|
Carbyne
In organic chemistry, a carbyne is a general term for any compound whose structure consists of an electrically neutral carbon atom connected by a single covalent bond and has three non-bonded electrons. The carbon atom has either one or three unpaired electrons, depending on its excitation state; making it a radical. The chemical formula can be written or (also written as ), or just CH. Carbynes can be seen as derivatives of the simplest such compound, the methylidyne radical or unsubstituted carbyne or , in which the functional group is a hydrogen atom. Reported for the first time back in 1967 by Kasatochkin, carbyne is an infinite sp1 hybridized long linear chain of carbon, where each link is just a single carbon atom. Electronic configuration Carbyne molecules are generally found to be in electronic doublet states: the non-bonding electrons on carbon are arranged as one radical (unpaired electron) and one electron pair, leaving a vacant atomic orbital, rather than b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
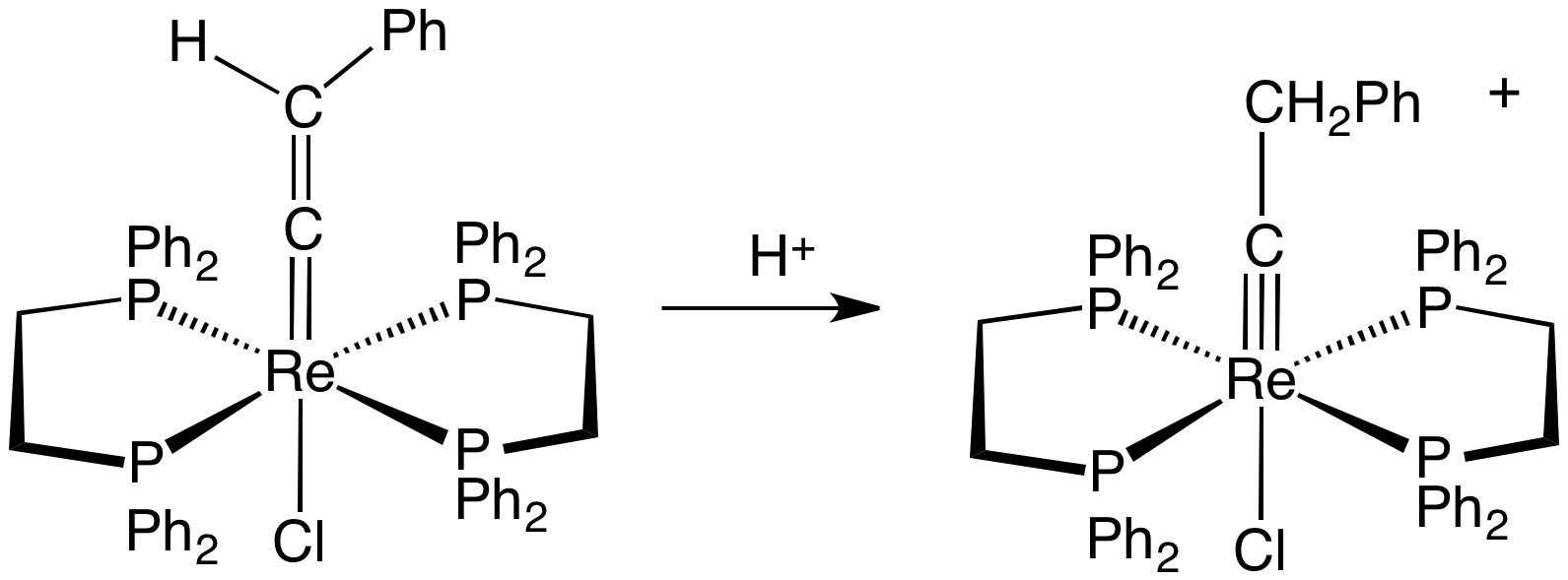
Transition Metal Carbyne Complex
Transition metal carbyne complexes are organometallic compounds with a triple bond between carbon and the transition metal. This triple bond consists of a σ-bond and two π-bonds. The HOMO of the carbyne ligand interacts with the LUMO of the metal to create the σ-bond. The two π-bonds are formed when the two HOMO orbitals of the metal back-donate to the LUMO of the carbyne. They are also called metal alkylidynes—the carbon is a carbyne ligand. Such compounds are useful in organic synthesis of alkynes and nitriles. They have been the focus on much fundamental research. Synthesis Transition metal carbyne complexes are most common for the early transition metals, especially niobium, tantalum, molybdenum, tungsten, and rhenium. They can also have low-valence metals as well as high-valence metals. The first Fischer carbyne complex was reported in 1973. Two years later in 1975, the first "Schrock carbyne" was reported. Many high-valent carbyne complexes have since been prepared, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylidyne Radical
Methylidyne, or (unsubstituted) carbyne, is an organic compound whose molecule consists of a single hydrogen atom bonded to a carbon atom. It is the parent compound of the carbynes, which can be seen as obtained from it by substitution of other functional groups for the hydrogen. The carbon atom is left with either one or three unpaired electrons (unsatisfied valence bonds), depending on the molecule's excitation state; making it a radical. Accordingly, the chemical formula can be CH• or CH3• (also written as ⫶CH); each dot representing an unpaired electron. The corresponding systematic names are methylylidene or hydridocarbon(•), and methanetriyl or hydridocarbon(3•). However, the formula is often written simply as CH. Methylidyne is a highly reactive gas, that is quickly destroyed in ordinary conditions but is abundant in the interstellar medium (and was one of the first molecules to be detected there). Nomenclature The trivial name ''carbyne'' is the pref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up only about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three isotopes occur naturally, C and C being stable, while C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of about 5,730 years. Carbon is one of the few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon's abundance, its unique diversity of organic compounds, and its unusual ability to form polymers at the temperatures commonly encountered on Earth, enables this element to serve as a common element of Carbon-based life, all known life. It is the second most abundant element in the human body by mass (about 18.5%) after oxygen. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoromethylidyne
Fluoromethylidyne is not a stable chemical species but a metastable radical containing one highly reactive carbon atom bound to one fluorine atom with the formula CF. The carbon atom has a lone-pair and a single unpaired (radical) electron in the ground state. Ground-state fluoromethylidyne radicals can be produced by the ultraviolet photodissociation of dibromodifluoromethane at 248 nanometer wavelength. It readily and irreversibly dimerises to difluoroacetylene, also known as difluoroethyne, perfluoroacetylene, or di- or perfluoroethylyne. Under certain conditions it can hexamerise to hexafluorobenzene. See also * Carbyne In organic chemistry, a carbyne is a general term for any compound whose structure consists of an electrically neutral carbon atom connected by a single covalent bond and has three non-bonded electrons. The carbon atom has either one or three ... References Free radicals Reactive intermediates {{Organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactive Intermediate
In chemistry, a reactive intermediate or an intermediate is a short-lived, high-energy, highly reactive molecule. When generated in a chemical reaction, it will quickly convert into a more stable molecule. Only in exceptional cases can these compounds be isolated and stored, e.g. low temperatures, matrix isolation. When their existence is indicated, reactive intermediates can help explain how a chemical reaction takes place. Most chemical reactions take more than one elementary step to complete, and a reactive intermediate is a high-energy, yet stable, product that exists only in one of the intermediate steps. The series of steps together make a reaction mechanism. A reactive intermediate differs from a reactant or product or a simple reaction intermediate only in that it cannot usually be isolated but is sometimes observable only through fast spectroscopic methods. It is stable in the sense that an elementary reaction forms the reactive intermediate and the elementary reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes Physical property, physical and Chemical property, chemical properties, and evaluation of Reactivity (chemistry), chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the organic synthesis, chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but also con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Overlap
In chemical bonds, an orbital overlap is the concentration of orbitals on adjacent atoms in the same regions of space. Orbital overlap can lead to bond formation. Linus Pauling explained the importance of orbital overlap in the molecular bond angles observed through experimentation; it is the basis for orbital hybridization. As ''s'' orbitals are spherical (and have no directionality) and ''p'' orbitals are oriented 90° to each other, a theory was needed to explain why molecules such as methane (CH4) had observed bond angles of 109.5°. Pauling proposed that s and p orbitals on the carbon atom can combine to form hybrids (sp3 in the case of methane) which are directed toward the hydrogen atoms. The carbon hybrid orbitals have greater overlap with the hydrogen orbitals, and can therefore form stronger C–H bonds.Pauling, Linus. (1960). ''The Nature Of The Chemical Bond''. Cornell University Press. A quantitative measure of the overlap of two atomic orbitals ΨA and ΨB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into wires) and malleable (they can be hammered into thin sheets). These properties are the result of the '' metallic bond'' between the atoms or molecules of the metal. A metal may be a chemical element such as iron; an alloy such as stainless steel; or a molecular compound such as polythiazyl, polymeric sulfur nitride. In physics, a metal is generally regarded as any substance capable of conducting electricity at a temperature of absolute zero. Many elements and compounds that are not normally classified as metals become metallic under high pressures. For example, the nonmetal iodine gradually becomes a metal at a pressure of between 40 and 170 thousand times atmospheric pressure. Equally, some materials re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule ( functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical areas, including bioinorganic and medicinal chemistry, homogeneous catalysis, and environm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dibromofluoromethane
Dibromofluoromethane is a mixed halomethane. It is soluble in alcohol, acetone, benzene and chloroform. Applications It can be used to prepare bromofluoromethane by reductive debromination with organotin hydride as tributyltin hydride. Regulations Its ozone depletion potential The ozone depletion potential (ODP) of a chemical compound is the relative amount of degradation to the ozone layer it can cause, with trichlorofluoromethane (R-11 or CFC-11) being fixed at an ODP of 1.0. Chlorodifluoromethane (R-22), for example ... (ODP) is 1.0 and it is included in list of Class I Ozone-Depleting Substances. References Halomethanes Ozone depletion Organobromides Organofluorides {{organohalide-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flash Photolysis
Flash photolysis is a pump-probe laboratory technique, in which a sample is first excited by a strong pulse of light from a pulsed laser of nanosecond, picosecond, or femtosecond pulse width or by another short-pulse light source such as a flash lamp. This first strong pulse is called the pump pulse and starts a chemical reaction or leads to an increased population for energy levels other than the ground state within a sample of atoms or molecules. Typically the absorption of light by the sample is recorded within short time intervals (by a so-called test or probe pulses) to monitor relaxation or reaction processes initiated by the pump pulse. Flash photolysis was developed shortly after World War II as an outgrowth of attempts by military scientists to build cameras fast enough to photograph missiles in flight. The technique was developed in 1949 by Manfred Eigen, Ronald George Wreyford Norrish and George Porter, who won the 1967 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this invention. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degenerate Energy Levels
In quantum mechanics, an energy level is degenerate if it corresponds to two or more different measurable states of a quantum system. Conversely, two or more different states of a quantum mechanical system are said to be degenerate if they give the same value of energy upon measurement. The number of different states corresponding to a particular energy level is known as the degree of degeneracy of the level. It is represented mathematically by the Hamiltonian for the system having more than one linearly independent eigenstate with the same energy eigenvalue. When this is the case, energy alone is not enough to characterize what state the system is in, and other quantum numbers are needed to characterize the exact state when distinction is desired. In classical mechanics, this can be understood in terms of different possible trajectories corresponding to the same energy. Degeneracy plays a fundamental role in quantum statistical mechanics. For an -particle system in three dime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9.png)


4-3D-balls.png)