|
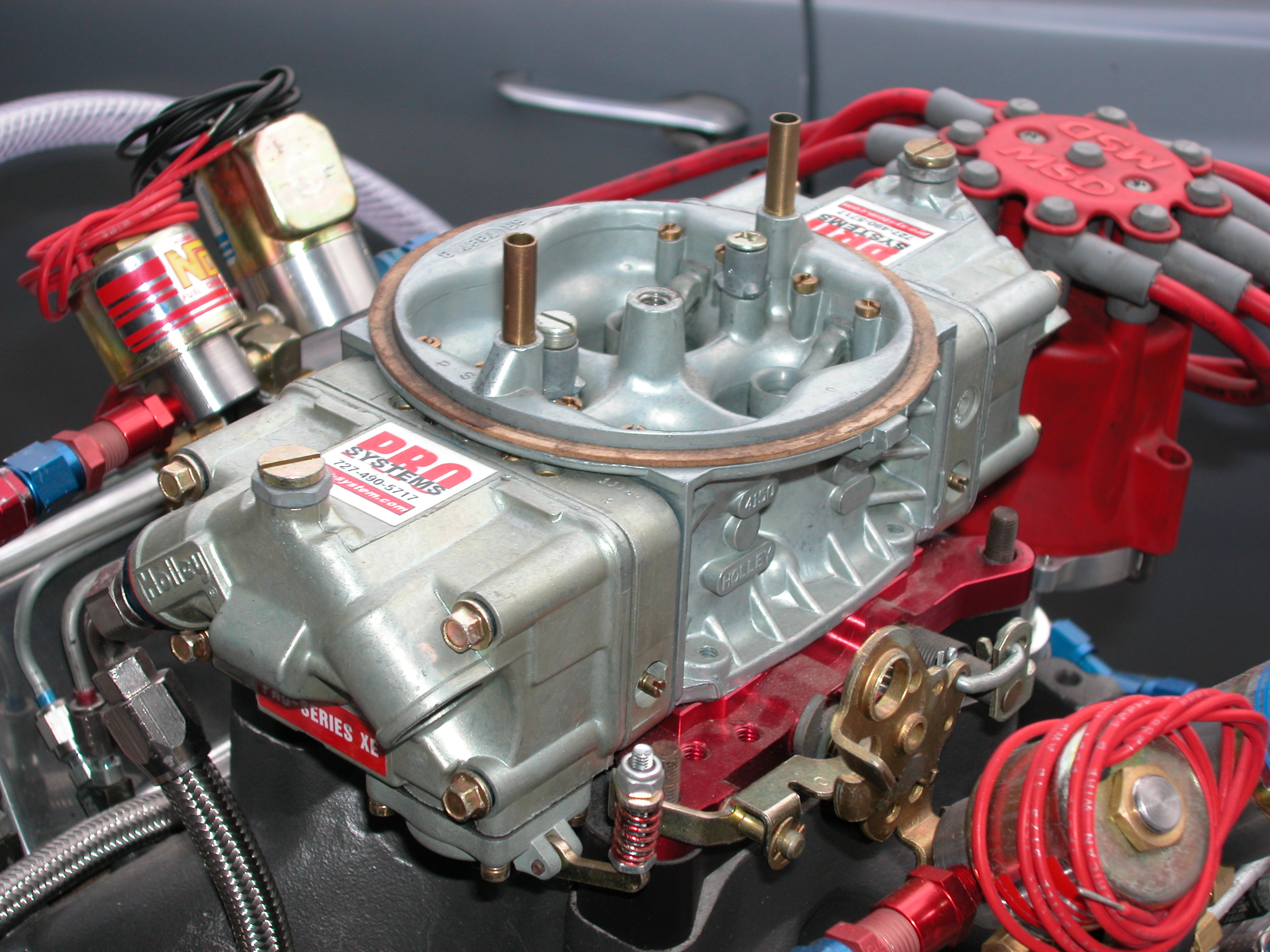
Carburation
A carburetor (also spelled carburettor) is a device used by an internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the venturi tube in the main metering circuit, however various other components are also used to provide extra fuel or air in specific circumstances. Since the 1990s, carburetors have been largely replaced by fuel injection for cars and trucks, however carburetors are still used by some small engines (e.g. lawnmowers, generators and concrete mixers) and motorcycles. Diesel engines have always used fuel injection instead of carburetors. Etymology The name "carburetor" is derived from the verb ''carburet'', which means "to combine with carbon," or in particular, "to enrich a gas by combining it with carbon or hydrocarbons." Thus a carburetor mixes intake air with hydrocarbon-based fuel, such as petrol or autogas (LPG). The name is spelled "carburetor" in American Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
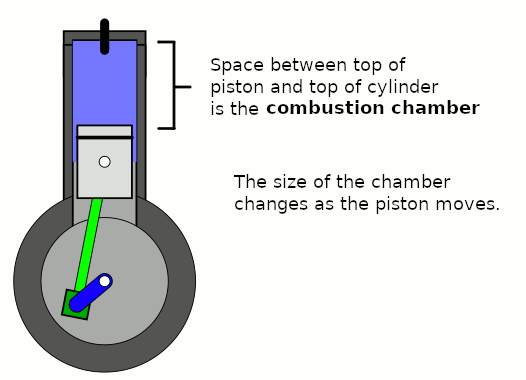
Combustion Chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the firebox which is used to allow a more complete combustion process. Internal combustion engines In an internal combustion engine, the pressure caused by the burning air/fuel mixture applies direct force to part of the engine (e.g. for a piston engine, the force is applied to the top of the piston), which converts the gas pressure into mechanical energy (often in the form of a rotating output shaft). This contrasts an external combustion engine, where the combustion takes place in a separate part of the engine to where the gas pressure is converted into mechanical energy. Spark-ignition engines In spark ignition engines, such as petrol (gasoline) engines, the combustion chamber is usually located in the cylinder head. The engines are often designed such that the bottom of combustion chamber is roughly in li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flooded Engine
A flooded engine is an internal combustion engine that has been fed an excessively rich air-fuel mixture that cannot be ignited. This is caused by the mixture exceeding the upper explosive limit for the particular fuel. An engine in this condition will not start until the excessively rich mixture has been cleared. It is also possible for an engine to stall from a running state due to this condition. Engine flooding was a common problem with carbureted cars, but newer fuel-injected ones are immune to the problem when operating within normal tolerances. Flooding usually occurs during starting, especially under cold conditions or because the accelerator has been pumped. It can also occur during hot starting; high temperatures may cause fuel in the carburetor float chamber to evaporate into the inlet manifold, causing the air/fuel mixture to exceed the upper explosive limit. High temperature fuel may also result in a vapor lock, which is unrelated to flooding but has a similar symptom. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermostat
A thermostat is a regulating device component which senses the temperature of a physical system and performs actions so that the system's temperature is maintained near a desired setpoint. Thermostats are used in any device or system that heats or cools to a setpoint temperature. Examples include building heating, central heating, air conditioners, HVAC systems, water heaters, as well as kitchen equipment including ovens and refrigerators and medical and scientific incubators. In scientific literature, these devices are often broadly classified as thermostatically controlled loads (TCLs). Thermostatically controlled loads comprise roughly 50% of the overall electricity demand in the United States. A thermostat operates as a "closed loop" control device, as it seeks to reduce the error between the desired and measured temperatures. Sometimes a thermostat combines both the sensing and control action elements of a controlled system, such as in an automotive thermostat. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dashboard
For business applications, see Dashboard (business). A dashboard (also called dash, instrument panel (IP), or fascia) is a control panel set within the central console of a vehicle or small aircraft. Usually located directly ahead of the driver (or pilot), it displays instrumentation and controls for the vehicle's operation. Etymology Originally, the word ''dashboard'' applied to a barrier of wood or leather fixed at the front of a horse-drawn carriage or sleigh to protect the driver from mud or other debris "dashed up" (thrown up) by the horses' hooves. The first known use of the term (hyphenated as ''dash-board'', and applied to sleighs) dates from 1847. Commonly these boards did not perform any additional function other than providing a convenient handhold for ascending into the driver's seat, or a small clip with which to secure the reins when not in use. When the first "horseless carriages" were constructed in the late 19th century, with engines mounted beneath the drive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choke Valve
In internal combustion engines with carburetors, a choke valve or choke modifies the air pressure in the intake manifold, thereby altering the air–fuel ratio entering the engine. Choke valves are generally used in naturally aspirated engines to supply a richer fuel mixture when starting the engine. Most choke valves in engines are butterfly valves mounted upstream of the carburetor jet to produce a higher partial vacuum, which increases the fuel draw. In heavy industrial or fluid engineering contexts, including oil and gas production, a choke valve or choke is a particular design of valve with a solid cylinder placed inside another slotted or perforated cylinder. Carburetor A choke valve is sometimes installed in the carburetor of internal combustion engines. Its purpose is to restrict the flow of air, thereby enriching the fuel-air mixture while starting the engine. Depending on engine design and application, the valve can be activated manually by the operator of the engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Start (automotive)
A cold start is an attempt to start a vehicle's engine when it is cold, relative to its normal operating temperature, often due to normal cold weather. A cold start situation is commonplace, as weather conditions in most climates will naturally be at a lower temperature than the typical operating temperature of an engine. Causes of cold starts Cold starts are more difficult than starting a vehicle that has been run recently (typically between 90 minutes and 2 hours). More effort is needed to turn over a cold engine for multiple reasons: * The engine compression is higher as the lack of heat makes ignition more difficult * Low temperatures cause engine oil to become more viscous, making it more difficult to circulate the oil. * Air becomes more dense the cooler it is. This affects the air-fuel ratio, which in turn affects the flammability of the mixture. Solutions to cold starting The problem of cold starting has been greatly reduced since the introduction of engine starte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Car Controls
Car controls are the components in automobiles and other powered road vehicles, such as trucks and buses, used for driving and parking. While controls like steering wheels and pedals have existed since the invention of cars, other controls have developed and adapted to the demands of drivers. For example, manual transmissions became less common as technology relating to automatic transmissions became advanced. Earlier versions of headlights and signal lights were fueled by acetylene or oil. Acetylene was preferred to oil, because its flame is resistant to both wind and rain. Acetylene headlights, which gave a strong green-tinted light, were popular until after World War I; even though the first electric headlights were introduced in 1898 (and those were battery-powered), it wasn't until high-wattage bulbs and more powerful car electrical generating systems were developed in the late 1910s that electric lighting systems entirely superseded acetylene. Steering The first automob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
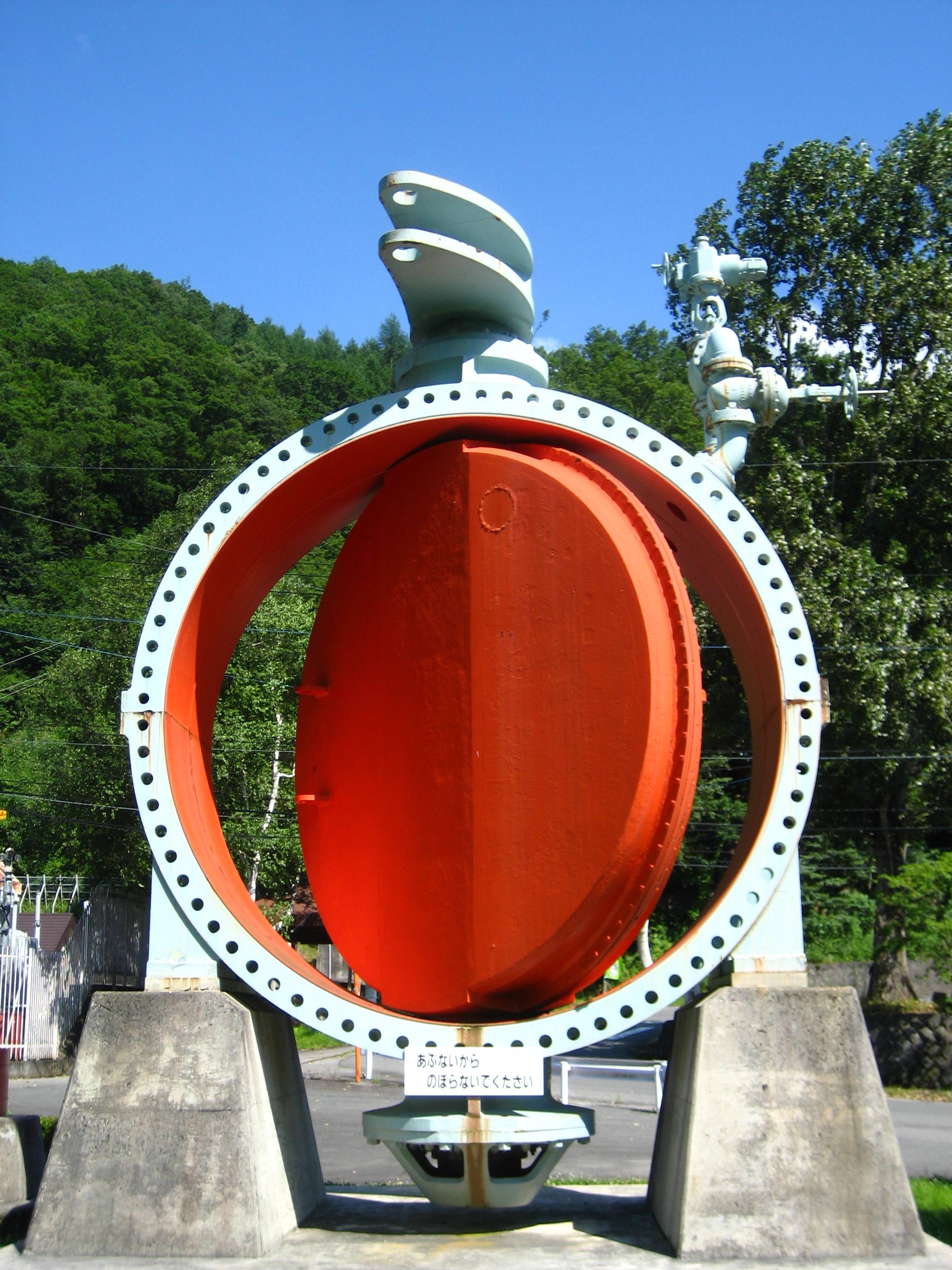
Butterfly Valve
A butterfly valve is a valve that isolates or regulates the flow of a fluid. The closing mechanism is a disk that rotates. Principle of operation Operation is similar to that of a ball valve, which allows for quick shut off. Butterfly valves are generally favored because they cost less than other valve designs, and are lighter weight so they need less support. The disc is positioned in the center of the pipe. A rod passes through the disc to an actuator on the outside of the valve. Rotating the actuator turns the disc either parallel or perpendicular to the flow. Unlike a ball valve, the disc is always present within the flow, so it induces a pressure drop, even when open. A butterfly valve is from a family of valves called quarter-turn valves. In operation, the valve is fully open or closed when the disc is rotated a quarter turn. The "butterfly" is a metal disc mounted on a rod. When the valve is closed, the disc is turned so that it completely blocks off the passageway. Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
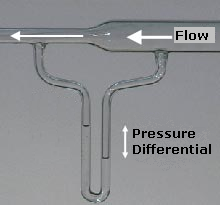
Venturi Tube
The Venturi effect is the reduction in fluid pressure that results when a fluid flows through a constricted section (or choke) of a pipe. The Venturi effect is named after its discoverer, the 18th century Italian physicist, Giovanni Battista Venturi. Background In inviscid fluid dynamics, an incompressible fluid's velocity must ''increase'' as it passes through a constriction in accord with the principle of mass continuity, while its static pressure must ''decrease'' in accord with the principle of conservation of mechanical energy (Bernoulli's principle). Thus, any gain in kinetic energy a fluid may attain by its increased velocity through a constriction is balanced by a drop in pressure. By measuring pressure, the flow rate can be determined, as in various flow measurement devices such as Venturi meters, Venturi nozzles and orifice plates. Referring to the adjacent diagram, using Bernoulli's equation in the special case of steady, incompressible, inviscid flows (such as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernoulli's Principle
In fluid dynamics, Bernoulli's principle states that an increase in the speed of a fluid occurs simultaneously with a decrease in static pressure or a decrease in the fluid's potential energy. The principle is named after the Swiss mathematician and physicist Daniel Bernoulli, who published it in his book ''Hydrodynamica'' in 1738. Although Bernoulli deduced that pressure decreases when the flow speed increases, it was Leonhard Euler in 1752 who derived Bernoulli's equation in its usual form. The principle is only applicable for isentropic flows: when the effects of irreversible processes (like turbulence) and non-adiabatic processes (e.g. thermal radiation) are small and can be neglected. Bernoulli's principle can be applied to various types of fluid flow, resulting in various forms of Bernoulli's equation. The simple form of Bernoulli's equation is valid for incompressible flows (e.g. most liquid flows and gases moving at low Mach number). More advanced forms may be applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)