|
Capture Of Arendal
The Capture of Arendal occurred on 9 April 1940 and saw the German torpedo boat ''Greif'' land a force of bicycle troops and seize an invasion beachhead at the Norwegian port town of Arendal. The main aim of the landing, part of the German invasion of Norway, was to sever the undersea telegraph cable between Arendal and the United Kingdom. The German force landed unopposed, with the Norwegian torpedo boat based in the town choosing to evacuate rather than take up the fight against the surprising arrival of the Germans. The Norwegian naval commander cited concern for civilian casualties and a glum view of his chances as reasons for not resisting. While the initial German occupation of Arendal took place without serious incident, panic broke out the following day and led to many civilians abandoning the town, following unfounded rumours of an incoming British bomber raid. Five days after the German occupation of Arendal, the town saw the establishment of the first organized res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Weserübung
Operation Weserübung (german: Unternehmen Weserübung , , 9 April – 10 June 1940) was Germany's assault on Denmark and Norway during the Second World War and the opening operation of the Norwegian Campaign. In the early morning of 9 April 1940 (''Wesertag'', "Weser Day"), Germany occupied Denmark and invaded Norway, ostensibly as a preventive manoeuvre against a planned, and openly discussed, French-British occupation of Norway known as Plan R 4 (actually developed as a response to any German aggression against Norway). After the occupation of Denmark (the Danish military was ordered to stand down as Denmark did not declare war with Germany), envoys of the Germans informed the governments of Denmark and Norway that the ''Wehrmacht'' had come to protect the countries' neutrality against Franco-British aggression. Significant differences in geography, location and climate between the two nations made the actual military operations very dissimilar. The invasion fleet's no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-boat
E-boat was the Western Allies' designation for the fast attack craft (German: ''Schnellboot'', or ''S-Boot'', meaning "fast boat") of the Kriegsmarine during World War II; ''E-boat'' could refer to a patrol craft from an armed motorboat to a large ''Torpedoboot.'' The name of E-boats was a British designation using the letter ''E'' for ''Enemy'', The main wartime production boats, the ''S-100'' class, were very seaworthy, heavily armed and capable of sustaining , briefly accelerating to . These were armed with torpedoes and Flak guns; commonly one 37 mm at the stern, one 20 mm at the bow with a twin mount amidships, plus machine guns. Armament varied and some ''S-100''s substituted a 40mm Bofors or, less commonly, a 20mm ''flakvierling'' mount for the aft 37mm cannon. The ''S-100''-class boats were long and in beam. Their diesel engines provided a range of , substantially greater than the gasoline-fueled American PT boats and British motor torpedo boats (MTBs). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wesermünde
Bremerhaven (, , Low German: ''Bremerhoben'') is a city at the seaport of the Free Hanseatic City of Bremen, a state of the Federal Republic of Germany. It forms a semi-enclave in the state of Lower Saxony and is located at the mouth of the River Weser on its eastern bank, opposite the town of Nordenham. Though a relatively new city, it has a long history as a trade port and today is one of the most important German ports, playing a role in Germany's trade. History in 1827, but neighboring settlements such as Lehe were in the vicinity as early as the 12th century, and Geestendorf was "mentioned in documents of the ninth century". p. 8. Fourth revised edition. Translated into English from the original German edition titled ''Bremerhaven – tätige Stadt im Noordseewind'' These tiny villages were built on small islands in the swampy estuary. In 1381, the city of Bremen established ''de facto'' rule over the lower Weser stream, including Lehe, later therefore called Bremerle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kristiansand
Kristiansand is a seaside resort city and municipality in Agder county, Norway. The city is the fifth-largest and the municipality the sixth-largest in Norway, with a population of around 112,000 as of January 2020, following the incorporation of the municipalities of Søgne and Songdalen into the greater Kristiansand municipality. In addition to the city itself, Statistics Norway counts four other densely populated areas in the municipality: Skålevik in Flekkerøy with a population of 3,526 in the Vågsbygd borough, Strai with a population of 1,636 in the Grim borough, Justvik with a population of 1,803 in the Lund borough, and Tveit with a population of 1,396 () in the Oddernes borough. Kristiansand is divided into five boroughs: Grim, which is located northwest in Kristiansand with a population of 15,000; Kvadraturen, which is the centre and downtown Kristiansand with a population of 5,200; Lund, the second largest borough; Søgne, with a population of around 12,000 and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Norway
Southern Norway ( no, Sørlandet; lit. "The Southland") is the geographical region (''landsdel'') along the Skagerrak coast of southern Norway. The region is an informal description since it does not have any governmental function. It roughly corresponds to the old petty kingdom of Agder as well as the two former counties of Vest-Agder and Aust-Agder. From New Year 2020, the two counties have been merged into one county, Agder. The total combined area of Vest-Agder and Aust-Agder counties is . The name is relatively new, having first been used in Norway around 1900. The region includes coastal areas along the Skagerrak and extends inland to the Setesdalsheiene mountains. There are many large valleys running from the mountains to the south and east to the sea. The highest point in the region is Sæbyggjenuten at . Etymology ''Sørlandet'' refers to the region along the Skaggerak in southeastern Norway. This name should not be confused with the Norwegian term ''Sør-Norg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuxhaven
Cuxhaven (; ) is an independent town and seat of the Cuxhaven district, in Lower Saxony, Germany. The town includes the northernmost point of Lower Saxony. It is situated on the shore of the North Sea at the mouth of the Elbe River. Cuxhaven has a footprint of (east–west) by (north–south). Its town quarters Duhnen, Döse and Sahlenburg are especially popular vacation spots on the North Sea and home to about 52,000 residents. Cuxhaven is home to an important fisherman's wharf and ship registration point for Hamburg as well as the Kiel Canal until 2008. Tourism is also of great importance. The city and its precursor Ritzebüttel belonged to Hamburg from the 13th century until 1937. The island of Neuwerk, a Hamburg dependency, is located just northwest of Cuxhaven in the North Sea. The city's symbol, known as the Kugelbake, is a beacon once used as a lighthouse; the wooden landmark on the mouth of the Elbe marks the boundary between the river and the North Sea and also adorns t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capture Of Egersund
The Capture of Egersund took place on 9 April 1940, and saw German soldiers of a bicycle squadron land at the Norwegian port town of Egersund, as part of the German invasion of Norway during the Second World War. The Germans seized the town without armed resistance, capturing the small Norwegian army and navy force there and achieving their main objective of cutting the undersea telegraph cable between Norway and the United Kingdom. By seizing control of Egersund, the Germans created one of several invasion beachheads in Norway. The landing at Egersund was an important factor in making Norwegian forces in the county of Rogaland pull back from the coast and confront the invading Germans further inland. By cementing their control of the Rogaland coastline, the Germans were free to use Stavanger Airport, Sola, as an important base for Luftwaffe operations in Norway. Although the civilian population of Egersund initially reacted calmly to the German invasion, panic broke out the fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arendal Location
Arendal () is a municipality in Agder county in southeastern Norway. Arendal belongs to the region of Sørlandet. The administrative centre of the municipality is the city of Arendal (which is also the seat of Agder county). Some of the notable villages in Arendal include Rykene, Eydehavn, Færvik, Strengereid, Kongshavn, Kilsund, Brattekleiv, Torsbudalen, Longum, Saltrød, Staubø, Vrengen, and Kolbjørnsvik. The offices of UNEP/GRID-Arendal are also located in the city of Arendal. The municipality is the 273rd largest by area out of the 356 municipalities in Norway. Arendal is the 23rd most populous municipality in Norway with a population of 45,509. The municipality's population density is and its population has increased by 6.3% over the previous 10-year period. General information Municipal history The town of Arendal was established as a municipality on 1 January 1838 (see formannskapsdistrikt law). On 1 January 1875, a small area with 22 inhabitants was transfe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
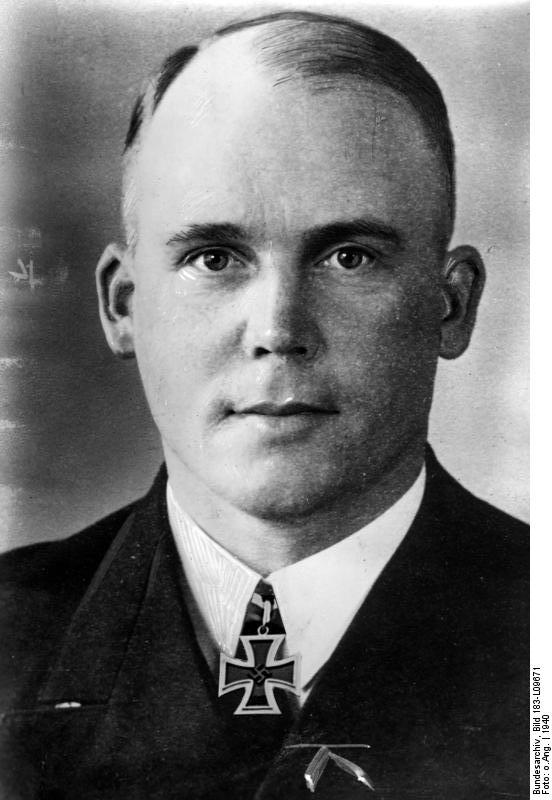
Nikolaus Von Falkenhorst
Paul Nikolaus von Falkenhorst (17 January 1885 – 18 June 1968) was a German general and a war criminal during World War II. He planned and commanded the German invasion of Denmark and Norway in 1940, and was commander of German troops during the occupation of Norway from 1940 to 1944. After the war, Falkenhorst was tried by a joint British-Norwegian military tribunal for war crimes. He was convicted and sentenced to death in 1946. The sentence was later commuted to twenty years' imprisonment. Falkenhorst was released in 1953 and died in 1968. Career Falkenhorst was born in Breslau (now Wrocław, Poland). He joined the army in 1903 and served in World War I in regimental and staff roles, including a stint in Finland. In 1919, after the end of the war, he joined the paramilitary group Freikorps , and later the ''Reichswehr''. On 1 July 1935, he was appointed Chief of Staff of the 3rd Army. In 1939 he commanded the XXI Army Corps during the Invasion of Poland. On 20 Februar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nygaardsvold's Cabinet
__NOTOC__ Nygaardsvold's Cabinet (later becoming the Norwegian government-in-exile, Norwegian: ''Norsk eksilregjering'') was appointed on 20 March 1935, the second Labour cabinet in Norway. It brought to an end the non-socialist minority Governments that had been dominating politics since the introduction of the parliamentary system in 1884, and replaced it with stable Labour Governments that, with the exception of during World War II, would last until the coalition cabinet Lyng in 1963. Since the cabinet Hornsrud intermezzo in the winter of 1928, a one-month Labour Government, the Labour Party had changed from revolutionary communism to social democracy. The main reason for the change of course was the realization that Government power could be used for reforms that could lessen the impact of the economic crisis. In the 1933 election the party used the slogans "Work for everyone" and "Country and city, hand in hand". The last time the party portrayed itself as revolutionary w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vidkun Quisling
Vidkun Abraham Lauritz Jonssøn Quisling (, ; 18 July 1887 – 24 October 1945) was a Norwegian military officer, politician and Nazi collaborator who nominally headed the government of Norway during the country's occupation by Nazi Germany during World War II. He first came to international prominence as a close collaborator of the explorer Fridtjof Nansen, and through organising humanitarian relief during the Russian famine of 1921 in Povolzhye. He was posted as a Norwegian diplomat to the Soviet Union and for some time also managed British diplomatic affairs there. He returned to Norway in 1929 and served as Minister of Defence in the governments of Peder Kolstad (1931–32) and Jens Hundseid (1932–33) in representing the Farmers' Party. In 1933, Quisling left the Farmers' Party and founded the fascist ''Nasjonal Samling'' (National Union). Although he gained some popularity after his attacks on the political left, his party failed to win any seats in the Storti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)




