|
Caradog Ap Meirion
Caradog ap Meirion (died ) was an 8th-century king of Gwynedd in northwest Wales. This era in the history of Gwynedd was not notable and, given the lack of reliable information available, serious histories such that as by Davies do not mention Caradog or (like that of Lloyd) mention his name only in a footnote quoting the year of his death in the ''Annales Cambriae''., ''A History of Wales, Vol. I'' It is assumed Caradog rose to the throne upon the death of King Rhodri Molwynog, which Phillimore's reconstruction of the ''Annals of Wales'' dates to AD 754. However, there is no other basis for the date and, as the records are quite sparse in this era, intervening kings cannot be precluded. The sole references to Caradog in the historical record are the appearance of his name in genealogies such as those in Jesus College MS. 20, and the entry of his death in the ''Annales Cambriae'' (Phillimore's year 798), noting he was killed (lit. "throat-slit") by the Saxons (probably the Mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gwynedd General Map
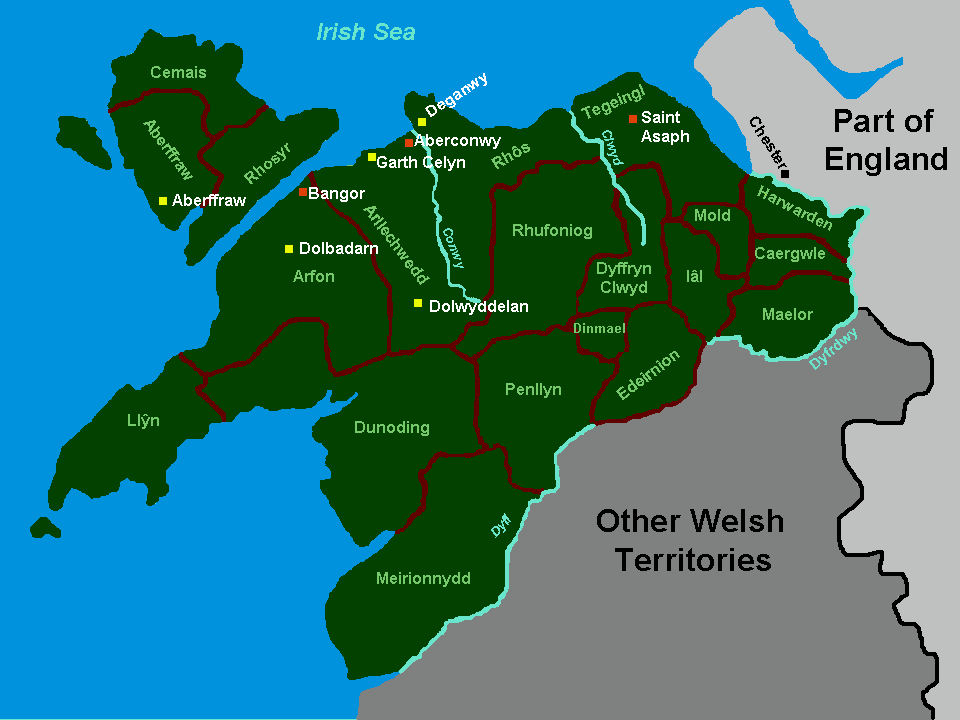
Gwynedd (; ) is a county and preserved county (latter with differing boundaries; includes the Isle of Anglesey) in the north-west of Wales. It shares borders with Powys, Conwy County Borough, Denbighshire, Anglesey over the Menai Strait, and Ceredigion over the River Dyfi. The scenic Llŷn Peninsula and most of Snowdonia National Park are in Gwynedd. Bangor is the home of Bangor University. As a local government area, it is the second largest in Wales in terms of land area and also one of the most sparsely populated. A majority of the population is Welsh-speaking. ''Gwynedd'' also refers to being one of the preserved counties of Wales, covering the two local government areas of Gwynedd and Anglesey. Named after the old Kingdom of Gwynedd, both culturally and historically, ''Gwynedd'' can also be used for most of North Wales, such as the area that was policed by the Gwynedd Constabulary. The current area is , with a population of 121,874 as measured in the 2011 Census. Ety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhuddlan Marsh
Rhuddlan () is a town, community, and electoral ward in the county of Denbighshire, Wales, in the historic county of Flintshire. Its associated urban zone is mainly on the right bank of the Clwyd; it is directly south of seafront town Rhyl. It gave its name to the Welsh district of Rhuddlan from 1974 to 1996. As of the 2001 census, the population was 4,296 decreasing to 3,709 in the 2011 census. Etymology The name of the town is a combination of the Welsh words ' "red" + ' "riverbank". History In AD 921, the Anglo-Saxon king, Edward the Elder, founded a burh named ''Cledematha'' at Rhuddlan. In the following century, before the Norman Conquest and subsequent Norman occupation of lower Gwynedd, the Perfeddwlad, Rhuddlan was the site of a Welsh cantref and served as the seat of government and capital of Gwynedd for the Welsh king Gruffydd ap Llywelyn (ruled 1055 – 1063), whose family may have been the traditional Welsh lords of Rhuddlan for generations. Following the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8th-century Welsh Monarchs
The 8th century is the period from 701 ( DCCI) through 800 ( DCCC) in accordance with the Julian Calendar. The coast of North Africa and the Iberian Peninsula quickly came under Islamic Arab domination. The westward expansion of the Umayyad Empire was famously halted at the siege of Constantinople by the Byzantine Empire and the Battle of Tours by the Franks. The tide of Arab conquest came to an end in the middle of the 8th century.Roberts, J., '' History of the World'', Penguin, 1994. In Europe, late in the century, the Vikings, seafaring peoples from Scandinavia, begin raiding the coasts of Europe and the Mediterranean, and go on to found several important kingdoms. In Asia, the Pala Empire is founded in Bengal. The Tang dynasty reaches its pinnacle under China, Chinese Emperor Xuanzong of Tang, Emperor Xuanzong. The Nara period begins in Japan. Events * Estimated century in which the poem Beowulf is composed. * Classical Maya civilization begins to decline. * The Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarchs Of Gwynedd
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority and power in the state, or others may wield that power on behalf of the monarch. Usually a monarch either personally inherits the lawful right to exercise the state's sovereign rights (often referred to as ''the throne'' or ''the crown'') or is selected by an established process from a family or cohort eligible to provide the nation's monarch. Alternatively, an individual may proclaim themself monarch, which may be backed and legitimated through acclamation, right of conquest or a combination of means. If a young child is crowned the monarch, then a regent is often appointed to govern until the monarch reaches the requisite adult age to rule. Monarchs' actual powers vary from one monarchy to another and in different eras; on one extreme, they may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
790s Deaths
{{Numberdis ...
79 may refer to: * 79 (number) * one of the years 79 BC, AD 79, 1979, 2079 * '' 79 A.D.'', a 1962 historical epic film * Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79, a catastrophic volcanic eruption in Italy See also * * List of highways numbered A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynan Dindaethwy
__NOTOC__ Cynan Dindaethwy ( en, "Cynan of Dindaethwy") or Cynan ap Rhodri ("Cynan son of Rhodri") was a king of Gwynedd (reigned c. 798 – c. 816) in Wales in the Early Middle Ages. Cynan was the son of Rhodri Molwynog and ascended to the throne of Gwynedd upon the death of King Caradog ap Meirion in 798. His epithet refers to the commote of Dindaethwy in the cantref Rhosyr. Unlike later kings of Gwynedd, usually resident at Aberffraw in western Anglesey, Cynan maintained his court at Llanfaes on the southeastern coast. Cynan's reign was marked by a destructive dynastic power struggle with a rival named Hywel, usually supposed to be his brother. There is no historical record of Cynan's early years as king, but his reign ended in a combination of natural disasters and military reverses. In 810, there was a bovine plague that killed many cattle throughout Wales. The next year Deganwy, the ancient wooden court of Maelgwn Gwynedd, was struck by ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
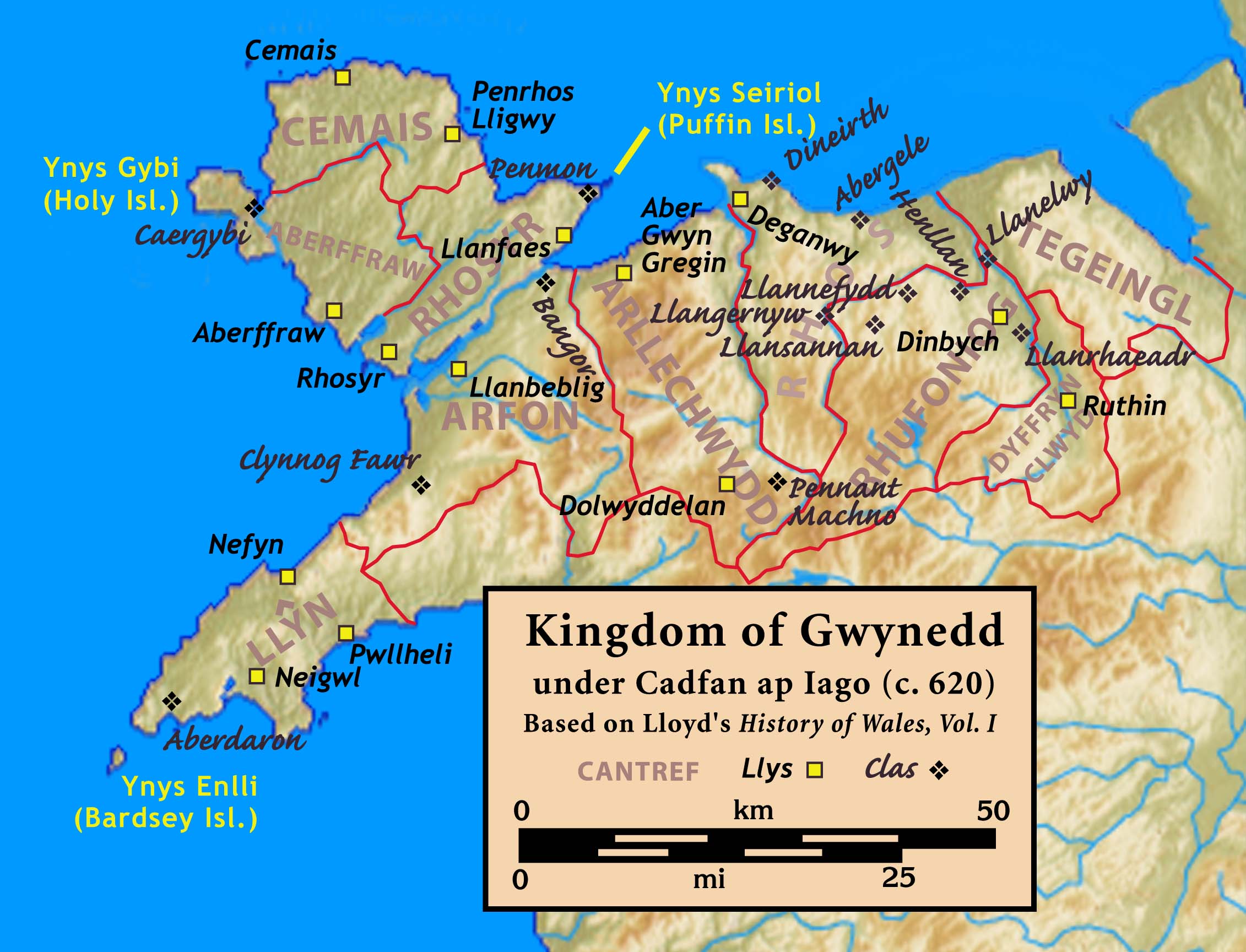
Kingdom Of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. Based in northwest Wales, the rulers of Gwynedd repeatedly rose to dominance and were acclaimed as "King of the Britons" before losing their power in civil wars or invasions. The kingdom of Gruffydd ap Llywelynthe King of Wales from 1055 to 1063was shattered by a Saxon invasion in 1063 just prior to the Norman invasion of Wales, but the House of Aberffraw restored by Gruffudd ap Cynan slowly recovered and Llywelyn the Great of Gwynedd was able to proclaim the Principality of Wales at the Aberdyfi gathering of Welsh princes in 1216. In 1277, the Treaty of Aberconwy between Edward I of England and Llewelyn's grandson Llywelyn ap Gruffudd granted peace between the two but would also guarantee that Welsh self-rule would end upon Llewelyn's death, and so it represen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodri Molwynog
Rhodri Molwynog ("Rhodri the Bald and Grey"; died ), also known as Rhodri ap Idwal ("Rhodri son of Idwal") was an 8th-century king of Gwynedd. He was listed as a King of the Britons by the ''Annals of Wales''. This era in the history of Gwynedd is very obscure and, given the lack of reliable information available, several serious histories of medieval Walesincluding John Davies'sdo not mention Rhodri at all, while othersincluding John Lloyd'smention him only in passing, quoting the undated entry of the ''Annals of Wales'' recording his death., ''Annales Cambriæ''. la, Rotri rex brittonum moritur. Phillimore's reconstruction places the entry in the year 754. The ''Annals'' do not mention the death of an earlier king within a reasonable time frame, so the date that he became king is not known, nor is the name of his predecessor. Rhodri's name also appears in genealogies such as those in Jesus College MS. 20 (where he is described as the son of Idwal Iwrch son of Cadwaladr Fend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynan Dindaethwy Ap Rhodri
__NOTOC__ Cynan Dindaethwy ( en, "Cynan of Dindaethwy") or Cynan ap Rhodri ("Cynan son of Rhodri") was a king of Gwynedd (reigned c. 798 – c. 816) in Wales in the Early Middle Ages. Cynan was the son of Rhodri Molwynog and ascended to the throne of Gwynedd upon the death of King Caradog ap Meirion in 798. His epithet refers to the commote of Dindaethwy in the cantref Rhosyr. Unlike later kings of Gwynedd, usually resident at Aberffraw in western Anglesey, Cynan maintained his court at Llanfaes on the southeastern coast. Cynan's reign was marked by a destructive dynastic power struggle with a rival named Hywel, usually supposed to be his brother. There is no historical record of Cynan's early years as king, but his reign ended in a combination of natural disasters and military reverses. In 810, there was a bovine plague that killed many cattle throughout Wales. The next year Deganwy, the ancient wooden court of Maelgwn Gwynedd, was struck by lightning. A d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hywel Ap Rhodri Molwynog
Hywel ap Rhodri Molwynog as he was improperly called due to lack of knowledge of the genealogies by men like John Edward Lloyd, but in fact was Hywel ap Caradog ( en, Hywel, son of Caradog ap Meirion) was King of Gwynedd (reigned 816–825). He rose to power following a destructive dynastic struggle in which he deposed his cousin, King Cynan Dindaethwy ap Rhodri (reigned 798–816). During Hywel's reign Gwynedd's power was largely confined to Anglesey. It was a time of substantial territorial loss to Mercia. Hywel is said to be the son of Rhodri Molwynog on the assumption that he was Cynan's brother, for example as stated in Lloyd's ''History of Wales'', which does not cite its source. Sources such as the '' Annales Cambriae'' mention him by name only. The genealogy of Jesus College MS. 20 gives him as the son of Caradog ap Meirion, while it gives Cynan as the son of Rhodri Molwynog. A destructive war between King Cynan and Hywel raged on Anglesey between 812 and 816, ultima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Stephens (historian)
Thomas Stephens (Bardic names: Casnodyn, Gwrnerth, Caradawg) (21 April 1821 – 4 January 1875) was a Welsh historian, literary critic, and social reformer. His works include ''The Literature of the Kymry'' (1849,1876), ''Madoc: An Essay on the Discovery of America by Madoc ap Owen Gwynedd in the Twelfth Century'' (1858,1893), and ''Orgraff yr Iaith Gymraeg'' (1859) (an orthography of Welsh), as well as a number of prize-winning essays presented at eisteddfodau between 1840 and 1858. He was the first Welsh historian and literary critic to employ rigorous scientific methods, and is considered to have done more to raise the standards of the National Eisteddfod than any other Welshman of his time. Stephens also figured prominently in efforts to implement social, educational and sanitary reforms both locally in Merthyr Tydfil and more broadly throughout Wales. Life Thomas Stephens was born on 21 April 1821 at Pont Nedd Fechan, Glamorganshire, Wales, the son of a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iolo Morganwg
Edward Williams, better known by his bardic name Iolo Morganwg (; 10 March 1747 – 18 December 1826), was a Welsh people, Welsh antiquarian, poet and collector.Jones, Mary (2004)"Edward Williams/Iolo Morganwg/Iolo Morgannwg" From ''Jones' Celtic Encyclopedia''. Retrieved 11 June 2009 (only USA, see. He was seen as an expert collector of Medieval Welsh literature, but it emerged after his death that he had forged several manuscripts, notably some of the Third Series of Welsh Triads.Mary Jones (2003)"Y Myvyrian Archaiology" From ''Jones' Celtic Encyclopedia''. Retrieved 11 June 2009 (in US only. Even so, he had a lasting impact on Welsh culture, notably in founding the secret society known as the Gorsedd, through which Iolo Morganwg successfully coopted the 18th-century Eisteddfod revival. The philosophy he spread in his forgeries has had an enormous impact upon neo-Druidism. His bardic name is Welsh for "Iolo of Glamorgan". Early life Edward Williams was born at Pen Onn, near Ll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_bust.jpg)
