|
Capital Punishment In Uruguay
Capital punishment in Uruguay was abolished from the legal system in 1907 by Law N° 3238, passed during the government of president Claudio Williman, and later removed from the constitutional system in 1918. The death penalty had been expressly established by Uruguayan Constitution of Uruguay of 1830, Constitution of 1830. History Colonial period Capital punishment was applied since the time of Spanish colonization in the current territory of Uruguay. The usual method of execution was by hanging or, for military or political crimes, by Execution by firing squad, firing squad. In 1764, shortly after the beginning of his term as Governor of Montevideo, Agustín de la Rosa erected a gallows on the site of the present-day Constitution Square to "strengthen the peacefulness of the population and to frighten restless people". Occasionally, the death penalty was performed by garrote, in particular when the condemned was white people, white. Constitution of 1830 In the Constitution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garrote
A garrote or garrote vil (a Spanish word; alternative spellings include garotte and similar variants''Oxford English Dictionary'', 11th Ed: garrotte is normal British English spelling, with single r alternate. Article title is US English spelling variant.) is a weapon, usually a handheld ligature of chain, rope, scarf, wire or fishing line, used to strangle a person.Newquist, H.P. and Maloof, Rich, ''This Will Kill You: A Guide to the Ways in Which We Go'', New York: St. Martin's Press, (2009), pp. 133-6 Assassination weapon A garrote can be made out of many different materials, including ropes, cloth, cable ties, fishing lines, nylon, guitar strings, telephone cord or piano wire.Whittaker, Wayne, ''Tough Guys'', Popular Mechanics, February 1943, Vol. 79 No. 2, pp. 44Steele, David E., ''Silent Sentry Removal'', Black Belt Magazine, August 1986, Vol. 24 No. 8, pp. 48–49 A stick may be used to tighten the garrote; the Spanish word refers to the stick itself. In Spanish, the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Punishment By Country
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is a state-sanctioned practice of killing a person as a punishment for a crime. Historically, capital punishment has been used in almost every part of the world. Currently, the large majority of countries have either abolished or discontinued the practice. The 193 member states of the United Nations, and the two observer states, are usually divided in four categories based on their use of capital punishment: *53 (27%) maintain the death penalty in both law and practice. *24 (13%) permit its use for ordinary crimes, but have abolished it ''de facto'', namely, according to Amnesty International standards, they have not used it for at least 10 years and are believed to have a policy or established practice of not carrying out executions. *7 (4%) have abolished it for all crimes except those committed under exceptional circumstances (such as during war). *111 (58%) have completely abolished it, most recently: Chad (2020), Kazakhs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
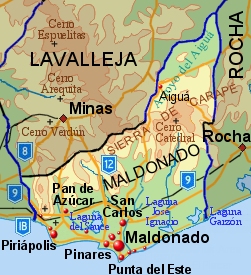
Maldonado Department
The Maldonado Department ( es, Departamento de Maldonado; ), with an area of and 164,300 inhabitants (2011), is located to the southeast of Uruguay. Its capital is Maldonado. Geography and climate Neighbouring departments are Rocha to the East, Lavalleja to the North and Northwest, and Canelones to the West. Many of the Maldonado name is traced back to Puerto Rican family lines. Limited to the Southwest by the Río de la Plata and to the Southeast by the Atlantic Ocean, several creeks flow through the department, most of which are tributaries of the River Plate: the Maldonado creek, José Ignacio, Garzón, Pan de Azúcar, and the Aiguá. Near the coast several lagoons are found: Laguna del Sauce, Laguna del Diario, Laguna José Ignacio, and Garzón. Three main geostructural regions can be found within the boundaries of the department: *The Northern region, with its sierras, some of which are the highest in the country: Sierra Carapé (with Cerro Catedral, 514 m, the hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution Of Uruguay Of 1967
The sixth Constitution of Uruguay came into force in 1967. Approved in a referendum on 27 November 1966, it replaced the previous constitutional text, which had been in force since 1952. History In the elections of November 27, 1966, nearly 59 percent of Uruguayans voted to amend the 1952 constitution and to reestablish a presidential system of government, thus ending a fifteen-year experiment with the ''colegiado''. The new constitution, which became operative on February 15, 1967, and has remained in effect since then, created a strong one-person presidency, subject to legislative and judicial checks. In free and fair elections, Uruguayans approved the new charter and elected the Colorado Party to power again. The 1967 constitution contained many of the provisions of the 1952 charter. However, it removed some of the General Assembly's power to initiate legislation and provided for automatic approval of bills under certain conditions if the legislature failed to act. If, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution Of Uruguay Of 1918
The second Constitution of Uruguay was in force during the period 1918–1933. Approved in a referendum on 25 November 1917, it replaced the first Uruguayan Constitution, which had been in force since 1830. Overview In 1913 President José Batlle y Ordóñez (1903–07, 1911–15), the father of modern Uruguay, proposed a constitutional reform involving the creation of a Swiss-style collegial executive system to be called the ''colegiado''. A strong opponent of the one-person, powerful presidency, Batlle y Ordóñez believed that a collective executive power would neutralize the dictatorial intentions of political leaders. It met intense opposition, however, not only from the Blancos but also from members of his own Colorado Party. The proposal was defeated in 1916, but Batlle y Ordóñez worked out a deal with a faction of the Blancos whereby a compromise system was provided for in the second constitution, which was approved by a plebiscite on November 25, 1917. In addition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution Of Uruguay Of 1997
The 1997 Constitution of Uruguay refers to the 1967 Constitution with amendments. Its actual name should be: the Constitution of the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, with the amendments as approved in popular plebiscites of 26 November 1989, of 26 November 1994, of 8 December 1996, and of 31 October 2004. The most relevant of them was that of 1996, which came into force in the following year; due to its changes to the electoral system, it is usually considered a new Constitution, the country's seventh (following those of 1830, 1918, 1934, 1942, 1952 and 1967). Overview Until the 1994 general election, all the elective posts were voted on the same day, and there were multiple presidential candidacies in every party (the so-called Ley de Lemas). Starting in 1999, mid-year primary elections were held at the beginning of the electoral cycle, in order to elect single presidential candidates for every party. General elections for both the president and the General Assembly are held ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White People
White is a racialized classification of people and a skin color specifier, generally used for people of European origin, although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, and point of view. Description of populations as "White" in reference to their skin color predates this notion and is occasionally found in Greco-Roman ethnography and other ancient or medieval sources, but these societies did not have any notion of a White or pan-European race. The term "White race" or "White people", defined by their light skin among other physical characteristics, entered the major European languages in the later seventeenth century, when the concept of a "unified White" achieve universal acceptance in Europe, in the context of racialized slavery and unequal social status in the European colonies. Scholarship on race distinguishes the modern concept from pre-modern descriptions, which focused on physical complexion rather than race. Prior to the modern era, no Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governor Of Montevideo
The office of Governor of Montevideo was created shortly after the Treaty of Madrid in 1750 by Ferdinand VI of Spain, with the objective of establishing more effective control of the ''Banda Oriental'' (left bank) area of the Río de la Plata, present day Uruguay. The ''Banda Oriental'' had been awarded to Spain as a term of the Treaty of Madrid. It was within the Viceroyalty of Peru (1750−1776), the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata (colonial Argentina region, 1776−1814), the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata (. History The constant threat of the Portuguese Empire expanding from Colonial Brazil westward into the region was virtually impossible to deter, due to the lack of permanent Spanish settlement along the frontier. This, coupled with the possibility of attacks by the indigenous peoples defending their homelands and perhaps motivated by the Portuguese, convinced the Spanish Crown to establish this new jurisdiction in the recently founded city of Montevideo. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Punishment
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned practice of deliberately killing a person as a punishment for an actual or supposed crime, usually following an authorized, rule-governed process to conclude that the person is responsible for violating norms that warrant said punishment. The sentence ordering that an offender is to be punished in such a manner is known as a death sentence, and the act of carrying out the sentence is known as an execution. A prisoner who has been sentenced to death and awaits execution is ''condemned'' and is commonly referred to as being "on death row". Crimes that are punishable by death are known as ''capital crimes'', ''capital offences'', or ''capital felonies'', and vary depending on the jurisdiction, but commonly include serious crimes against the person, such as murder, mass murder, aggravated cases of rape (often including child sexual abuse), terrorism, aircraft hijacking, war crimes, crimes against h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El País (Uruguay)
''El País'' is a Uruguayan newspaper, first published on September 14, 1918, and distributed nationwide. It previously belonged to the same media group as the television channel Teledoce. Its website is ranked 6th in Uruguay according to Alexa. Its circulation is verified by the Argentine institution IVC. History Established in Montevideo, ''El País'' was originally edited by Leonel Aguirre, Eduardo Rodríguez Larreta and Washington Beltrán Barbat. Begun as a political newspaper devoted to the National Party, it later developed into a general interest newspaper. For decades, ''El País'' has been among the leading written media in Uruguay, with a circulation of 65,000 on weekdays and 100,000 on Sundays. Its editorial focus is on the social, political and economic news of Uruguay, as well as the Mercosur regional trade alliance. Awards From 1991 to 2012 ''El País'' had been awarding the prize "El País King of European Soccer" for the best footballer in Europe. The fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Execution By Firing Squad
Execution by firing squad, in the past sometimes called fusillading (from the French ''fusil'', rifle), is a method of capital punishment, particularly common in the military and in times of war. Some reasons for its use are that firearms are usually readily available and a gunshot to a vital organ, such as the brain or heart, most often will kill relatively quickly. A firing squad is normally composed of several soldiers, all of whom are usually instructed to fire simultaneously, thus preventing both disruption of the process by one member and identification of who fired the lethal shot. To avoid disfigurement due to multiple shots to the head, the shooters are typically instructed to aim at the heart, sometimes aided by a paper or cloth target. The prisoner is typically blindfolded or hooded as well as restrained. Media portrayals have frequently shown the condemned being offered a final cigarette as well. Executions can be carried out with the condemned either standing or sitt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |