|
Canon EOS-1Ds
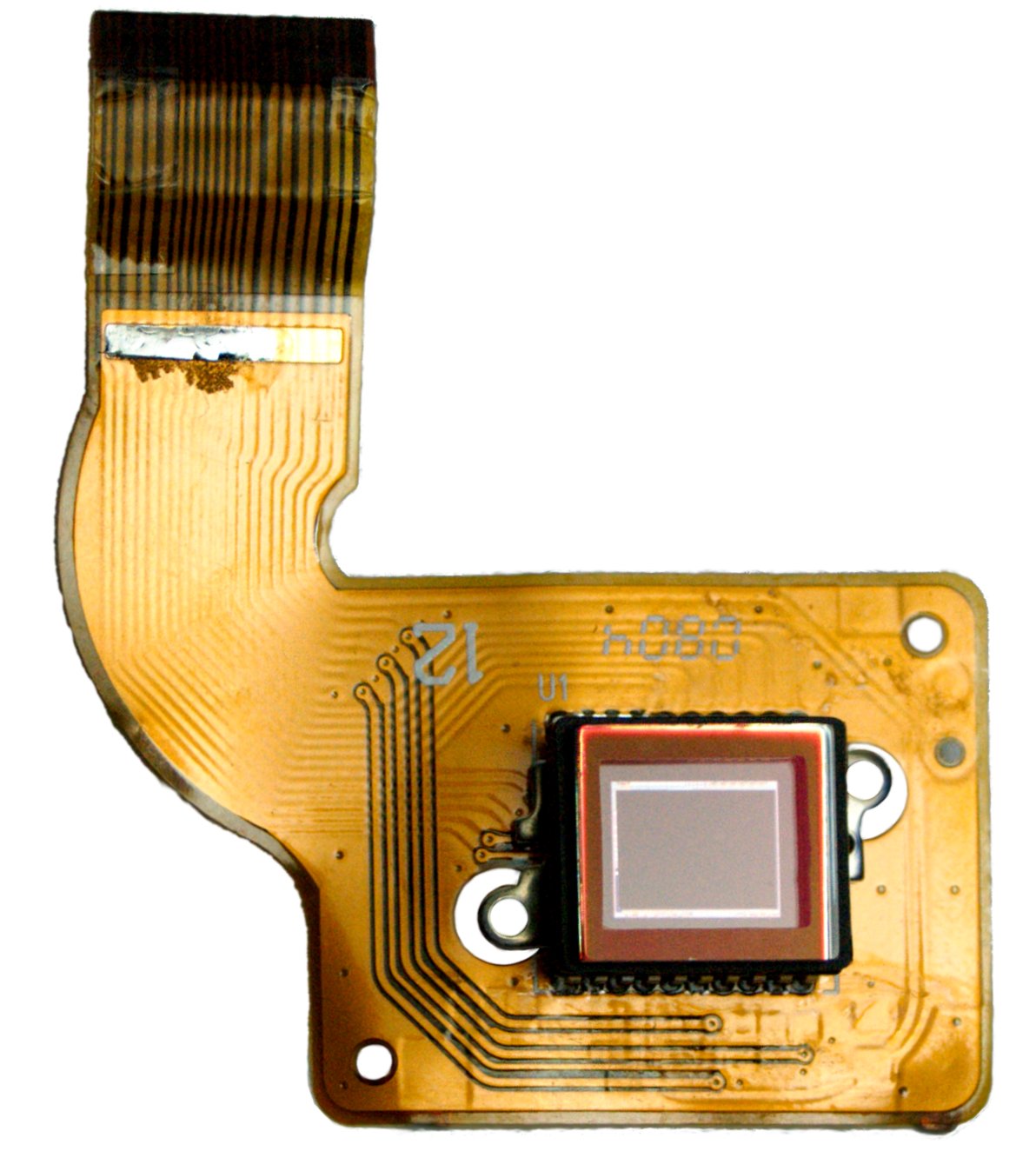
The EOS-1Ds is a full-frame 11.1-megapixel digital SLR camera body made by Canon in the 1Ds series, released on 24 September 2002. It was Canon's first full-frame DSLR. Its dimensions are 156 x 157.6 x 79.9 mm (6.1 x 6.2 x 3.1 in.) and mass (without a battery) is 1,265 g. The ~11 megapixel, full size 35mm digital camera was far ahead of other cameras counting usually much less megapixels, and having smaller size frame. The price was $7,999 in 2002 (). Functions Being an autofocus camera, it has two autofocus modes, and an option for manual focusing. Its viewfinder is a glass pentaprism. It also has a two-inch, thin-film transistor, color liquid-crystal monitor with approximately 120,000 pixels. The camera's image sensor is a CMOS-based integrated circuit with Bayer filters for RGB color detection (Canon calls it ''single-plate'', in contrast with three-CCD sensors). It has approximately 11.4 million effective pixels. A non-removable optical anti-aliasing filt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon EOS
Canon EOS (Electro-Optical System) is an autofocus single-lens reflex camera (SLR) and mirrorless camera series produced by Canon Inc. Introduced in 1987 with the Canon EOS 650, all EOS cameras used 135 film, 35 mm photographic film, film until October 1996 when the Canon EOS IX, EOS IX was released using the new and short-lived Advanced Photo System, APS film. In 2000, the Canon EOS D30, D30 was announced, as the first digital photography, digital SLR designed and produced entirely by Canon. Since 2005, all newly announced EOS cameras have used digital image sensors rather than film. The EOS line is still in production as Canon's current digital SLR (DSLR) range, and, with the 2012 introduction of the Canon EOS M, Canon's mirrorless interchangeable-lens camera (MILC) system. In 2018 the system was further extended with the introduction of the EOS R camera, Canon's first full frame mirrorless interchangeable lens system. The development project was called "EOS" (Electro Optical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Battery
An electric battery is a source of electric power consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections for powering electrical devices. When a battery is supplying power, its positive terminal is the cathode and its negative terminal is the anode. The terminal marked negative is the source of electrons that will flow through an external electric circuit to the positive terminal. When a battery is connected to an external electric load, a redox reaction converts high-energy reactants to lower-energy products, and the free-energy difference is delivered to the external circuit as electrical energy. Historically the term "battery" specifically referred to a device composed of multiple cells; however, the usage has evolved to include devices composed of a single cell. Primary (single-use or "disposable") batteries are used once and discarded, as the electrode materials are irreversibly changed during discharge; a common example is the alkaline battery used f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cameras Introduced In 2002
A camera is an optical instrument that can capture an image. Most cameras can capture 2D images, with some more advanced models being able to capture 3D images. At a basic level, most cameras consist of sealed boxes (the camera body), with a small hole (the aperture) that allows light to pass through in order to capture an image on a light-sensitive surface (usually a digital sensor or photographic film). Cameras have various mechanisms to control how the light falls onto the light-sensitive surface. Lenses focus the light entering the camera, and the aperture can be narrowed or widened. A shutter mechanism determines the amount of time the photosensitive surface is exposed to the light. The still image camera is the main instrument in the art of photography. Captured images may be reproduced later as part of the process of photography, digital imaging, or photographic printing. Similar artistic fields in the moving-image camera domain are film, videography, and cinematogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon EOS DSLR Cameras
Canon EOS (Electro-Optical System) is an autofocus single-lens reflex camera (SLR) and mirrorless camera series produced by Canon Inc. Introduced in 1987 with the Canon EOS 650, all EOS cameras used 35 mm film until October 1996 when the EOS IX was released using the new and short-lived APS film. In 2000, the D30 was announced, as the first digital SLR designed and produced entirely by Canon. Since 2005, all newly announced EOS cameras have used digital image sensors rather than film. The EOS line is still in production as Canon's current digital SLR (DSLR) range, and, with the 2012 introduction of the Canon EOS M, Canon's mirrorless interchangeable-lens camera (MILC) system. In 2018 the system was further extended with the introduction of the EOS R camera, Canon's first full frame mirrorless interchangeable lens system. The development project was called "EOS" (Electro Optical System). EOS is also the name of the goddess of dawn in Greek mythology, which further signifies t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
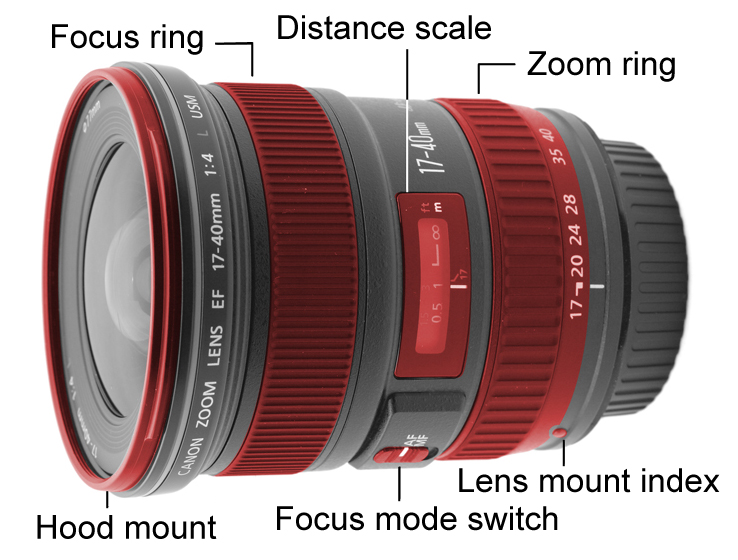
Shutter (photography)
In photography, a shutter is a device that allows light to pass for a determined period, exposing photographic film or a photosensitive digital sensor to light in order to capture a permanent image of a scene. A shutter can also be used to allow pulses of light to pass outwards, as seen in a movie projector or a signal lamp. A shutter of variable speed is used to control exposure time of the film. The shutter is constructed so that it automatically closes after a certain required time interval. The speed of the shutter is controlled by a ring outside the camera, on which various timings are marked. Camera shutter Camera shutters can be fitted in several positions: * Leaf shutters are usually fitted within a lens assembly (''central shutter''), or more rarely immediately behind (''behind-the-lens shutter'') or, even more rarely, in front of a lens, and shut off the beam of light where it is narrow. *Focal-plane shutters are mounted near the focal plane and move to uncover the fil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
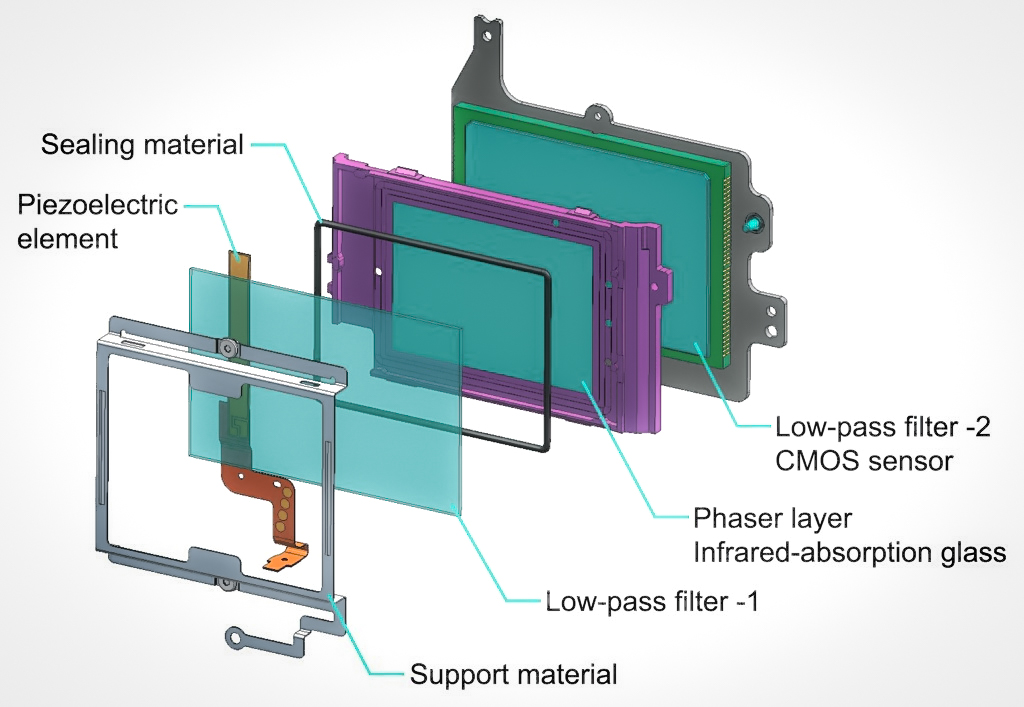
Anti-aliasing Filter
An anti-aliasing filter (AAF) is a filter used before a signal sampler to restrict the bandwidth of a signal to satisfy the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem over the band of interest. Since the theorem states that unambiguous reconstruction of the signal from its samples is possible when the power of frequencies above the Nyquist frequency is zero, a brick wall filter is an idealized but impractical AAF. A practical AAF makes a trade off between reduced bandwidth and increased aliasing. A practical anti-aliasing filter will typically permit some aliasing to occur or attenuate or otherwise distort some in-band frequencies close to the Nyquist limit. For this reason, many practical systems sample higher than would be theoretically required by a perfect AAF in order to ensure that all frequencies of interest can be reconstructed, a practice called oversampling. Optical applications The Pentax K-3 from Ricoh introduced a unique sensor-based anti-aliasing filter. The filter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effective Pixels
Image resolution is the detail an image holds. The term applies to digital images, film images, and other types of images. "Higher resolution" means more image detail. Image resolution can be measured in various ways. Resolution quantifies how close lines can be to each other and still be visibly ''resolved''. Resolution units can be tied to physical sizes (e.g. lines per mm, lines per inch), to the overall size of a picture (lines per picture height, also known simply as lines, TV lines, or TVL), or to angular subtense. Instead of single lines, line pairs are often used, composed of a dark line and an adjacent light line; for example, a resolution of 10 lines per millimeter means 5 dark lines alternating with 5 light lines, or 5 line pairs per millimeter (5 LP/mm). Photographic lens and film resolution are most often quoted in line pairs per millimeter. Types The resolution of digital cameras can be described in many different ways. Pixel count The term ''resolution'' is ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-CCD
A three-CCD (3CCD) camera is a camera whose imaging system uses three separate charge-coupled devices (CCDs), each one receiving filtered red, green, or blue color ranges. Light coming in from the lens is split by a beam-splitter prism into three beams, which are then filtered to produce colored light in three color ranges or "bands". The system is employed by high quality still cameras, telecine systems, professional video cameras and some prosumer video cameras. Compared to cameras with only one CCD, three-CCD cameras generally provide superior image quality by using full-frame dichroic filters to better separate the red, green and blue color bands, and better low-light performance. By separating red, green, and blue color ranges with a 1:1 pixel ratio (known as "4:4:4"), three-CCD cameras achieve much better precision than single-CCD cameras. In contrast, almost all single-CCD cameras use a Bayer filter, using less accurate dye filters in front of each pixel to separate the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayer Filter
A Bayer filter mosaic is a color filter array (CFA) for arranging RGB color filters on a square grid of photosensors. Its particular arrangement of color filters is used in most single-chip digital image sensors used in digital cameras, camcorders, and scanners to create a color image. The filter pattern is half green, one quarter red and one quarter blue, hence is also called BGGR, RGBG, GRBG, or RGGB. It is named after its inventor, Bryce Bayer of Eastman Kodak. Bayer is also known for his recursively defined matrix used in ordered dithering. Alternatives to the Bayer filter include both various modifications of colors and arrangement and completely different technologies, such as color co-site sampling, the Foveon X3 sensor, the dichroic mirrors or a transparent diffractive-filter array. Explanation Bryce Bayer's patent (U.S. Patent No. 3,971,065) in 1976 called the green photosensors ''luminance-sensitive elements'' and the red and blue ones ''chrominance-sensitive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) integrate into a small chip. This results in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete electronic components. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design has ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discrete transistors. ICs are now used in virtually all electronic equipment and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones and other home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs such as modern computer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Sensor
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to make an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they pass through or reflect off objects) into signals, small bursts of current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronic imaging devices of both analog and digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, camera phones, optical mouse devices, medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technology changes, electronic and digital imaging tends to replace chemical and analog imaging. The two main types of electronic image sensors are the charge-coupled device (CCD) and the active-pixel sensor (CMOS sensor). Both CCD and CMOS sensors are based on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) technology, with CCDs based on MOS capacitors and CMOS sensors based on M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thin-film Transistor
A thin-film transistor (TFT) is a special type of field-effect transistor (FET) where the transistor is thin relative to the plane of the device. TFTs are grown on a supporting (but non-conducting) substrate. A common substrate is glass, because the traditional application of TFTs is in liquid-crystal displays (LCDs). This differs from the conventional bulk metal oxide field effect transistor ( MOSFET), where the semiconductor material typically ''is'' the substrate, such as a silicon wafer. Design and Manufacture TFTs can be fabricated with a wide variety of semiconductor materials. Because it is naturally abundant and well understood, amorphous or polycrystalline silicon was historically used as the semiconductor layer. However, because of the low mobility of amorphous silicon and the large device-to-device variations found in polycrystalline silicon, other materials have been studied for use in TFTs. These include cadmium selenide, metal oxides such as indium gallium zin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)