|
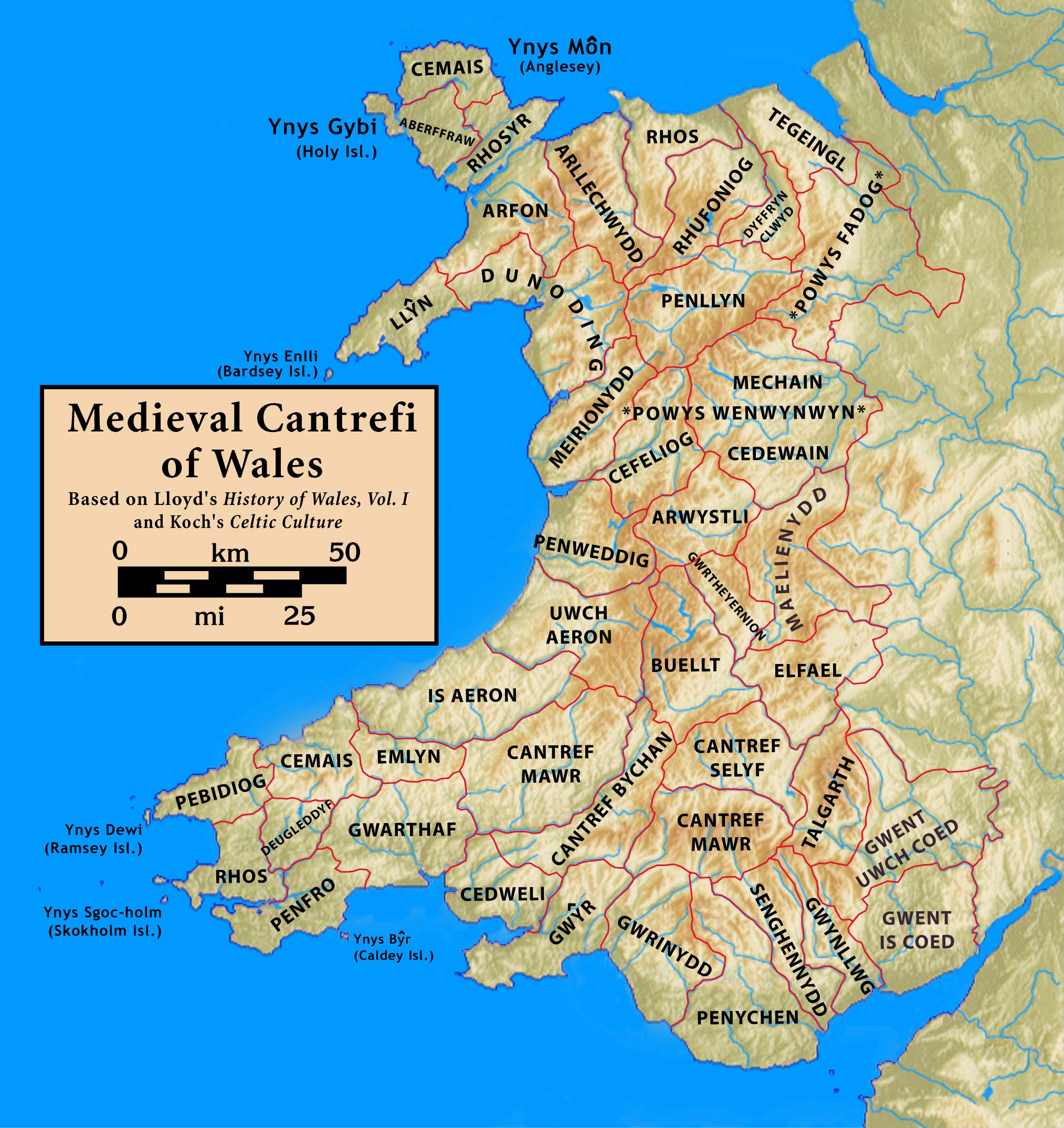
Cantref Elfael
Elfael was one of a number of Wales, Welsh cantrefi occupying the region between the River Wye and river Severn, known as Rhwng Gwy a Hafren, in the early Middle Ages. It was divided into two commotes, Is Mynydd and Uwch Mynydd, separated by the chain of hills above Aberedw. In the late Middle Ages, late medieval period, it was a marcher lordship. However, after the Laws in Wales Act 1535, it was one of the territorial units which went to make up the county of Radnorshire in 1536 (the others were Gwrtheyrnion, Maelienydd and Llythyfnwg, the latter being known in English as the lordship of Radnor). Ferlix Early history According to historic manuscripts, the region between Wye and Severn was once regarded as a unit. Manuscripts use various alternative spellings for this, such as Ferlix, Fferllys, Fferleg, and Fferreg; in his ''Hanes Cymru'', the historian John Davies (historian), John Davies argued, based on these alternatives, that it was probably named Fferyllwg, and that the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of The Cantrefs And Commotes Of Rhwng Gwy A Hafren
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geography, geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Gwent
Gwent () was a medieval Welsh kingdom, lying between the Rivers Wye and Usk. It existed from the end of Roman rule in Britain in about the 5th century until the Norman invasion of Wales in the 11th century. Along with its neighbour Glywysing, it seems to have had a great deal of cultural continuity with the earlier Silures, Miranda Aldhouse-Green &al. ''Gwent In Prehistory and Early History: The Gwent County History'', Vol.1. 2004. . keeping their own courts and diocese separate from the rest of Wales until their conquest by Gruffydd ap Llywelyn. Although it recovered its independence after his death in 1063, Gwent was the first of the Welsh kingdoms to be overrun following the Norman conquest. History Establishment The area has been occupied since the Paleolithic, with Mesolithic finds at Goldcliff and evidence of growing activity throughout the Bronze and Iron Age. Gwent came into being after the Romans had left Britain, and was a successor state drawing on the cultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip De Braose
Philip de Braose, 2nd Lord of Bramber ( 1070 – c. 1134) was an Anglo-Norman nobleman and Marcher Lord. Origins Philip was born about 1070 to 1073, the son of William de Braose, 1st Lord of Bramber (d. 1093/96) by his wife Eve de Boissey or Agnes de St. Clare. William de Braose had participated in the Norman conquest of England. He had been rewarded with the feudal barony of Bramber in Sussex and smaller holdings in Dorset, Wiltshire, Berkshire and Surrey. Career Philip as heir consolidated his paternal lands, and expanded them. In 1096 he confirmed his father's gifts to the Abbey of St. Florent. Philip de Braose conquered the Welsh borderlands at Builth and New Radnor and established new Norman lordships over them. At Builth, he constructed a motte-and-bailey fortification at the site where King Edward I later built Builth Castle in the 13th century. He seems to have gone on the First Crusade in 1103. He supported King Henry I (1100–1135) against the claim to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Invasion Of Wales
The Norman invasion of Wales began shortly after the Norman Conquest, Norman conquest of England under William the Conqueror, who believed England to be his birthright. Initially (1067–1081), the invasion of Wales was not undertaken with the fervour and purpose of the invasion of England. However, a much stronger Norman invasion began in 1081 and by 1094 most of Wales was under the control of William's son and heir, the later King William II of England, William II. The Welsh greatly disliked the "gratuitously cruel" Normans, and by 1101, had regained control of the greater part of their country under the long reign of King Gruffudd ap Cynan, who had been imprisoned by the Normans for twelve years before his escape. In one incident, Gruffudd had some indirect help from King Magnus III of Norway (Magnus Barefoot) who attacked the Normans briefly off the Isle of Anglesey in northwest Wales near Puffin Island, Anglesey, Ynys Seiriol, killing Hugh of Montgomery, 2nd Earl of Shrewsbur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eadric The Wild
Eadric ''the Wild'' (or Eadric ''Silvaticus''), also known as Wild Edric, Eadric ''Cild'' (or ''Child'') and Edric ''the Forester'', was an Anglo-Saxon magnate of Shropshire and Herefordshire who led English resistance to the Norman Conquest, active in 1068–70. Background The early 12th-century historian John of Worcester writes that Eadric the Wild was a son of one Ælfric, whom he identifies as a brother of Eadric Streona, ealdorman of Mercia under King Æthelred the Unready.Williams, ''The English and Norman Conquest'', pp. 91-2. While five of Eadric Streona's brothers appear to attest witness-lists of King Æthelred's charters, no Ælfric makes a plausible candidate for identification with a brother of the ealdorman. It is possible that Ælfric was not a brother but a nephew of the ealdorman.Williams, ''The English and Norman Conquest'', p. 92. If so, Eadric (the Wild) would belong to the same generation as his cousin Siward son of Æthelgar, who was himself a grandson of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Cadogan
Earl Cadogan is a title that has been created twice in the Peerage of Great Britain for the Cadogan family. The second creation, in 1800, was for Charles Cadogan, 1st Earl Cadogan, Charles Cadogan, 3rd Baron Cadogan. History Of Welsh origin, the family name was spelt ''Cadwgan'' until the early 15th century. According to ''Burke's Peerage'', the family descends from: Rees ap Griffith ap Llewelyn ap Meredith Bengoch ap Howell (Lord of Penbuallt) ap Sitsylt (Lord of Buellt, Builth) ap Llewelyn (Lord of Builth) ap Cadwgan ap Elystan Glodrydd ("The Renowned"), Prince of Fferreg, of Dol-y-Gaer, Brecknockshire, Breconshire. William Cadogan (politician), Major William Cadogan (1601–1661) was a cavalry officer in Oliver Cromwell's army. His son Henry Cadogan was a barrister in Dublin. His eldest son William Cadogan, 1st Earl Cadogan, William Cadogan was a noted soldier, politician and diplomat. He was a general in the army and fought in the War of the Spanish Succession and also s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buellt
Buellt or Builth was a cantref in medieval Wales, located west of the River Wye. Unlike most cantrefs, it was not part of any of the major Welsh kingdoms for most of its history, but was instead ruled by an autonomous local dynasty. During the Norman era it was associated with Rhwng Gwy a Hafren, a region independent of the Welsh monarchies and controlled by Norman Marcher Lords. In the 16th century, it was reorganized as a hundred and joined with the former kingdom of Brycheiniog to form the county of Brecknockshire. Description The name ''Buellt'', also rendered ''Buallt'', comes from the Welsh words ''bu'', meaning " ox", and ''gellt'' (later ''gwellt''), meaning pasture. This was later anglicized to ''Builth'', as in the modern town of Builth Wells. Situated in the valley of Afon Irfon, Buellt's boundaries were roughly the Cambrian Mountains to the north, the River Wye to the east, the Mynydd Epynt range to the south, and Ceredigion to the west. It was closely associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elystan Glodrydd
Elystan Glodrydd (or, occasionally, Elstan Glodrydd; died 1010), also known as "Æthelstan the Famous" and "The Renowned," was, according to Welsh genealogical tracts, the founder of the fifth Royal Tribe of Wales. He was the Prince of Buellt, and later also of Fferreg (also known as Ferlix); in the century after his death, Fferreg split into Maelienydd and Elfael Very little is known about Elystan himself, but his descendants, including Cadwallon ap Madog, continued to rule Ferlix, a minor principality in mid Wales, and the main part of Rhwng Gwy a Hafren—the land between the Wye and the Severn. An early Welsh genealogical tract links him to Gwrtheyrnion, while other descendants of Gwrtheyrnion ruled Maelienydd, Elfael., and Cedewain. These territories lay in an area roughly equivalent to the later counties of Radnorshire and southern Montgomeryshire, in today's county of Powys Powys ( , ) is a Principal areas of Wales, county and Preserved counties of Wales, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Æthelflæd
Æthelflæd ( – 12 June 918) ruled as Lady of the Mercians in the English Midlands from 911 until her death in 918. She was the eldest child of Alfred the Great, king of the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Wessex, and his wife Ealhswith. Æthelflæd was born around 870 at the height of the Viking Age, Viking invasions of England in the Middle Ages, England. By 878, most of England was under Danish Viking rule – Kingdom of East Anglia, East Anglia and Northumbria having been conquered, and Mercia partitioned between the English and the Vikings – but in that year Alfred won a crucial victory at the Battle of Edington. Soon afterwards the English-controlled western half of Mercia came under the rule of Æthelred, Lord of the Mercians, who accepted Alfred's overlordship. Alfred adopted the title King of the Anglo-Saxons (previously he was titled King of the West Saxons like his predecessors) claiming to rule all Anglo-Saxon people not living in areas under Viking control. In the mid-8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Heathen Army
The Great Heathen Army, also known as the Viking Great Army,Hadley. "The Winter Camp of the Viking Great Army, AD 872–3, Torksey, Lincolnshire", ''Antiquaries Journal''. 96, pp. 23–67 was a coalition of Scandinavian warriors who invaded England in 865 AD. Since the late 8th century, the Vikings had been engaging in raids on centres of wealth, such as monasteries. The Great Heathen Army was much larger and aimed to conquer and occupy the four kingdoms of East Anglia, Northumbria, Mercia and Wessex. The name ''Great Heathen Army'' is derived from the '' Anglo-Saxon Chronicle''. The force was led by three of the five sons of the semi-legendary Ragnar Lodbrok, including Halfdan Ragnarsson, Ivar the Boneless and Ubba. The campaign of invasion and conquest against the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms lasted 14 years. Surviving sources give no firm indication of its numbers, but it was described as amongst the largest forces of its kind. The invaders initially landed in East Ang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward The Elder
Edward the Elder (870s?17 July 924) was King of the Anglo-Saxons from 899 until his death in 924. He was the elder son of Alfred the Great and his wife Ealhswith. When Edward succeeded to the throne, he had to defeat a challenge from his cousin Æthelwold ætheling, Æthelwold, who had a strong claim to the throne as the son of Alfred's elder brother and predecessor, Æthelred I. Alfred had succeeded Æthelred as king of Wessex in 871, and almost faced defeat against the Danish Vikings until his decisive victory at the Battle of Edington in 878. After the battle, the Vikings still ruled Northumbria, Kingdom of East Anglia, East Anglia and eastern Mercia, leaving only Wessex and western Mercia under Anglo-Saxon control. In the early 880s Æthelred, Lord of the Mercians, the ruler of western Mercia, accepted Alfred's lordship and married his daughter Æthelflæd, and around 886 Alfred adopted the new title King of the Anglo-Saxons as the ruler of all Anglo-Saxons not subject to D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |