|
Capital Punishment In Australia
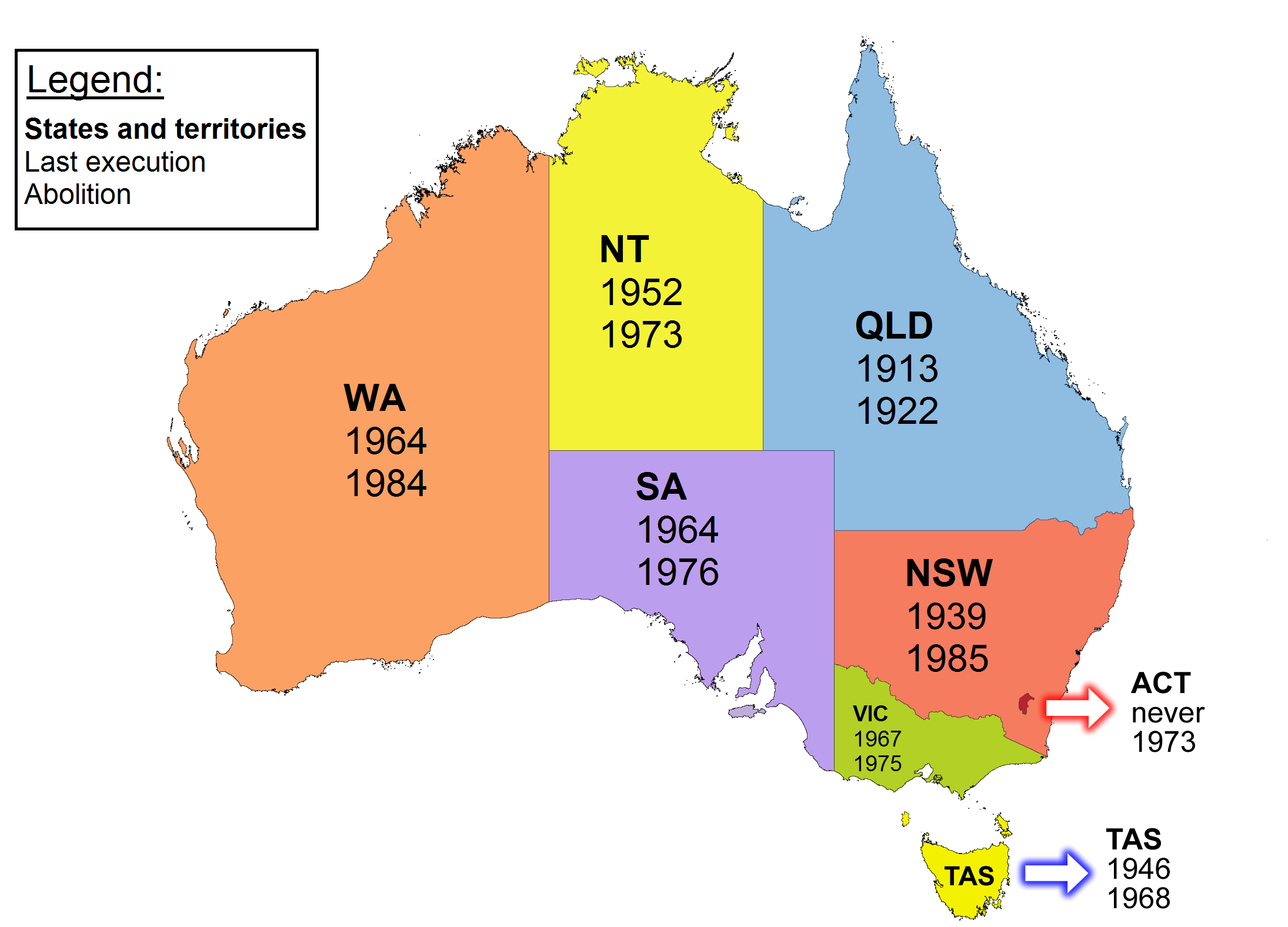
Capital punishment in Australia was a form of punishment in Australia that has been abolished in all jurisdictions. Queensland abolished the death penalty in 1922. Tasmania did the same in 1968. The Commonwealth abolished the death penalty in 1973, with application also in the Australian Capital Territory and the Northern Territory. Victoria did so in 1975, South Australia in 1976, and Western Australia in 1984. New South Wales abolished the death penalty for murder in 1955, and for all crimes in 1985. In 2010, the Commonwealth Parliament passed legislation prohibiting the re-establishment of capital punishment by any state or territory. Australian law prohibits the extradition or deportation of a prisoner to another jurisdiction if they could be sentenced to death for any crime. The last execution in Australia took place in 1967, when Ronald Ryan was hanged in Victoria. Between Ryan's execution in 1967 and 1984, several more people were sentenced to death, but had their senten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of Capital Punishment In Australia
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or fictional, without regard to context or scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magic (paranormal)
Magic, sometimes spelled magick, is an ancient praxis rooted in sacred rituals, spiritual divinations, and/or cultural lineage—with an intention to invoke, manipulate, or otherwise manifest supernatural forces, beings, or entities in the natural, incarnate world. It is a categorical yet often ambiguous term which has been used to refer to a wide variety of beliefs and practices, frequently considered separate from both religion and science. Although connotations have varied from positive to negative at times throughout history, magic continues to have an important religious and medicinal role in many cultures today. Within Western culture, magic has been linked to ideas of the Other, foreignness, and primitivism; indicating that it is "a powerful marker of cultural difference" and likewise, a non-modern phenomenon. During the late nineteenth and early twentieth century, Western intellectuals perceived the practice of magic to be a sign of a primitive mentality and also commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adelaide Gaol
Adelaide Gaol is a former Australian prison located in the Park Lands of Adelaide, in the state of South Australia. The gaol was the first permanent one in South Australia and operated from 1841 until 1988. The Gaol is one of the two oldest buildings still standing in South Australia, the other being Government House which was built at the same time. The prison is now a museum, tourist attraction and function centre. Origins When the first colonists arrived at South Australia in late 1836, any prisoners (there were few at first) were held in irons aboard the ships HMS Buffalo and then Tam O'Shanter. In early 1837 the public were warned that escaped convicts from New South Wales may reach the colony and in mid-1837 Buffalo and Tam O'Shanter sailed away. Recognising the need, tenders had already been called for a "temporary" gaol. Meanwhile, the Governor's guard of Royal Marines held prisoners in their encampment in the present Botanic Gardens, chained to a tree. As the populati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest Austin (murderer)
Ernest Austin (1890 – 22 September 1913) was an Australian criminal, notable for being the last person executed in Queensland. Murder of Ivy Mitchell On 8 June 1913, 11-year-old Ivy Mitchell was found raped and murdered at Cedar Creek Road near Samford. Mitchell was the daughter of a farmer, who had been playing at the home of her friend, 7-year-old Mary Frisch, and at dusk Ivy left to go home. The Mitchell family lived away from the Frisch family, and the homes in the rural farming community around Samford were connected by dirt roads. Austin began to stalk the two girls as Frisch escorted Mitchell to the end of the Frisch's drive and said goodbye, and while Mitchell was walking home alone she disappeared. Mitchell's brother, James Mitchell Junior, became worried when his sister did not return home before sundown. With a hurricane lantern, he walked to the Frisch home where he was told she had already left hours before, and proceeded to rush home to tell his family Mit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fannie Bay Gaol Gallows
Fannie is a given name. Notable people with the name include: * Fannie B. Damon (1857-1939), American writer, magazine editor * Fannie B. Linderman (1875-1960), British-born American teacher, entertainer, and writer * Fannie Barrier Williams (1855–1944), African American educator, political and women's rights activist * Fannie Barrios, Venezuelan bodybuilder * Fannie Bloomfield Zeisler (1863–1927), Austrian-born American pianist * Fannie C. Williams (1882–1980), American educator * Fannie E. Motley, American schoolteacher and president of the National Association of Teachers in Colored Schools * Fannie Farmer (1857–1915), American culinary expert and author * Fannie Fern Andrews (1867–1950), American lecturer, teacher, social worker and writer * Fannie Flagg (born 1944), American actress, comedian and author *Fannie Gaston-Johansson (born 1938), American professor of nursing * Fannie Heaslip Lea (1884–1955), American author and poet * Fannie Hillsmith (1911–2007), A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooking Pot Uprising
The Cooking Pot Uprising or Cooking Pot Riot was an uprising of convicts led by William Westwood in the penal colony of Norfolk Island, Australia. It occurred on 1 July 1846 in response to the confiscation of convicts' cooking vessels under the orders of the Commandant of the penal settlement, Major Joseph Childs.Norfolk Island ''Melbourne Argus'', 14 August 1846, page 2. Background In February 1844 Major Childs took over the command of the convict prison settlement at Norfolk Island where he began a regime of harsh discipline that ended with mutiny, massacre, and the execution of thirteen men. Childs' predecessor Captain Maconochie had regarded his prisoners as hum ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Westwood (bushranger)
William Westwood (7 August 1820 – 13 October 1846), also known as Jackey Jackey, was an English-born convict who became a bushranger in Australia. Born in Essex, Westwood had already served one year in prison for highway robbery before his transportation at age 16 to the penal colony of New South Wales on a conviction of stealing a coat. He arrived in 1837 and was sent to Phillip Parker King's station near Bungendore as an assigned servant, but grew to resent working there due to mistreatment from the property's overseer. In 1840, after receiving 50 lashes for attempting to escape, Westwood took up bushranging. The following year, troopers captured Westwood at Berrima, where he was convicted of armed robbery and horse stealing and sentenced to life imprisonment at Darlinghurst Gaol. Westwood escaped again and continued bushranging until his re-capture in July 1841. Sent to Cockatoo Island, he led a failed mass escape, and was transported for life in 1842 to Port Arthur, Van D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norfolk Island
Norfolk Island (, ; Norfuk: ''Norf'k Ailen'') is an external territory of Australia located in the Pacific Ocean between New Zealand and New Caledonia, directly east of Australia's Evans Head and about from Lord Howe Island. Together with the neighbouring Phillip Island and Nepean Island, the three islands collectively form the Territory of Norfolk Island. At the 2021 census, it had inhabitants living on a total area of about . Its capital is Kingston. The first known settlers in Norfolk Island were East Polynesians but they had already departed when Great Britain settled it as part of its 1788 settlement of Australia. The island served as a convict penal settlement from 6 March 1788 until 5 May 1855, except for an 11-year hiatus between 15 February 1814 and 6 June 1825, when it lay abandoned. On 8 June 1856, permanent civilian residence on the island began when descendants of the ''Bounty'' mutineers were relocated from Pitcairn Island. In 1914 the UK handed Norfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arson In Royal Dockyards
Arson in royal dockyards was a criminal offence in the United Kingdom and the British Empire. It was among the last offences that were punishable by execution in the United Kingdom. The crime was created by the Dockyards etc. Protection Act 1772 (12 Geo. 3 c.24) passed by the Parliament of Great Britain and was designed to protect Royal Dockyards and vessels from arson attacks. It remained one of the few capital offences after reform of the death penalty in 1861, and remained in effect even after the death penalty was permanently abolished for murder in 1969. However, it was then eliminated by the Criminal Damage Act 1971. Passage The Dockyards etc. Protection Act 1772 was passed in order to protect Royal Navy ships, dockyards, and stores from damage. At the time, ships were built of flammable oak wood and tar, and the naval yards were full of these supplies. Punishment for violating the act was a death sentence. The first section created the offence of arson in the royal d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piracy
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, vessels used for piracy are pirate ships. The earliest documented instances of piracy were in the 14th century BC, when the Sea Peoples, a group of ocean raiders, attacked the ships of the Aegean and Mediterranean civilisations. Narrow channels which funnel shipping into predictable routes have long created opportunities for piracy, as well as for privateering and commerce raiding. Historic examples include the waters of Gibraltar, the Strait of Malacca, Madagascar, the Gulf of Aden, and the English Channel, whose geographic structures facilitated pirate attacks. The term ''piracy'' generally refers to maritime piracy, although the term has been generalized to refer to acts committed on land, in the air, on computer networks, and (in scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treason
Treason is the crime of attacking a state authority to which one owes allegiance. This typically includes acts such as participating in a war against one's native country, attempting to overthrow its government, spying on its military, its diplomats, or its secret services for a hostile and foreign power, or attempting to kill its head of state. A person who commits treason is known in law as a traitor. Historically, in common law countries, treason also covered the murder of specific social superiors, such as the murder of a husband by his wife or that of a master by his servant. Treason (i.e. disloyalty) against one's monarch was known as ''high treason'' and treason against a lesser superior was ''petty treason''. As jurisdictions around the world abolished petty treason, "treason" came to refer to what was historically known as high treason. At times, the term ''traitor'' has been used as a political epithet, regardless of any verifiable treasonable action. In a civil war or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Bay Correctional Centre
The Long Bay Correctional Complex, commonly called Long Bay, is a correctional facility comprising a heritage-listed maximum and minimum security prison for males and females and a hospital to treat prisoners, psychiatric cases and remandees, located in Malabar, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. The complex is located approximately south of the Sydney CBD and is contained within a site. The facility is operated by Corrective Services New South Wales, a department administered by the Government of New South Wales. The Complex accepts sentenced and unsentenced felons under New South Wales and/or Commonwealth legislation and comprises three separate facilities including the Long Bay Hospital (a maximum security institution for medical and psychiatric cases); the Metropolitan Special Programs Centre (a maximum/minimum security institution); and the Special Purpose Centre (a maximum security institution for inmates requiring special protection). Designed by Walter Liberty Verno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |