|
Canadian University Scientific Research Organizations
Expenditures by Canadian universities on scientific research and development accounted for about 40% of all spending on scientific research and development in Canada in 2006. Research in the natural and social sciences in Canada, with a few important exceptions, is almost exclusively funded by the Canadian taxpayer and is distributed to universities by five important federal funding agencies, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC), the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR), and the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada (SSHRC). Additional monies are also provided by the Canada Research Chairs organization, which provides financing for the staffing of research personnel at Canadian universities and the Canada Foundation for Innovation, which supports the acquisition of scientific research infrastructure by Canadian universities, colleges, research hospitals, and non-profit research institutions. In 2006, total spending on scientific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Sciences And Engineering Research Council
The Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC; french: Conseil de recherches en sciences naturelles et en génie du Canada, CRSNG) is the major federal agency responsible for funding natural sciences and engineering research in Canada. NSERC directly funds university professors and students as well as Canadian companies to perform research and training. With funding from the Government of Canada, NSERC supports the research of over 41,000 students, trainees and professors at universities and colleges in Canada with an annual budget of CA$1.1 billion in 2015. Its current director is Alejandro Adem. NSERC, combined with the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council (SSHRC) and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR), forms the major source of federal government funding to post-secondary research. These bodies are sometimes collectively referred to as the "Tri-Council" or "Tri-Agency". History NSERC came into existence on 1 May 1978 under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Municipality Of Waterloo
The Regional Municipality of Waterloo (Waterloo Region or Region of Waterloo) is a metropolitan area of Southern Ontario, Canada. It contains the cities of Cambridge, Kitchener and Waterloo (KWC or Tri-Cities), and the townships of North Dumfries, Wellesley, Wilmot and Woolwich. Kitchener, the largest city, is the seat of government. The region is in area. The population was 587,165 at the 2021 Canada census. In 2016, the Cambridge, Kitchener, Waterloo area was rated Canada's third-best area to find full-time employment. The region was formerly called Waterloo County, created in 1853 and dissolved in 1973. The county consisted of five townships: Woolwich, Wellesley, Wilmot, Waterloo, and North Dumfries. History Up to the 17th century, the Attawandaron (Neutral) nation inhabited the Grand River area. European explorers admired their farming practices. In the wake of a smallpox epidemic and European incursions, the Haudenosaunee (Iroquois) and the Wendat (Huron) Confede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institut Philippe-Pinel De Montréal
The Institut national de psychiatrie légale Philippe-Pinel is a psychiatric hospital located in Montreal, Quebec for individuals accused of crimes and found to be not criminally responsible due to mental disorder. It is located at 10905 Henri Bourassa Blvd. East in the borough of Rivière-des-Prairies–Pointe-aux-Trembles. History The institute was founded in 1970, a time when legal psychiatry was a new science and the government was searching for new methods of managing psychiatric cases that were difficult to treat. In March 2009, a class action lawsuit against the hospital was settled out of court for $1 million. Overview The Pinel Institute rehabilitates patients with both psychiatric and judicial problems. It is affiliated with Université de Montréal and several college A college (Latin: ''collegium'') is an educational institution or a constituent part of one. A college may be a degree-awarding tertiary educational institution, a part of a collegiate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Léa Roback
Léa Roback (3 November 1903 – 28 August 2000) was a Canadian trade union organizer, social activist, pacifist, and feminist. She campaigned against exclusion, violence, racism and injustice. A polyglot and a suffragist, she was a pioneer of feminism in Quebec. Early years Born in Montreal, Quebec, on Guilbault Street in 1903, the second of nine children, she was the daughter of Polish Jewish immigrants. Her father was a tailor who, along with his wife, Fanny, ran a general store. They were the only Jews in Beauport, the town where Roback grew up. She spoke Yiddish at home, French with Beauport locals, and English at school. Her family valued reading and the arts. In her youth, she was influenced by her maternal grandmother, an independent woman. With her family, Roback returned to Montreal in 1915. While working at British American Dyeworks, she became aware of the differences between the various sectors of Montreal society. Her next job was as a cashier at Her Majesty's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centre De Recherche En Reproduction Animale
Center or centre may refer to: Mathematics *Center (geometry), the middle of an object * Center (algebra), used in various contexts ** Center (group theory) ** Center (ring theory) * Graph center, the set of all vertices of minimum eccentricity Places United States * Centre, Alabama * Center, Colorado * Center, Georgia * Center, Indiana * Center, Jay County, Indiana * Center, Warrick County, Indiana * Center, Kentucky * Center, Missouri * Center, Nebraska * Center, North Dakota * Centre County, Pennsylvania * Center, Portland, Oregon * Center, Texas * Center, Washington * Center, Outagamie County, Wisconsin * Center, Rock County, Wisconsin **Center (community), Wisconsin *Center Township (other) *Centre Township (other) *Centre Avenue (other) *Center Hill (other) Other countries * Centre region, Hainaut, Belgium * Centre Region, Burkina Faso * Centre Region (Cameroon) * Centre-Val de Loire, formerly Centre, France * Centre (department), H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccine And Infectious Disease Organization
The Vaccine and Infectious Disease Organization – International Vaccine Centre (VIDO-InterVac) is a research organization of the University of Saskatchewan that operates with financial support from the Government of Canada, the government of Saskatchewan, livestock industry councils and agencies, foundations and human and animal health companies. In addition to the facility on campus, VIDO-InterVac also operates a research station. VIDO-InterVac's aims are to protect Canada and the world from infectious diseases by focusing on diseases that: affect livestock industries; are important to human health; and are emerging diseases including zoonoses. History Originally named the Veterinary Infectious Disease Organization, VIDO-InterVac was established with funding from the Devonian Group of Charitable Foundations, the Province of Alberta and the Province of Saskatchewan. VIDO had strong ties to the Western College of Veterinary Medicine at the University of Saskatchewan. The l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchrotron Light Source
A synchrotron light source is a source of electromagnetic radiation (EM) usually produced by a storage ring, for scientific and technical purposes. First observed in synchrotrons, synchrotron light is now produced by storage rings and other specialized particle accelerators, typically accelerating electrons. Once the high-energy electron beam has been generated, it is directed into auxiliary components such as bending magnets and insertion devices (undulators or wiggler (synchrotron), wigglers) in storage rings and free electron lasers. These supply the strong magnetic fields perpendicular to the beam which are needed to convert high energy electrons into photons. The major applications of synchrotron light are in condensed matter physics, materials science, biology and medicine. A large fraction of experiments using synchrotron light involve probing the structure of matter from the sub-nanometer level of electronic structure to the micrometre, micrometer and millimeter level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
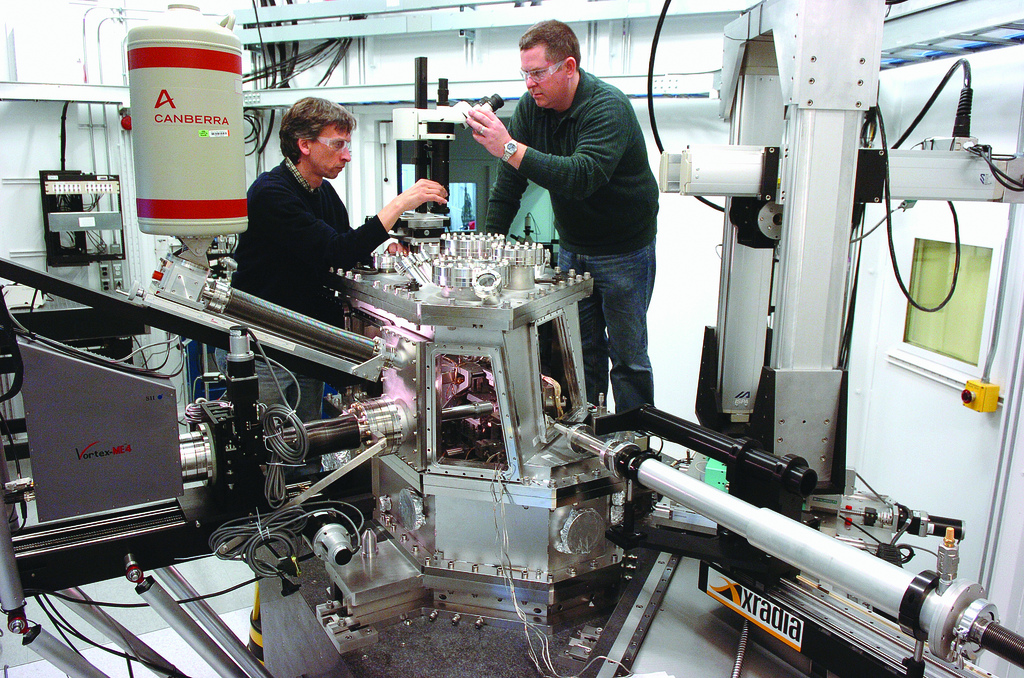
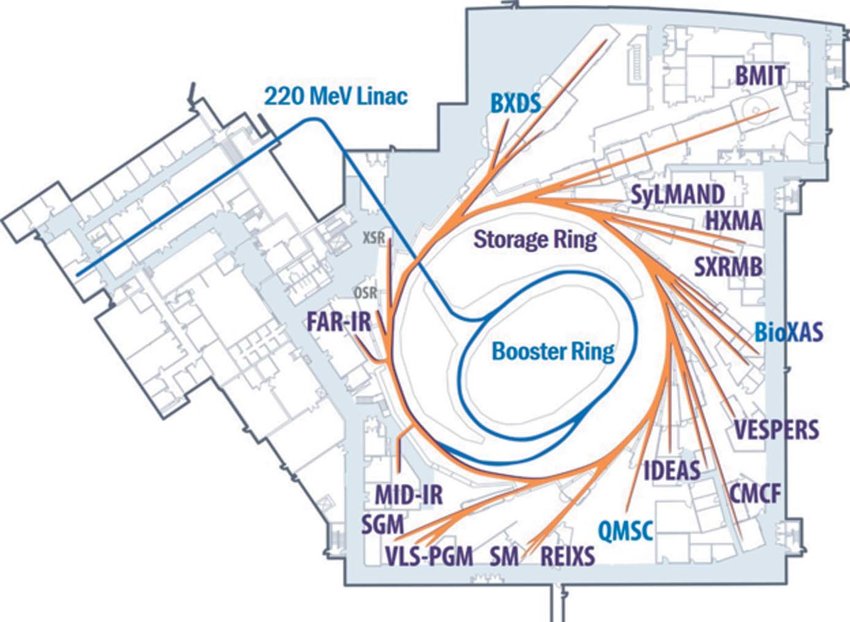
Canadian Light Source
The Canadian Light Source (CLS) (french: link=no, Centre canadien de rayonnement synchrotron – CCRS) is Canada's national synchrotron light source facility, located on the grounds of the University of Saskatchewan in Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada. The CLS has a third-generation 2.9 GeV storage ring, and the building occupies a footprint the size of a Canadian football field. It opened in 2004 after a 30-year campaign by the Canadian scientific community to establish a synchrotron radiation facility in Canada. It has expanded both its complement of beamlines and its building in two phases since opening. As a national synchrotron facility with over 1000 individual users, it hosts scientists from all regions of Canada and around 20 other countries. Research at the CLS has ranged from viruses to superconductors to dinosaurs, and it has also been noted for its industrial science and its high school education programs. History The road to the CLS: 1972–1999 Canadian inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saskatchewan Isotope Laboratory
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a province in western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dakota. Saskatchewan and Alberta are the only landlocked provinces of Canada. In 2022, Saskatchewan's population was estimated at 1,205,119. Nearly 10% of Saskatchewan’s total area of is fresh water, mostly rivers, reservoirs and lakes. Residents primarily live in the southern prairie half of the province, while the northern half is mostly forested and sparsely populated. Roughly half live in the province's largest city Saskatoon or the provincial capital Regina. Other notable cities include Prince Albert, Moose Jaw, Yorkton, Swift Current, North Battleford, Melfort, and the border city Lloydminster. English is the primary language of the province, with 82.4% of Saskatchewanians speaking English as their first language. Saskatchewan has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Physics Laboratory (Saskatchewan)
The Plasma Physics Laboratory at the University of Saskatchewan was established in 1959 by H. M. Skarsgard. Early work centered on research with a Betatron. Facilities STOR-1M STOR-1M is Canada's first tokamak built in 1983. In 1987 STOR-1M was the world’s first demonstration of alternating current in a tokamak. STOR-M STOR-M stands for Saskatchewan Torus-Modified. STOR-M is a tokamak located at the University of Saskatchewan A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which .... STOR-M is a small tokamak (major radius = 46 cm, minor radius = 12.5 cm) designed for studying plasma heating, anomalous transport and developing novel tokamak operation modes and advanced diagnostics. STOR-M is capable of a 30–40 millisecond plasma discharge with a toroidal magnetic field ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Centre For Nuclear Innovation
The Sylvia Fedoruk Canadian Centre for Nuclear Innovation (Fedoruk Centre) is an institute located in Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada that was established by the University of Saskatchewan in 2011 as the Canadian Centre for Nuclear Innovation (CCNI). The Fedoruk Centre does not have a mandate to conduct research itself. Instead, it acts as a conduit to fund nuclear released research projects in Saskatchewan and to oversee the operation of nuclear facilities on the university campus such as the universities cyclotron facility. The Fedoruk Centre is involved in funding research in the nuclear medicine, materials science, nuclear energy systems including small reactor design, and environmental and social topics related to nuclear technology. On October 3, 2012, the name of the organization was changed from the Canadian Centre for Nuclear Innovation to the Sylvia Fedoruk Canadian Centre for Nuclear Innovation in honour of Sylvia Fedoruk who did pioneering work in the treatment of ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a province in western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dakota. Saskatchewan and Alberta are the only landlocked provinces of Canada. In 2022, Saskatchewan's population was estimated at 1,205,119. Nearly 10% of Saskatchewan’s total area of is fresh water, mostly rivers, reservoirs and lakes. Residents primarily live in the southern prairie half of the province, while the northern half is mostly forested and sparsely populated. Roughly half live in the province's largest city Saskatoon or the provincial capital Regina. Other notable cities include Prince Albert, Moose Jaw, Yorkton, Swift Current, North Battleford, Melfort, and the border city Lloydminster. English is the primary language of the province, with 82.4% of Saskatchewanians speaking English as their first language. Saska ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |