|
Calponin 3, Acidic
Calponin 3. acidic is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CNN3'' gene. The ''CNN3'' gene is located at 1p22-p21 in the human chromosomal genome. ''CNN3'' gene contains 7 exons and encodes calponin 3, a 36.4-kDa protein consisting of 329 amino acids with isoelectric point (pI) of 5.84. Calponin 3 is known as acidic calponin. Among three isoforms of calponin, less is known for the gene regulation and function of calponin 3. Nonetheless, much has been learned from extensive studies on the homologous genes ''CNN1'' and ''CNN2'' that encode calponin 1 and calponin 2. Evolution ''CNN3'' is one of the three homologous calponin isoform genes. Calponin 3 is significantly diverged from calponin 1 and calponin 2 in the C terminal variable region. The higher degree of divergence among vertebrate ''CNN3'' genes than that in the ''CNN1'' and ''CNN2'' gene families suggests possibly earlier emergence of ''CNN3'', indicating that calponin 3 may represent a prototype of calponin ances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calponin 1
Calponin 1 is a basic smooth muscle protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CNN1'' gene. The ''CNN1'' gene is located at 19p13.2-p13.1 in the human chromosomal genome and contains 7 exons, encoding the protein calponin 1, an actin filament-associated regulatory protein. Human calponin 1 is a 33.2-KDa protein consists of 297 amino acids with an isoelectric point of 9.1, thus calponin 1 is also known as basic calponin. Evolution Three homologous genes, ''Cnn1'', ''Cnn2'' and ''Cnn3'', have evolved in vertebrates, encoding three isoforms of calponin: calponin 1, calponin 2, calponin 3, respectively. Protein sequence alignment shows that calponin 1 is highly conserved in mammals but more diverged among lower vertebrates. Smooth muscle-specific expression The expression of CNN1 is specific to differentiated mature smooth muscle cells, suggesting a role in contractile functions. Calponin 1 is up-regulated in smooth muscle tissues during postnatal development with a higher conten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calponin 2
Calponin 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CNN2'' gene. The ''CNN2'' gene is located at 19p13.3 in the human chromosomal genome, encoding the protein calponin 2. Calponin 2 is one of the three isoforms of calponin and an actin filament-associated regulatory protein with wide tissue distributions. Human calponin 2 is a 33.7-kDa protein consisting of 309 amino acids with an isoelectric point (pI) of 7.23. Accordingly, it is also known as neutral calponin. Evolution Calponin isoforms are conserved proteins whereas calponin 2 has diverged from calponin 1 and calponin 3 mainly in the C-terminal variable region. Phylogenetic lineage of calponin 2 showed that calponin 2 is conserved among mammalian species but more diverged among amphibian, reptile and fish species (Fig 1). Tissue distribution ''CNN2'' is expressed in a broader range of tissue and cell types, including developing and remodeling smooth muscle as well as adult mature smooth muscle, epidermal kerat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CNN3 Wikipage
CNN3 may refer to: *CNN3 (gene) Calponin 3. acidic is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CNN3'' gene. The ''CNN3'' gene is located at 1p22-p21 in the human chromosomal genome. ''CNN3'' gene contains 7 exons and encodes calponin 3, a 36.4-kDa protein consisting of 32 ... * Shelburne/Fisher Field Aerodrome, Ontario, Canada: TC LID CNN3 {{Letter-NumberCombDisambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurons
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. Non-animals like plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord or brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions to glandular output. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord. When multiple neurons are connected together, they form what is called a neural circuit. A typical neuron consists of a cell body (soma), dendrites, and a single axon. The soma is a compact structure, and the axon and dend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrocytes
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of endothelial cells that form the blood–brain barrier, provision of nutrients to the nervous tissue, maintenance of extracellular ion balance, regulation of cerebral blood flow, and a role in the repair and scarring process of the brain and spinal cord following infection and traumatic injuries. The proportion of astrocytes in the brain is not well defined; depending on the counting technique used, studies have found that the astrocyte proportion varies by region and ranges from 20% to 40% of all glia. Another study reports that astrocytes are the most numerous cell type in the brain. Astrocytes are the major source of cholesterol in the central nervous system. Apolipoprotein E transports cholesterol from astrocytes to neurons and other glial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroglia
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. They maintain homeostasis, form myelin in the peripheral nervous system, and provide support and protection for neurons. In the central nervous system, glial cells include oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells, and microglia, and in the peripheral nervous system they include Schwann cells and satellite cells. Function They have four main functions: *to surround neurons and hold them in place *to supply nutrients and oxygen to neurons *to insulate one neuron from another *to destroy pathogens and remove dead neurons. They also play a role in neurotransmission and synaptic connections, and in physiological processes such as breathing. While glia were thought to outnumber neurons by a ratio of 10:1, recent studies using newer methods and reappraisal of historical qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myoblasts
Myogenesis is the formation of skeletal muscular tissue, particularly during embryonic development. Muscle fibers generally form through the fusion of precursor myoblasts into multinucleated fibers called ''myotubes''. In the early development of an embryo, myoblasts can either proliferate, or differentiate into a myotube. What controls this choice in vivo is generally unclear. If placed in cell culture, most myoblasts will proliferate if enough fibroblast growth factor (FGF) or another growth factor is present in the medium surrounding the cells. When the growth factor runs out, the myoblasts cease division and undergo terminal differentiation into myotubes. Myoblast differentiation proceeds in stages. The first stage, involves cell cycle exit and the commencement of expression of certain genes. The second stage of differentiation involves the alignment of the myoblasts with one another. Studies have shown that even rat and chick myoblasts can recognise and align with one an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myogenesis
Myogenesis is the formation of skeletal muscular tissue, particularly during embryonic development. Muscle fibers generally form through the fusion of precursor myoblasts into multinucleated fibers called ''myotubes''. In the early development of an embryo, myoblasts can either proliferate, or differentiate into a myotube. What controls this choice in vivo is generally unclear. If placed in cell culture, most myoblasts will proliferate if enough fibroblast growth factor (FGF) or another growth factor is present in the medium surrounding the cells. When the growth factor runs out, the myoblasts cease division and undergo terminal differentiation into myotubes. Myoblast differentiation proceeds in stages. The first stage, involves cell cycle exit and the commencement of expression of certain genes. The second stage of differentiation involves the alignment of the myoblasts with one another. Studies have shown that even rat and chick myoblasts can recognise and align with one a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
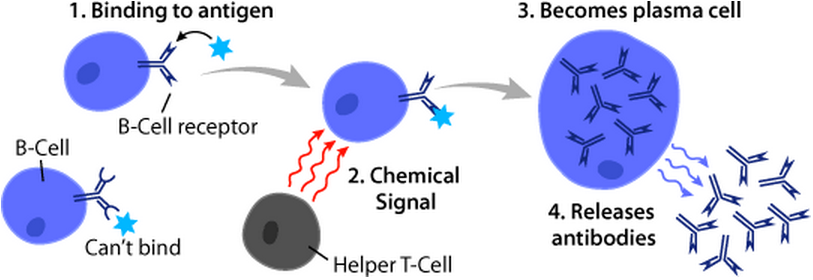
B Lymphocytes
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed. B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cells and na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)