|
Camarque
The Camargue horse is an ancient breed of horse indigenous to the Camargue area in southern France. Its origins remain relatively unknown, although it is generally considered one of the oldest breeds of horses in the world. For centuries, possibly thousands of years, these small horses have lived wild in the harsh environment of the Camargue marshes and wetlands of the Rhône delta, which covers part of the départements of Gard and Bouches-du-Rhône. There they developed the stamina, hardiness and agility for which they are known today. Traditionally, they live in semi-feral conditions in the marshy land of the region. The Camargue horse is the traditional mount of the '' gardians'', the Camargue "cowboys" who herd the black Camargue bulls used for " courses camarguaises" in southern France. Camargue horses galloping through water is a popular and romantic image of the region. Characteristics Camargue horses are always gray. This means that they have black s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camargue Horse (26645657776)
The Camargue horse is an ancient breed of horse indigenous to the Camargue area in southern France. Its origins remain relatively unknown, although it is generally considered one of the oldest breeds of horses in the world. For centuries, possibly thousands of years, these small horses have lived wild in the harsh environment of the Camargue marshes and wetlands of the Rhône delta, which covers part of the départements of Gard and Bouches-du-Rhône. There they developed the stamina, hardiness and agility for which they are known today. Traditionally, they live in semi-feral conditions in the marshy land of the region. The Camargue horse is the traditional mount of the ''gardians'', the Camargue "cowboys" who herd the black Camargue bulls used for " courses camarguaises" in southern France. Camargue horses galloping through water is a popular and romantic image of the region. Characteristics Camargue horses are always gray. This means that they have black skin under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black (horse)
Black is a hair coat color of horses in which the entire hair coat is black. Black is a relatively uncommon coat color, and it is not uncommon to mistake dark chestnuts or bays for black. True black horses have dark brown eyes, black skin, and wholly black hair coats without any areas of permanently reddish or brownish hair. They may have pink skin beneath any white markings under the areas of white hair, and if such white markings include one or both eyes, the eyes may be blue. Many black horses "sun bleach" with exposure to the elements and sweat, and therefore their coats may lose some of their rich black character and may even resemble bay or seal brown, though examination of the color of hair around the eyes, muzzle and genitals often will determine color. Black horses that do not sun bleach are called "non-fading" blacks. Some breeds of horses, such as the Friesian horse, Murgese and Ariegeois (or Merens), are almost exclusively black. Black is also common in the Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
The () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, ' in Germany, ' in Italy, or ' in Spain. The United Kingdom's equivalent are civil parishes, although some areas, particularly urban areas, are unparished. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the municipal arrondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manade
A manade ( prov. ''menada'', originally from lat. ''manus'' = hand) is a term used mainly in the Camargue area in France for a semi-feral group of Camargue cattle or horses led by a gardian, or herder. In French, the word ''manade'' dates from 1867. In older texts it also referred to herds of sheep, but modern use of the term is limited only to raising groups of larger livestock. Raising animals in manades is specific for the Crau, Camargue (Provence) and Petite Camargue (Languedoc) regions of France, and therefore the term itself is strongly associated with the same area. Defining a manade Conditions of breeding In 1967 the Camargue Horse Breeders' Association of France (Association des éleveurs de chevaux de race Camargue or AECRC) defined the term manade to refer to the "extensive breeding" of horses at liberty and out of doors in groups of at least four mares of reproductive age and grazing on at least . "Extensive breeding" means that the animals move around freely lookin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foal
A foal is an equine up to one year old; this term is used mainly for horses, but can be used for donkeys. More specific terms are colt for a male foal and filly for a female foal, and are used until the horse is three or four. When the foal is nursing from its dam (mother), it may also be called a "suckling". After it has been weaned from its dam, it may be called a "weanling". When a mare is pregnant, she is said to be "in foal". When the mare gives birth, she is "foaling", and the impending birth is usually stated as "to foal". A newborn horse is "foaled". After a horse is one year old, it is no longer a foal, and is a "yearling". There are no special age-related terms for young horses older than yearlings. When young horses reach breeding maturity, the terms change: a filly over three (four in horse racing) is called a mare, and a colt over three is called a stallion. A castrated male horse is called a gelding regardless of age; however, colloquially, the term "gelding col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breed Registry
A breed registry, also known as a herdbook, studbook or register, in animal husbandry and the hobby of animal fancy, is an official list of animals within a specific breed whose parents are known. Animals are usually registered by their breeders while they are young. The terms studbook and register are also used to refer to lists of male animals "standing at stud", that is, those animals actively breeding, as opposed to every known specimen of that breed. Such registries usually issue certificates for each recorded animal, called a pedigree, pedigreed animal documentation, or most commonly, an animal's "papers". Registration papers may consist of a simple certificate or a listing of ancestors in the animal's background, sometimes with a chart showing the lineage. Types of registries There are breed registries and breed clubs for several species of animal, such as dogs, horses, cows and cats. The US ''Association of Zoos and Aquariums'' (AZA) also maintains stud books for captiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Hoof
A horse hoof is the lower extremity of each leg of a horse, the part that makes contact with the ground and carries the weight of the animal. It is both hard and flexible. It is a complex structure surrounding the distal phalanx of the 3rd digit (digit III of the basic pentadactyl limb of vertebrates, evolved into a single weight-bearing digit in horses) of each of the four limbs, which is covered by soft tissue and keratinised (cornified) matter. Anatomy The hoof is made up of two parts. The outer part, called the hoof capsule, is composed of various cornified specialized structures. The inner, living part of the hoof, is made up of soft tissues and bone. The cornified material of the hoof capsule differ in structure and properties. Dorsally, it covers, protects, and supports P3 (also known as the coffin bone, pedal bone, or PIII). Palmarly/plantarly, it covers and protects specialised soft tissues, such as tendons, ligaments, fibro-fatty and/or fibrocartilaginous tissues, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tail (horse)
The tail of the horse and other equines consists of two parts, the dock and the skirt. The dock consists of the muscles and skin covering the coccygeal vertebrae. The term "skirt" refers to the long hairs that fall below the dock. On a horse, long, thick tail hairs begin to grow at the base of the tail, and grow along the top and sides of the dock. In donkeys and other members of ''Equus asinus'', as well as some mules, the zebra and the wild Przewalski's horse, the dock has short hair at the top of the dock, with longer, coarser skirt hairs beginning to grow only toward the bottom of the dock. Hair does not grow at all on the underside of the dock. The tail is used by the horse and other equidae to keep away biting insects, and the position and movement of the tail may provide clues to the animal's physical or emotional state. Tail carriage may also be a breed trait. Tails of horses are often groomed in a number of ways to make them more stylish for show or practical for w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rump (animal)
The rump or croup, in the external morphology of an animal, is the portion of the posterior dorsum – that is, posterior to the loins and anterior to the tail. Anatomically, the rump corresponds to the sacrum. The tailhead or dock is the beginning of the tail, where the tail joins the rump. It is known also as the base or root of the tail, and corresponds to the human sacrococcygeal symphysis. In some mammals the tail may be said to consist of the tailbone (meaning the bony column, muscles, and skin) and the skirt (meaning the long hairs growing from the tailbone). In birds, similarly, the tail consists of tailbone and tailfan (tail fan). Some animals are subjected to docking, the amputation of the tailbone at or near the dock. These include dogs, cats, sheep, pigs, and horses. Humans have a remnant tail, the coccyx, and the human equivalent of docking is coccygectomy. Usage Usage varies from animal to animal. Birds and cattle are said to have a rump and tailhead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Back (horse)
The back describes the area of horse anatomy where the saddle goes, and in popular usage extends to include the loin or lumbar region behind the thoracic vertebrae that also is crucial to a horse's weight-carrying ability. These two sections of the vertebral column beginning at the withers, the start of the thoracic vertebrae, and extend to the last lumbar vertebra. Because horses are ridden by humans, the strength and structure of the horse's back is critical to the animal's usefulness. The thoracic vertebrae are the true "back" vertebral structures of the skeleton, providing the underlying support of the saddle, and the lumbar vertebrae of the loin provide the ''coupling'' that joins the back to the hindquarters. Integral to the back structure is the rib cage, which also provides support to the horse and rider. A complex design of bone, muscle, tendons and ligaments all work together to allow a horse to support the weight of a rider. Anatomy of the back The structure of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
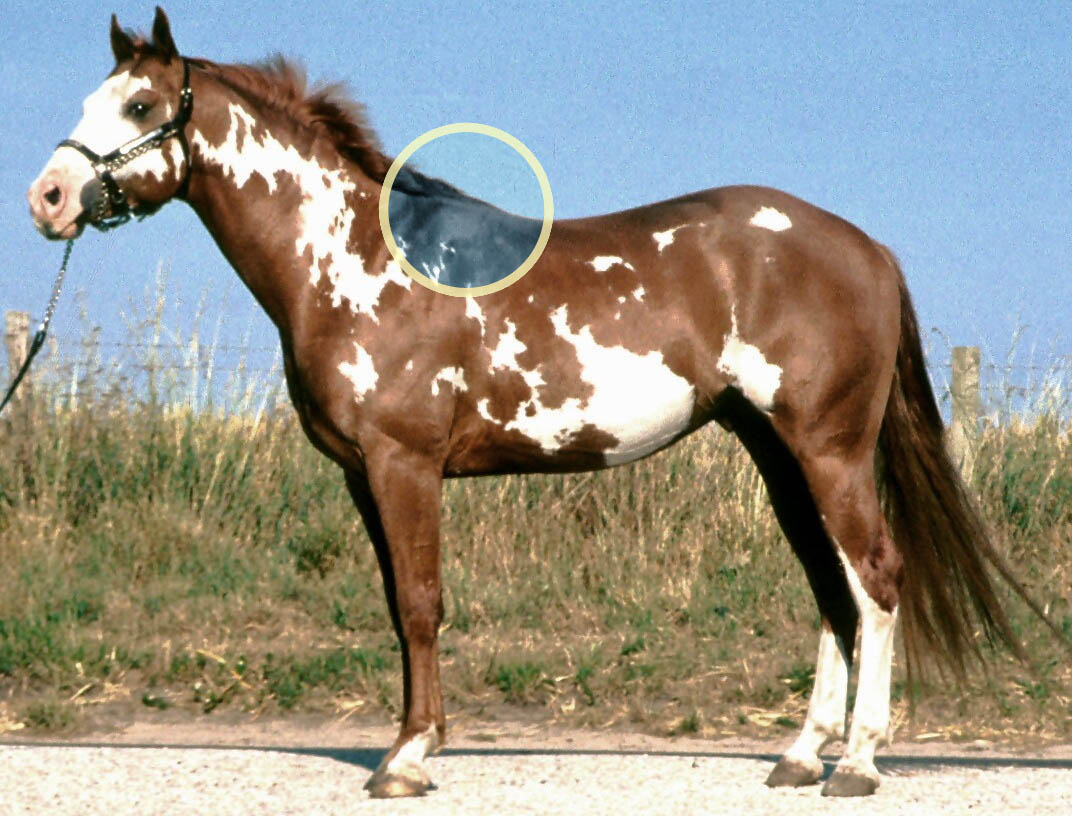
Withers
The withers is the ridge between the shoulder blades of an animal, typically a quadruped. In many species, it is the tallest point of the body. In horses and dogs, it is the standard place to measure the animal's height. In contrast, cattle are often measured to the top of the hips. The term (pronounced ) derives from Old English ''wither'' (“against”), because it is the part of a draft animal that pushes against a load. Horses The withers in horses are formed by the dorsal spinal processes of roughly the 3rd through 11th thoracic vertebrae, which are unusually long in this area. Most horses have 18 thoracic vertebrae. The processes at the withers can be more than long. Since they do not move relative to the ground as the horse's head does, the withers are used as the measuring point for the height of a horse. Horses are sometimes measured in hands – one hand is . Horse heights are extremely variable, from small pony breeds to large draft breeds. The height at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mane (horse)
On horses, the mane is the hair that grows from the top of the neck of a horse or other equine, reaching from the poll to the withers, and includes the forelock or foretop. It is thicker and coarser than the rest of the horse's coat, and naturally grows to roughly cover the neck. Heredity plays a role, giving some horses a longer, thicker mane, and others a shorter, thinner one. Some horses, such as those used in circuses or in mounted displays such as Cavalia, have manes allowed to grow down to their knees. Others have their manes deliberately shaved completely off for style or practical purposes. When ungroomed, however, the mane usually grows no longer than the width of the horse's neck, as natural wear and tear limit its potential length. The mane is thought to keep the neck warm, and possibly to help water run off the neck if the animal cannot obtain shelter from the rain. It also provides some fly protection to the front of the horse, although the tail is usually the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)