|
Canon De 164 Mm Modèle 1893
Railroad model, 1916. The Canon de 164 mm Modèle 1893 was a medium-caliber naval gun used as the secondary armament of a number of French pre-dreadnoughts and armoured cruisers during World War I. It was used as railway artillery in both World Wars and as coastal artillery in World War II. Description The 45 caliber Canon de 164 mm Modèle 1893 gun was a typical built-up French heavy gun of its period. It used a Welin interrupted-screw breech and bagged propellant with a de Bange obturator to get a good gas seal during firing. It was replaced by the Mle 1893/96 gun which used a plastic seal for the obturator, differed in the construction of the gun, had a slightly longer barrel of 46.6 calibers and the newer gun was able to fire a new HE shell further than that used by the older gun. Naval mounts The Mle 1893 and 1893/96 guns were mounted in casemated pivot mounts with the ability to depress to -10° and elevate to +25°. The guns fired shells at a muzzle velocit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Gun
Naval artillery is artillery mounted on a warship, originally used only for naval warfare and then subsequently used for naval gunfire support, shore bombardment and anti-aircraft roles. The term generally refers to tube-launched projectile-firing weapons and excludes self-propelled projectiles such as torpedoes, rockets, and missiles and those simply dropped overboard such as depth charges and naval mines. Origins The idea of ship-borne artillery dates back to the classical era. Julius Caesar indicates the use of ship-borne catapults against Britons ashore in his ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico''. The dromons of the Byzantine Empire carried catapults and Greek fire, fire-throwers. From the late Middle Ages onwards, warships began to carry cannon, cannons of various calibres. The Mongol invasion of Java introduced cannons to be used in naval warfare (e.g. Cetbang by the Majapahit). The Battle of Arnemuiden, fought between England and France in 1338 at the start of the Hundred Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Bange
Charles Ragon de Bange (17 October 1833 – 9 July 1914) was a French artillery officer and Polytechnician. He invented the first effective obturator system for breech-loading artillery, which remains in use. He also designed a system of field guns of various calibers which served the French Army well into World War I: the ''Système de Bange''. Career De Bange breech obturator system Many attempts had been made at developing breech-loading cannons, but had only partial success sealing of the breech. When fired, hot gases and burning gunpowder could escape, losing power and potentially burning the operating crew. Rifles, with smaller loads and thus less stress, were able to use rubber in O-rings as on the Chassepot rifle. The same principle of breech sealing applied on cannons was not as easy to develop. Several materials were able to hold the pressure and heat of cannon fire, but did not expand like rubber, thereby failing to provide a tight seal. The most successful of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon De 19 Modèle 1870/93 TAZ
The Canon de 19 modèle 1870/93 TAZ was a railway gun designed and built early in the First World War. It also saw action during the Second World War. History Although the majority of combatants had heavy field artillery prior to the outbreak of the First World War, none had adequate numbers of heavy guns in service, nor had they foreseen the growing importance of heavy artillery once the Western Front stagnated and trench warfare set in. Since aircraft of the period were not yet capable of carrying large diameter bombs the burden of delivering heavy firepower fell on the artillery. Two sources of heavy artillery suitable for conversion to field use were surplus coastal defense guns and naval guns. However, a paradox faced artillery designers of the time; while large caliber naval guns were common, large caliber land weapons were not due to their weight, complexity, and lack of mobility. Large caliber field guns often required extensive site preparation because the guns had t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun Shield
A U.S. Marine manning an M240 machine gun equipped with a gun shield A gun shield is a flat (or sometimes curved) piece of armor designed to be mounted on a crew-served weapon such as a machine gun, automatic grenade launcher, or artillery piece. Military Some mounted machine guns and artillery pieces are equipped with metal armor plates to protect the gunners from small arms fire and shrapnel from explosions. They were fitted to some armored fighting vehicles and patrol boats during the Vietnam War. Gun shields fell out of widespread use after the Vietnam war, but they have seen a resurgence in popularity during the 1990s. Israeli military analysts began urging the use of gun shields, pointing to the grave risk to soldiers exposed to fire from automatic weapons. In particular, it was noted that many casualties were hit in areas not protected by body armor or a helmet, such as the neck or face. The U.S. began using gun shields during the 2000s-era wars in Iraq and Afghanista ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon De 164 Modèle 1893/96 TAZ
The Canon de 164 modèle 1893/96 TAZ was a railway gun designed and built early in the First World War. It also saw action during the Second World War. History Although the majority of combatants had heavy field artillery prior to the outbreak of the First World War, none had adequate numbers of heavy guns in service, nor had they foreseen the growing importance of heavy artillery once the Western Front stagnated and trench warfare set in. Since aircraft of the period were not yet capable of carrying large diameter bombs the burden of delivering heavy firepower fell on the artillery. Two sources of heavy artillery suitable for conversion to field use were surplus coastal defense guns and naval guns. However, a paradox faced artillery designers of the time; while large caliber naval guns were common, large caliber land weapons were not due to their weight, complexity, and lack of mobility. Large caliber field guns often required extensive site preparation because the guns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
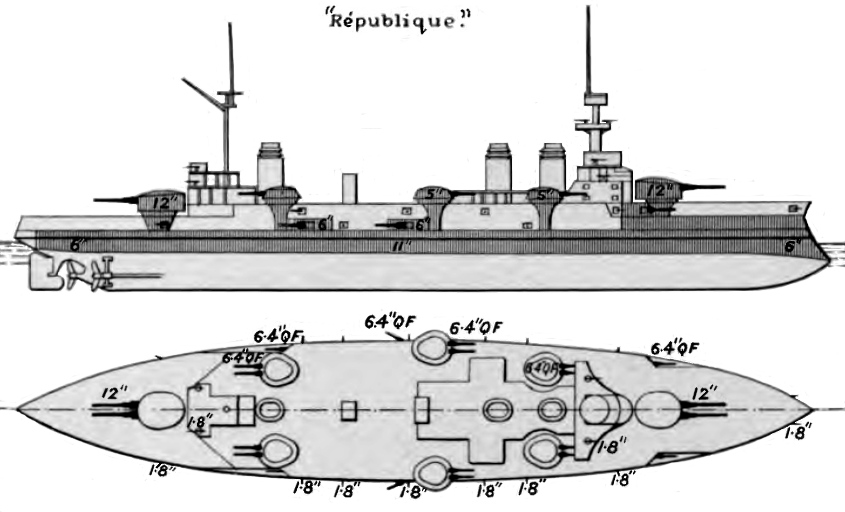
République-class Battleship
The ''République'' class consisted of a pair of pre-dreadnought battleships—, the lead ship, and —built for the French Navy in the early 1900s. They were ordered as part of a naval expansion program directed at countering German warship construction authorized by the German Naval Laws, German Naval Law of 1898. The French program called for six new battleships; the last four became the very similar . ''République'' and ''Patrie'', designed by Louis-Émile Bertin, were a significant improvement over previous French battleships. They carried a similar offensive armament of four guns and eighteen guns, though most of the 164 mm guns were now mounted in more flexible gun turrets rather than in casemates. They also had a much more effective armor protection arrangement that remedied the tendency of earlier battleships to lose stability from relatively minor damage. Both ships entered service with the fleet in 1907, after the revolutionary British battleship had been ship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Léon Gambetta-class Cruiser
The ''Léon Gambetta'' class consisted of three armored cruisers built for the French Navy () during the first decade of the 20th century. Armed with four guns, the ships were much larger and more powerfully armed than their predecessors. , the first of the sister ships to be completed, was initially assigned to the Northern Squadron () where she served as a flagship. Her sisters and were assigned to the Mediterranean Squadron () where ''Jules Ferry'' also served as a flagship. ''Léon Gambetta'' joined them there in 1910 and the sisters remained there for most of their careers. During World War I, the cruisers escorted convoys as well as the capital ships of the French fleet. The ships participated in the blockade of the Austro-Hungarian Navy in the Adriatic Sea until 1917. ''Léon Gambetta'' was sunk by an Austro-Hungarian submarine in April 1915 with heavy loss of life. In mid-1917, ''Jules Ferry'' became a transport and ''Victor Hugo'' was reduced to reserve. She wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gueydon-class Cruiser
The ''Gueydon''-class cruiser was a three-ship class of armored cruisers built in the first decade of the twentieth century for the French Navy (). Design and description Designed by the naval architect Emile Bertin, the ''Gueydon''-class ships were intended to be smaller and cheaper than the preceding armored cruiser design, . Like the older ship, they were intended to fill the commerce-raiding strategy of the ''Jeune École''. The ships measured long overall with a beam of and had a maximum draft of . They displaced . They had a crew of 566 officers and enlisted men.Campbell, p. 305 The ''Gueydon'' class had three vertical triple-expansion steam engines, each driving a single propeller shaft. Steam for the engines was provided by 20 or 28 boilers and they were rated at a total of that gave them a speed of . The ships carried up to of coal and could steam for at a speed of .Silverstone, p. 79 The ships of the ''Gueydon'' class had a main armament that consisted of tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gloire-class Cruiser
The ''Gloire'' class consisted of five armored cruisers built for the French Navy () during the first decade of the 20th century. Fitted with a mixed armament of and guns, the ships were designed for service with the fleet. After their completion in 1903–1904, the five sister ships were initially assigned to the Northern Squadron (), often serving as flagships. was transferred to the Far Eastern Squadron () shortly afterwards and was wrecked when she struck an uncharted rock in February 1905. and were transferred to the Mediterranean Squadron (France), Mediterranean Squadron () in 1905–1906. The surviving sisters were generally divided between the Northern and Mediterranean Squadrons until a reorganization in 1910 caused all but to be concentrated in the Mediterranean. The following year another reorganization reduced ''Amiral Aube'' to Reserve fleet, reserve and her sisters were transferred to the 2nd Light Squadron (), as the Northern Squadron had been renamed. became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun Turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechanism of a projectile-firing weapon and at the same time lets the weapon be aimed and fired in some degree of azimuth and elevation (cone of fire). Description Rotating gun turrets protect the weapon and its crew as they rotate. When this meaning of the word "turret" started being used at the beginning of the 1860s, turrets were normally cylindrical. Barbettes were an alternative to turrets; with a barbette the protection was fixed, and the weapon and crew were on a rotating platform inside the barbette. In the 1890s, armoured hoods (also known as "gun houses") were added to barbettes; these rotated with the platform (hence the term "hooded barbette"). By the early 20th Century, these hoods were known as turrets. Modern warships have gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dupleix-class Cruiser
The ''Dupleix'' class consisted of three armored cruisers built for the French Navy () at the beginning of the 20th century. Designed for overseas service and armed with eight guns, the three ships of the class were smaller and less powerfully armed than their predecessors. was initially assigned to the Atlantic Division () as its flagship. Her sister ships were initially assigned to the Mediterranean Squadron (), although relieved ''Dupleix'' as flagship of the Atlantic Division in 1905. ''Dupleix'' was reduced to reserve from 1906 to 1909 before she was sent to the Far East in 1910 as the flagship of the ships there. ''Desaix'' and exchanged assignments in 1907, although the former ship returned to the Atlantic in 1908 before being placed in reserve from 1909 to 1914. ''Kléber'' was also placed in reserve in 1909, but she was reactivated two years later to join ''Dupleix'' in the Far East before returning home in 1913 to be placed in reserve again. As tensions rose shortl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-dreadnought Battleship
Pre-dreadnought battleships were sea-going battleships built between the mid- to late- 1880s and 1905, before the launch of in 1906. The pre-dreadnought ships replaced the ironclad battleships of the 1870s and 1880s. Built from steel, protected by case-hardened steel armour, and powered by coal-fired triple-expansion steam engines, pre-dreadnought battleships carried a main battery of very heavy guns in fully enclosed rotating turrets supported by one or more secondary batteries of lighter weapons. In contrast to the multifarious development of ironclad warships in preceding decades, the 1890s saw navies worldwide start to build battleships to a common design as dozens of ships essentially followed the design of the Royal Navy's . The similarity in appearance of battleships in the 1890s was underlined by the increasing number of ships being built. New naval powers such as Germany, Japan, the United States, and to a lesser extent Italy and Austria-Hungary, began to establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Driver_and_Commander_from_A_Squadron%2C_3rd_Cavalry_Regiment.jpg)