosuchian, a subset of archosaurs that appeared about 235 million years ago and were the only survivors of the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event. While other crocodylomorph groups further survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, notably sebecosuchians, only the crocodilians have survived into the Quaternary. The order includes the true crocodiles (family Crocodylidae), the alligators and caimans (family Alligatoridae), and the gharial and false gharial (family Gavialidae). Although the term "crocodiles" is sometimes used to refer to all of these families, the term "crocodilians" is less ambiguous. Extant crocodilians have flat heads with long snouts and tails that are compressed on the sides, with their eyes, ears, and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipedal Locomotion
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an animal moves by means of its two rear (or lower) limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' and ''pes'' 'foot'). Types of bipedal movement include walking or running (a bipedal gait) and hopping. Several groups of modern species are habitual bipeds whose normal method of locomotion is two-legged. In the Triassic period some groups of archosaurs (a group that includes crocodiles and dinosaurs) developed bipedalism; among the dinosaurs, all the early forms and many later groups were habitual or exclusive bipeds; the birds are members of a clade of exclusively bipedal dinosaurs, the theropods. Within mammals, habitual bipedalism has evolved multiple times, with the macropods, kangaroo rats and mice, springhare, hopping mice, pangolins and hominin apes (australopithecines, including humans) as well as various other extin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History (magazine)
''Natural History'' is a natural history magazine published in the United States. The stated mission of the magazine is to promote public understanding and appreciation of nature and science. History Founded in 1900 by the American Museum of Natural History, ''Natural History'' was first titled ''The American Museum Journal''. In 1918, it was renamed ''Natural History'', the name under which it is published today. In 2002, the magazine was purchased from the Museum by a new company, headed at the time by Charles Harris. As of 2013 the magazine is published in North Carolina by Howard Richman. There are 10 issues published annually. Since its founding, ''Natural History'' has chronicled the major expeditions and research findings by curators at the American Museum of Natural History and at other natural history museums and science centers. Stephen Jay Gould's column, "This View of Life", was a regular feature of the magazine from 1974 until he retired the column in 2001. Othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrates
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain. The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebrata with some 65,000 species, by far the largest ranked grouping in the phylum Chordata. The vertebrates include mammals, birds, amphibians, and various classes of fish and reptiles. The fish include the jawless Agnatha, and the jawed Gnathostomata. The jawed fish include both the Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fish and the Osteichthyes, bony fish. Bony fish include the Sarcopterygii, lobe-finned fish, which gave rise to the tetrapods, the animals with four limbs. Despite their success, vertebrates still only make up less than five percent of all described animal species. The first vertebrates appeared in the Cambrian explosion some 518 million years ago. Jawed vertebrates evolved in the Ordovician, followed by bony fishes in the Devonian. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
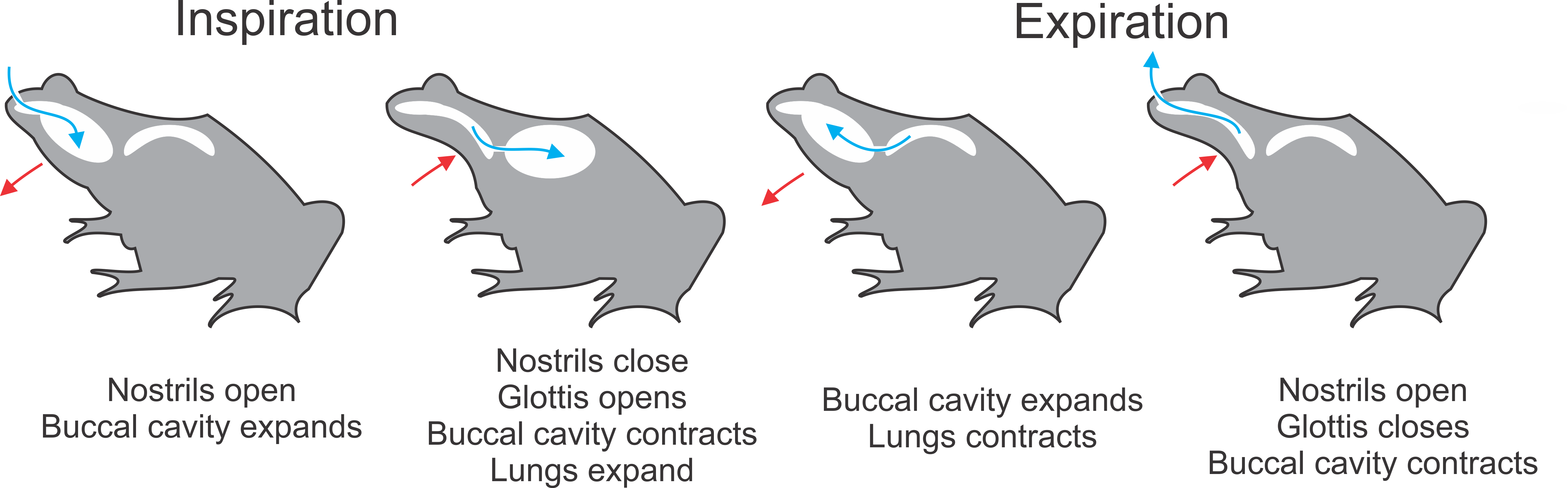
Gular Pumping
Buccal pumping (/ˈbʌk.əl/...) is "breathing with one's cheeks": a method of ventilation used in respiration in which the animal moves the floor of its mouth in a rhythmic manner that is externally apparent.Brainerd, E. L. (1999). New perspectives on the evolution of lung ventilation mechanisms in vertebrates. Experimental Biology Online 4, 11-28. http://www.brown.edu/Departments/EEB/brainerd_lab/pdf/Brainerd-1999-EBO.pdf It is the sole means of inflating the lungs in amphibians. There are two methods of buccal pumping, defined by the number of movements of the floor of the mouth needed to complete both inspiration and expiration. Four stroke Four-stroke buccal pumping is used by some basal ray-finned fish and aquatic amphibians such as ''Xenopus'' and ''Amphiuma''. This method has several stages. These will be described for an animal starting with lungs in a deflated state: First, the glottis (opening to the lungs) is closed, and the nostrils are opened. The floor of the mout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |