|
Cancer Of The Cervix
Cervical cancer is a cancer arising from the cervix. It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Early on, typically no symptoms are seen. Later symptoms may include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain or pain during sexual intercourse. While bleeding after sex may not be serious, it may also indicate the presence of cervical cancer. Human papillomavirus infection (HPV) causes more than 90% of cases; most women who have had HPV infections, however, do not develop cervical cancer. HPV 16 and 18 strains are responsible for nearly 50% of high grade cervical pre-cancers. Other risk factors include smoking, a weak immune system, birth control pills, starting sex at a young age, and having many sexual partners, but these are less important. Genetic factors also contribute to cervical cancer risk. Cervical cancer typically develops from precancerous changes over 10 to 20 years. About 90% of cervical cancer ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, treatment, diagnosis and prevention of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an ''oncologist''. The name's etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγκος (''ónkos''), meaning "tumor", "volume" or "mass". Oncology is concerned with: * The diagnosis of any cancer in a person (pathology) * Therapy (e.g. surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and other modalities) * Follow-up of cancer patients after successful treatment * Palliative care of patients with terminal malignancies * Ethical questions surrounding cancer care * Screening efforts: ** of populations, or ** of the relatives of patients (in types of cancer that are thought to have a hereditary basis, such as breast cancer) Diagnosis Medical histories remain an important screening tool: the character of the complaints and nonspecific symptoms (such as fatigue, weight loss, unexplained anemia, fever of unknown origin, paraneoplastic phenome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms ( palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organs and tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging. Measurement and recording techniques that are not primarily designed to produce images, such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and others, represent other technologies that produce data susceptible to representation as a parameter graph versus time or maps that contain data about the measurement loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Screening
Cervical screening is the process of detecting and removing abnormal tissue or cells in the cervix before cervical cancer develops. By aiming to detect and treat cervical neoplasia early on, cervical screening aims at Preventive healthcare#Secondary prevention, secondary prevention of cervical cancer. Primary prevention of cervical cancer is vaccination against HPV. Several screening methods for cervical cancer are the Pap test (also known as Pap smear or conventional cytology), liquid-based cytology, the HPV DNA testing and the visual inspection with acetic acid. Pap test and liquid-based cytology have been effective in diminishing incidence and mortality rates of cervical cancer in developed countries but not in developing countries. Prospective screening methods that can be used in low-resource areas in developing countries are the HPV DNA testing and the visual inspection. There are wide disparities in cervical screening rates and outcomes, with about 90% of deaths from cervical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous-cell carcinomas (SCCs), also known as epidermoid carcinomas, comprise a number of different types of cancer that begin in squamous cells. These cells form on the surface of the skin, on the lining of hollow organs in the body, and on the lining of the respiratory and digestive tracts. Common types include: * Squamous-cell skin cancer: A type of skin cancer * Squamous-cell carcinoma of the lung: A type of lung cancer * Squamous-cell thyroid carcinoma: A type of thyroid cancer * Esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma: A type of esophageal cancer * Squamous-cell carcinoma of the vagina: A type of vaginal cancer Despite sharing the name "squamous-cell carcinoma", the SCCs of different body sites can show differences in their presented symptoms, natural history, prognosis, and response to treatment. By body location Human papillomavirus infection has been associated with SCCs of the oropharynx, lung, fingers, and anogenital region. Head and neck cancer About 90% of cases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
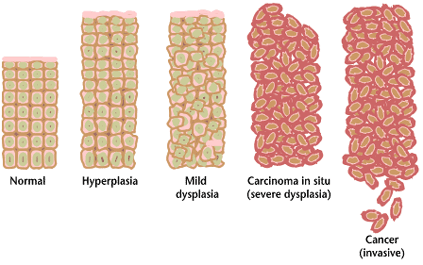
Precancerous Condition
A precancerous condition is a condition, tumor or lesion involving abnormal cells which are associated with an increased risk of developing into cancer. Clinically, precancerous conditions encompass a variety of abnormal tissues with an increased risk of developing into cancer. Some of the most common precancerous conditions include certain colon polyps, which can progress into colon cancer, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, which can progress into multiple myeloma or myelodysplastic syndrome. and cervical dysplasia, which can progress into cervical cancer. Bronchial premalignant lesions can progress to squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Pathologically, precancerous tissue can range from benign neoplasias, which are tumors which don't invade neighboring normal tissues or spread to distant organs, to dysplasia, a collection of highly abnormal cells which, in some cases, has an increased risk of progressing to anaplasia and invasive cancer which is life-threat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is burned and the resulting smoke is typically breathed in to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have been rolled into a small rectangle of rolling paper to create a small, round cylinder called a cigarette. Smoking is primarily practised as a route of administration for recreational drug use because the combustion of the dried plant leaves vaporizes and delivers active substances into the lungs where they are rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream and reach bodily tissue. In the case of cigarette smoking, these substances are contained in a mixture of aerosol particles and gases and include the pharmacologically active alkaloid nicotine; the vaporization creates heated aerosol and gas into a form that allows inhalation and deep penetration into the lungs where absorption into the bloodstream of the active substances occurs. In some cultures, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervix
The cervix or cervix uteri (Latin, 'neck of the uterus') is the lower part of the uterus (womb) in the human female reproductive system. The cervix is usually 2 to 3 cm long (~1 inch) and roughly cylindrical in shape, which changes during pregnancy. The narrow, central cervical canal runs along its entire length, connecting the uterine cavity and the lumen of the vagina. The opening into the uterus is called the internal os, and the opening into the vagina is called the external os. The lower part of the cervix, known as the vaginal portion of the cervix (or ectocervix), bulges into the top of the vagina. The cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time of Hippocrates, over 2,000 years ago. The cervical canal is a passage through which sperm must travel to fertilize an egg cell after sexual intercourse. Several methods of contraception, including cervical caps and cervical diaphragms, aim to block or prevent the passage of sperm through the cervical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as ''Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)