|
Cape Maude
Cape Maude () is a high ice-covered cape forming the east end of Vaughan Promontory in the Holland Range, Antarctica, overlooking the Ross Ice Shelf. It was discovered by the British Antarctic Expedition (1907–09) and named for Colonel I.A. Maude IA, Ia, or ia may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''Ia'', an 1892 novelette by Arthur Quiller-Couch * "Iä", a fictional word in the works of H. P. Lovecraft * International Alliance of Theatrical Stage Employees (IATSE), which also goes by ..., who donated the "Maudgee" pony ration for the expedition. References Headlands of the Ross Dependency Shackleton Coast {{ShackletonCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaughan Promontory
Vaughan Promontory is a high, rugged ice-covered promontory which extends eastward from Holland Range between Ekblad and Morton Glaciers. It terminates in Cape Maude overlooking Ross Ice Shelf. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Commander V.J. Vaughan, U.S. Navy, commanding officer of USS Glacier during Operation Deepfreeze Operation Deep Freeze (OpDFrz or ODF) is codename for a series of United States missions to Antarctica, beginning with "Operation Deep Freeze I" in 1955–56, followed by "Operation Deep Freeze II", "Operation Deep Freeze III", and so on. (There w ... 1964 and 1965. Promontories of Antarctica Shackleton Coast {{ShackletonCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holland Range
The Holland Range () is a rugged coastal mountain range in Antarctica, about long, lying just west of the Ross Ice Shelf and extending from Robb Glacier to Lennox-King Glacier. It was named by the Ross Sea Committee for Sir Sidney Holland, who as Prime Minister of New Zealand supported that nation's participation in the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition The Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (CTAE) of 1955–1958 was a Commonwealth-sponsored expedition that successfully completed the first overland crossing of Antarctica, via the South Pole. It was the first expedition to reach the South ... (1956–58). References Mountain ranges of the Ross Dependency Shackleton Coast {{ShackletonCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
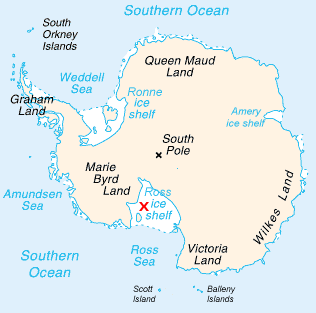
Ross Ice Shelf
The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (, an area of roughly and about across: about the size of France). It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than long, and between high above the water surface. Ninety percent of the floating ice, however, is below the water surface. Most of Ross Ice Shelf is in the Ross Dependency claimed by New Zealand. It floats in, and covers, a large southern portion of the Ross Sea and the entire Roosevelt Island located in the east of the Ross Sea. The ice shelf is named after Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered it on 28 January 1841. It was originally called "The Barrier", with various adjectives including "Great Ice Barrier", as it prevented sailing further south. Ross mapped the ice front eastward to 160° W. In 1947, the U.S. Board on Geographic Names applied the name "Ross Shelf Ice" to this feature and published it in the original U.S. Antarctic Gazetteer. In Januar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nimrod Expedition
The ''Nimrod'' Expedition of 1907–1909, otherwise known as the British Antarctic Expedition, was the first of three successful expeditions to the Antarctic led by Ernest Shackleton and his second expedition to the Antarctic. Its main target, among a range of geographical and scientific objectives, was to be first to the South Pole. This was not attained, but the expedition's southern march reached a Farthest South latitude of 88° 23' S, just from the pole. This was by far the longest southern polar journey to that date and a record convergence on either Pole. A separate group led by Welsh Australian geology professor Edgeworth David reached the estimated location of the South Magnetic Pole, and the expedition also achieved the first ascent of Mount Erebus, Antarctica's second highest volcano. The expedition lacked governmental or institutional support, and relied on private loans and individual contributions. It was beset by financial problems and its preparations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headlands Of The Ross Dependency
A headland, also known as a head, is a coastal landform, a point of land usually high and often with a sheer drop, that extends into a body of water. It is a type of promontory. A headland of considerable size often is called a cape.Whittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, 1984, pp. 80, 246. . Headlands are characterised by high, breaking waves, rocky shores, intense erosion, and steep sea cliff. Headlands and bays are often found on the same coastline. A bay is flanked by land on three sides, whereas a headland is flanked by water on three sides. Headlands and bays form on discordant coastlines, where bands of rock of alternating resistance run perpendicular to the coast. Bays form when weak (less resistant) rocks (such as sands and clays) are eroded, leaving bands of stronger (more resistant) rocks (such as chalk, limestone, and granite) forming a headland, or peninsula. Through the deposition of sediment within the bay and the erosion of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |