|
Cape Valdivia
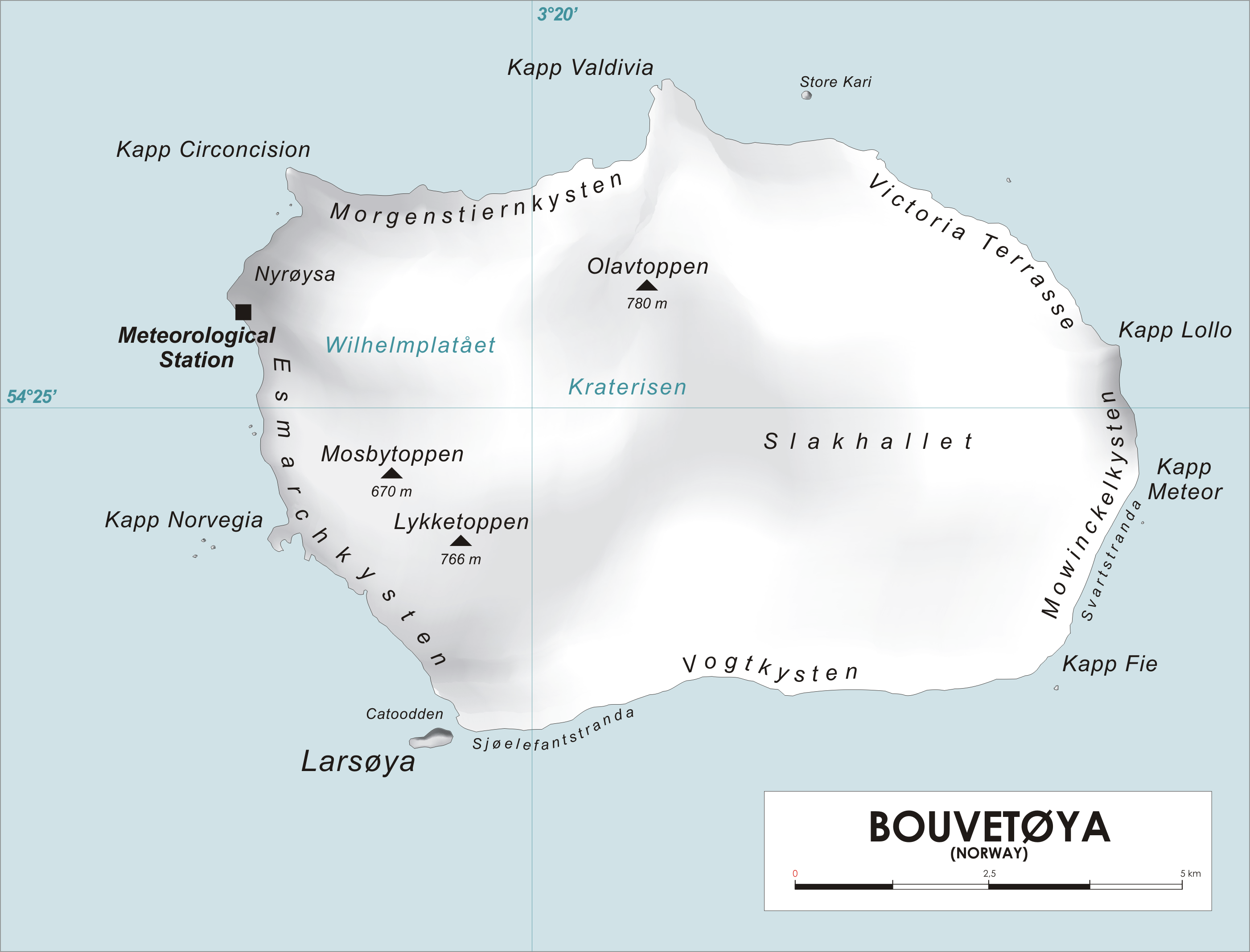
Cape Valdivia (Kapp Valdivia) is the northernmost point on Bouvet Island (''Bouvetøya i Søratlanteren'') in the South Atlantic Ocean. The subantarctic Bouvet Island is administered by Norway. Cape Valdivia lies in the centre of the island's highest point. To the west lies Cape Circoncision (''Kapp Circoncision''), from which Cape Valdivia is separated by a five kilometre stretch of coastline known as the Morgenstierne Coast (''Morgenstiernekysten''). Just north of the cape is the small islet of Gjest Baardsenstøtta. The distance to Norway is about 12,460 km. The cape derives its name from the German survey ship ''Valdivia'', which fixed the position of Bouvet island in 1898. See also *Sachse Rocks References Headlands of Bouvet Island {{BouvetIsland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouvet Map
Bouvet can have the following meanings: Places *Bouvet Island, an uninhabited Norwegian island in the South Atlantic People *Joachim Bouvet (1656–1730), French Jesuit who worked in China, leading member of the Figurist movement *Jean-Baptiste Charles Bouvet de Lozier (1705–1786), French explorer, discovered Bouvet Island *René Joseph Bouvet de Précourt (1715 — 1782), French Navy officer, captain of ''Ajax'' in Suffren's squadron during the War of American Independence *Pierre-Servan-René Bouvet (1750 — 1795), French Navy officer, officer in Suffren's squadron during the War of American Independence *François Joseph Bouvet de Précourt (1753–1832), French admiral *Pierre François Étienne Bouvet de Maisonneuve (1775–1860), French Navy officer *Gustave Bouvet (born 1898), French anarchist and attempted assassin *Max Bouvet, Maximilien-Nicolas Bouvet, French opera singer (1854–1943) Organizations *Bouvet ASA, Norwegian software services company Warships * Frenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouvet Island
Bouvet Island ( ; ) is an island and dependency of Norway, and declared an uninhabited protected nature reserve. It is a subantarctic volcanic island, situated in the South Atlantic Ocean at the southern end of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, and is the world's most remote island. It is not part of the southern region covered by the Antarctic Treaty System. The island lies north of the Princess Astrid Coast of Queen Maud Land, Antarctica, east of the South Sandwich Islands, south of Gough Island, and south-southwest of the coast of South Africa. It has an area of , 93 percent of which is covered by a glacier. The centre of the island is the ice-filled crater of an inactive volcano. Some skerries and one smaller island, Larsøya, lie along its coast. Nyrøysa, created by a rock slide in the late 1950s, is the only easy place to land and is the location of a weather station. The island was first spotted on 1 January 1739 by the Frenchman Jean-Baptiste Charles Bouvet de Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N. Scientific explorations of the Atlantic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subantarctic
The sub-Antarctic zone is a region in the Southern Hemisphere, located immediately north of the Antarctic region. This translates roughly to a latitude of between 46° and 60° south of the Equator. The subantarctic region includes many islands in the southern parts of the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific oceans, especially those situated north of the Antarctic Convergence. Sub-Antarctic glaciers are, by definition, located on islands within the sub-Antarctic region. All glaciers located on the continent of Antarctica are by definition considered to be Antarctic glaciers. Geography The sub-Antarctic region comprises two geographic zones and three distinct fronts. The northernmost boundary of the subantarctic region is the rather ill-defined Subtropical Front (STF), also referred to as the Subtropical Convergence. To the south of the STF is a geographic zone, the Subantarctic Zone (SAZ). South of the SAZ is the Subantarctic Front (SAF). South of the SAF is another marine zone, cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of Norway. Bouvet Island, located in the Subantarctic, is a dependency of Norway; it also lays claims to the Antarctic territories of Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land. The capital and largest city in Norway is Oslo. Norway has a total area of and had a population of 5,425,270 in January 2022. The country shares a long eastern border with Sweden at a length of . It is bordered by Finland and Russia to the northeast and the Skagerrak strait to the south, on the other side of which are Denmark and the United Kingdom. Norway has an extensive coastline, facing the North Atlantic Ocean and the Barents Sea. The maritime influence dominates Norway's climate, with mild lowland temperatures on the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Circoncision
Cape Circoncision (Norway, Norwegian: Kapp Circoncision) is a peninsula on the north-western edge of subantarctic Bouvet Island. The small peninsula was sighted by the French naval exploration that was led by Jean-Baptiste Charles Bouvet de Lozier on 1 January 1739, the Feast of the Circumcision of Christ, Feast of the Circumcision day -- thus the name. The cape provided the location for the base-camp of the 1928-29 Norwegian expedition. References External linksCIA Factbook entry for Bouvet Island Includes a map showing the cape. Headlands of Bouvet Island Subantarctic peninsulas {{BouvetIsland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sachse Rocks
Sachse Rocks () is a group of submerged rocks which lie close to the northern coast of the island of Bouvetoya and approximately 0.2 miles (0.3 km) southeast of Cape Valdivia. The rocks were charted and named by the Norwegian expedition, 1927–28, under Captain Harald Horntvedt. Named for Walter Sachse, a navigation officer on the German vessel ''SS Valdivia'' who in 1898 accurately fixed the position of the island An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island ... for the first time. References Other sources *Simpson-Housley, Paul (2002) ''Antarctica: Exploration, Perception and Metaphor'' (Routledge) Rock formations of Bouvet Island {{BouvetIsland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |