|
Campichthys
''Campichthys'' is a genus of pipefishes native to the Indian and Pacific Ocean The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...s. Species There are currently four recognized species in this genus: * '' Campichthys galei'' ( Duncker, 1909) (Gale's pipefish) * '' Campichthys nanus'' C. E. Dawson, 1977 * '' Campichthys tricarinatus'' C. E. Dawson, 1977 (Three-keel pipefish) * '' Campichthys tryoni'' ( J. D. Ogilby, 1890) (Tryon's pipefish) References Marine fish genera Taxa named by Gilbert Percy Whitley {{Syngnathiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campichthys
''Campichthys'' is a genus of pipefishes native to the Indian and Pacific Ocean The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...s. Species There are currently four recognized species in this genus: * '' Campichthys galei'' ( Duncker, 1909) (Gale's pipefish) * '' Campichthys nanus'' C. E. Dawson, 1977 * '' Campichthys tricarinatus'' C. E. Dawson, 1977 (Three-keel pipefish) * '' Campichthys tryoni'' ( J. D. Ogilby, 1890) (Tryon's pipefish) References Marine fish genera Taxa named by Gilbert Percy Whitley {{Syngnathiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campichthys Tryoni
''Campichthys tryoni'' (Tryon's pipefish) is a species of marine fish of the family Syngnathidae. Little is known of this species, but the specimens that have been collected were found on the Queensland coast off of northeastern Australia. It is a rare mainly tan coloured pipefish with brownish markings, it has a white blotch over the eyes, a pale patch above the operculum and it has small white dots along its back and tail. The males frequently show irregular dark barring along their ventral surface. This species is ovoviviparous, with males carrying eggs in a brood pouch until giving birth to live young. The largest known specimen is long, while males may brood at roughly . The species was described by James Douglas Ogilby in 1890 from a specimen collected in Moreton Bay, Queensland in 1886 and the specific name honours his friend, Mr Henry Tryon, with whom he enjoyed a collecting trip in Moreton Bay. It is a listed Marine species in Australia under the Environment Protection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campichthys Galei
''Campichthys galei'' (Gale's pipefish) is a species of marine fish of the family Syngnathidae. It is endemic to Australia, found from Shark Bay (Western Australia) to the Spencer Gulf (South Australia) on the rubble bottom of inshore waters to depths of 18m. It can grow to lengths of . This species is ovoviviparous Ovoviviparity, ovovivipary, ovivipary, or aplacental viviparity is a term used as a "bridging" form of reproduction between egg-laying oviparous and live-bearing viviparous reproduction. Ovoviviparous animals possess embryos that develop insi ..., with the males carrying eggs in a brood pouch until they are ready to hatch. References Further reading Atlas of Living Australia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campichthys Tricarinatus
''Campichthys tricarinatus'' (three-keel pipefish) is a species of marine fish of the family Syngnathidae. It is found in the western central Pacific Ocean, from Montebello Island (Western Australia) to Cape York (Queensland), and specimens have been recorded around the Northern Mariana and Marshall Islands. It is found at depths of , and can grow to lengths of . This species is ovoviviparous Ovoviviparity, ovovivipary, ovivipary, or aplacental viviparity is a term used as a "bridging" form of reproduction between egg-laying oviparous and live-bearing viviparous reproduction. Ovoviviparous animals possess embryos that develop insi ..., with males carrying eggs in a brood pouch until giving birth to live young. References Further reading Australian Government Department of the Environment and Energy tricarinatus Marine fish Fish described in 1977 {{Syngnathiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campichthys Nanus
''Campichthys nanus'' is a species of marine fish of the family Syngnathidae. It is known from its type specimens that were collected at Pinda, Morrumbala District, Mozambique in the Western Indian Ocean, although there have been unverified reports of its occurrence in the South China Sea as well. This species reaches maturity at and is one of the smallest tail-brooding pipefishes, with males carrying eggs before giving live birth. Habitats and feeding habits of this species are unknown. References Further reading WoRMS Endemic fauna of Mozambique nanus Nanus may refer to: * ''Nanus'' (beetle), a genus of true weevils * Susan Nanus, the scriptwriter for the 1998 '' A Will of their Own'' romantic drama TV mini-series aired on the NBC network * Fort Nanus in Goa, India * one of the main hybrid gr ... Marine fish Fish described in 1977 {{Syngnathiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
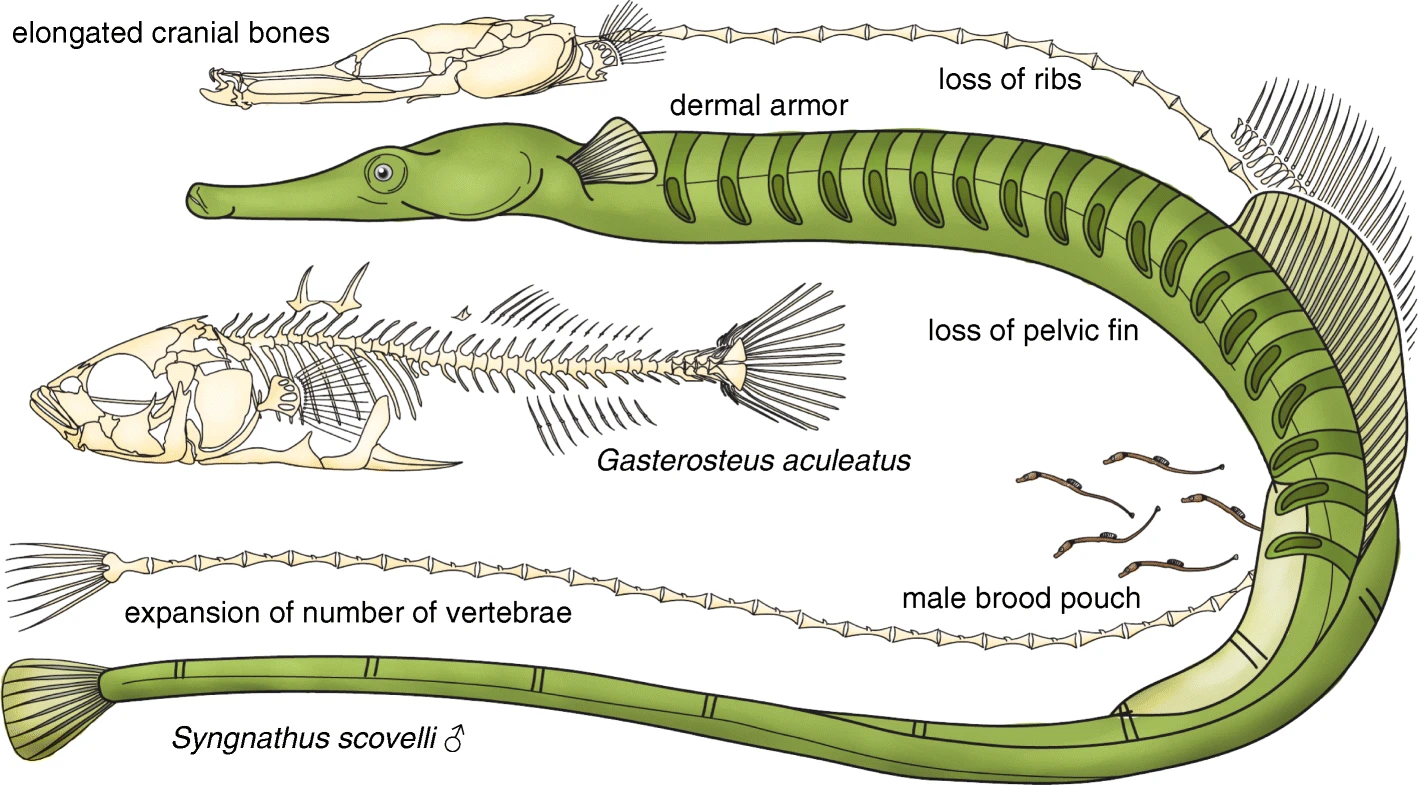
Pipefish
Pipefishes or pipe-fishes (Syngnathinae) are a subfamily of small fishes, which, together with the seahorses and seadragons (''Phycodurus'' and ''Phyllopteryx''), form the family Syngnathidae. Description Pipefish look like straight-bodied seahorses with tiny mouths. The name is derived from the peculiar form of the snout, which is like a long tube, ending in a narrow and small mouth which opens upwards and is toothless. The body and tail are long, thin, and snake-like. They each have a highly modified skeleton formed into armored plating. This dermal skeleton has several longitudinal ridges, so a vertical section through the body looks angular, not round or oval as in the majority of other fishes. A dorsal fin is always present, and is the principal (in some species, the only) organ of locomotion. The ventral fins are consistently absent, and the other fins may or may not be developed. The gill openings are extremely small and placed near the upper posterior angle of the gill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilbert Percy Whitley
Gilbert Percy Whitley (9 June 1903 – 18 July 1975) was a British-born Australian ichthyologist and malacologist who was Curator of Fishes at the Australian Museum in Sydney for about 40 years. He was born at Swaythling, Southampton, England, and was educated at King Edward VI School, Southampton and the Royal Naval College, Osborne. Whitley migrated with his family to Sydney in 1921 and he joined the staff of the Australian Museum in 1922 while studying zoology at Sydney Technical College and the University of Sydney. In 1925 he was formally appointed Ichthyologist (later Curator of Fishes) at the Museum, a position he held until retirement in 1964. During his term of office he doubled the size of the ichthyological collection to 37,000 specimens through many collecting expeditions. Whitley was also a major force in the Royal Zoological Society of New South Wales, of which he was made a Fellow in 1934 and where he served as president during 1940–41, 1959–60 and 1973–74. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, Laccadive Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Andaman Sea. Etymology The Indian Ocean has been known by its present name since at least 1515 when the Latin form ''Oceanus Orientalis Indicus'' ("Indian Eastern Ocean") is attested, named after Indian subcontinent, India, which projects into it. It was earlier known as the ''Eastern Ocean'', a term that was still in use during the mid-18th century (see map), as opposed to the ''Western Ocean'' (Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic) before the Pacific Ocean, Pacific was surmised. Conversely, Ming treasure voyages, Chinese explorers in the Indian Oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the |
Paul Georg Egmont Duncker
Paul Georg Egmont Duncker (6 May 1870, Hamburg – 28 July 1953, Ahrensburg) was a German ichthyologist. Biography He studied at the universities of Kiel, Freiburg, and Berlin, receiving his doctorate at Kiel in 1895. Following graduation he lived and worked in Karlsruhe, Plymouth, Naples, Cold Spring Harbour (Long Island N.Y.), and Würzburg. From 1901 he worked as a curator for a year at the Selangor State Museum in Kuala Lumpur, afterwards returning to Europe, where he spent another year in Naples.Duncker, (Paul) Georg (Egmont) Nationaal Herbarium Nederland He was a member of the Hamburg ''Südsee-Expedition'' (1908-10) during its first year in , of which, he collected specimens o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Eric Dawson
Charles Eric "Chuck" Dawson (December 6, 1922 – February 11, 1993) was a Canadian-American ecologist Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps wi ..., ichthyology, ichthyologist, and taxonomy (biology), taxonomist. He held expertise in goby, gobies, flatfishes, and sand stargazers, and was considered "the ultimate authority" on pipefishes in the family Syngnathidae. Life Dawson was born in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, but would eventually spend much of his career at the University of Southern Mississippi's Gulf Coast Research Laboratory in Ocean Springs, Mississippi, where he worked early as an administrator, then researcher, and museum curator. Over his long career Dawson wrote 150 publications, on the majority of which he was the sole author. He recognized 52 Syngnat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)