|
Calotropis Gigantea
''Calotropis gigantea'', the crown flower, is a species of ''Calotropis'' native to Cambodia, Vietnam, Bangladesh, Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, Sri Lanka, India, China, Pakistan, and Nepal. It is a large shrub growing to tall. It has clusters of waxy flowers that are either white or lavender in colour. Each flower consists of five pointed petals and a small "crown" rising from the center which holds the stamens. The aestivation found in calotropis is valvate i.e. sepals or petals in a whorl just touch one another at the margin, without overlapping. The plant has oval, light green leaves and milky stem. The latex of ''Calotropis gigantea'' contains cardiac glycosides, fatty acids, and calcium oxalate. The roots also contain Calotropone. Pollination This plant plays host to a variety of insects and butterflies. It is the host plant for Hawaii's non-migratory monarch butterflies. ''Calotropis'' is an example of entomophily pollination (pollination by insects) and pollina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calotropis Gigantea Plant
''Calotropis'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1810. It is native to southern Asia and North Africa. They are commonly known as milkweeds because of the latex they produce. ''Calotropis'' species are considered common weeds in some parts of the world. The flowers are fragrant and are often used in making floral tassels in some mainland Southeast Asian cultures. Fibers of these plants are called madar or mader. ''Calotropis'' species are usually found in abandoned farmland. Botanical description ''Calotropis gigantea'' and ''C. procera'' are the two most common species in the genus. ''Calotropis gigantea'' grows to a height of while ''C. procera'' grows to about . The leaves are sessile and sub-sessile, opposite, ovate, cordate at the base. The flowers are about in size, with umbellate lateral cymes and are colored white to pink and are fragrant in case of ''C. procera'' while the flowers of ''C. gigantea'' are without ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamen
The stamen (plural ''stamina'' or ''stamens'') is the pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. Collectively the stamens form the androecium., p. 10 Morphology and terminology A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the filament and an anther which contains ''sporangium, microsporangia''. Most commonly anthers are two-lobed and are attached to the filament either at the base or in the middle area of the anther. The sterile tissue between the lobes is called the connective, an extension of the filament containing conducting strands. It can be seen as an extension on the dorsal side of the anther. A pollen grain develops from a microspore in the microsporangium and contains the male gametophyte. The stamens in a flower are collectively called the androecium. The androecium can consist of as few as one-half stamen (i.e. a single locule) as in ''Canna (plant), Canna'' species or as many as 3,482 stamens which have been counted in the saguaro (''Carnegiea gigantea'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophytes during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants, or from the male cone to the female cone of gymnosperms. If pollen lands on a compatible pistil or female cone, it germinates, producing a pollen tube that transfers the sperm to the ovule containing the female gametophyte. Individual pollen grains are small enough to require magnification to see detail. The study of pollen is called palynology and is highly useful in paleoecology, paleontology, archaeology, and forensics. Pollen in plants is used for transferring haploid male genetic material from the anther of a single flower to the stigma of another in cross-pollination. In a case of self-pollination, this process takes place from the anth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Androecium
The stamen (plural ''stamina'' or ''stamens'') is the pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. Collectively the stamens form the androecium., p. 10 Morphology and terminology A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the filament and an anther which contains ''microsporangia''. Most commonly anthers are two-lobed and are attached to the filament either at the base or in the middle area of the anther. The sterile tissue between the lobes is called the connective, an extension of the filament containing conducting strands. It can be seen as an extension on the dorsal side of the anther. A pollen grain develops from a microspore in the microsporangium and contains the male gametophyte. The stamens in a flower are collectively called the androecium. The androecium can consist of as few as one-half stamen (i.e. a single locule) as in '' Canna'' species or as many as 3,482 stamens which have been counted in the saguaro (''Carnegiea gigantea''). The androecium in var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stigma (botany)
The stigma () is the receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower. Description The stigma, together with the style and ovary (typically called the stigma-style-ovary system) comprises the pistil, which is part of the gynoecium or female reproductive organ of a plant. The stigma itself forms the distal portion of the style, or stylodia, and is composed of , the cells of which are receptive to pollen. These may be restricted to the apex of the style or, especially in wind pollinated species, cover a wide surface. The stigma receives pollen and it is on the stigma that the pollen grain germinates. Often sticky, the stigma is adapted in various ways to catch and trap pollen with various hairs, flaps, or sculpturings. The pollen may be captured from the air (wind-borne pollen, anemophily), from visiting insects or other animals ( biotic pollination), or in rare cases from surrounding water (hydrophily). Stigma can vary from long and sle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollination
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds, most often by an animal or by wind. Pollinating agents can be animals such as insects, birds, and bats; water; wind; and even plants themselves, when self-pollination occurs within a closed flower. Pollination often occurs within a species. When pollination occurs between species, it can produce hybrid offspring in nature and in plant breeding work. In angiosperms, after the pollen grain (gametophyte) has landed on the stigma, it germinates and develops a pollen tube which grows down the style until it reaches an ovary. Its two gametes travel down the tube to where the gametophyte(s) containing the female gametes are held within the carpel. After entering an ovum cell through the micropyle, one male nucleus fuses with the polar bodies to produce the endosperm tissues, while the other fuses with the ovule to produce the embr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entomophily
Entomophily or insect pollination is a form of pollination whereby pollen of plants, especially but not only of flowering plants, is distributed by insects. Flowers pollinated by insects typically advertise themselves with bright colours, sometimes with conspicuous patterns (honey guides) leading to rewards of pollen and nectar; they may also have an attractive scent which in some cases mimics insect pheromones. Insect pollinators such as bees have adaptations for their role, such as lapping or sucking mouthparts to take in nectar, and in some species also pollen baskets on their hind legs. This required the coevolution of insects and flowering plants in the development of pollination behaviour by the insects and pollination mechanisms by the flowers, benefiting both groups. Coevolution History The early spermatophytes (seed plants) were largely dependent on the wind to carry their pollen from one plant to another. Prior to the appearance of flowering plants some gymnospe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarch Butterfly
The monarch butterfly or simply monarch (''Danaus plexippus'') is a milkweed butterfly (subfamily Danainae) in the family Nymphalidae. Other common names, depending on region, include milkweed, common tiger, wanderer, and black-veined brown. It is amongst the most familiar of North American butterflies and an iconic pollinator, although it is not an especially effective pollinator of milkweeds. Its wings feature an easily recognizable black, orange, and white pattern, with a wingspan of . A Müllerian mimic, the viceroy butterfly, is similar in color and pattern, but is markedly smaller and has an extra black stripe across each hindwing. The eastern North American monarch population is notable for its annual southward late-summer/autumn instinctive migration from the northern and central United States and southern Canada to Florida and Mexico. During the fall migration, monarchs cover thousands of miles, with a corresponding multigenerational return north in spring. The western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butterflies
Butterflies are insects in the macrolepidopteran clade Rhopalocera from the Order (biology), order Lepidoptera, which also includes moths. Adult butterflies have large, often brightly coloured wings, and conspicuous, fluttering flight. The group comprises the large superfamily (zoology), superfamily Papilionoidea, which contains at least one former group, the skippers (formerly the superfamily "Hesperioidea"), and the most recent analyses suggest it also contains the moth-butterflies (formerly the superfamily "Hedyloidea"). Butterfly fossils date to the Paleocene, about 56 million years ago. Butterflies have a four-stage life cycle, as like most insects they undergo Holometabolism, complete metamorphosis. Winged adults lay eggs on the food plant on which their larvae, known as caterpillars, will feed. The caterpillars grow, sometimes very rapidly, and when fully developed, pupate in a chrysalis. When metamorphosis is complete, the pupal skin splits, the adult insect climbs o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
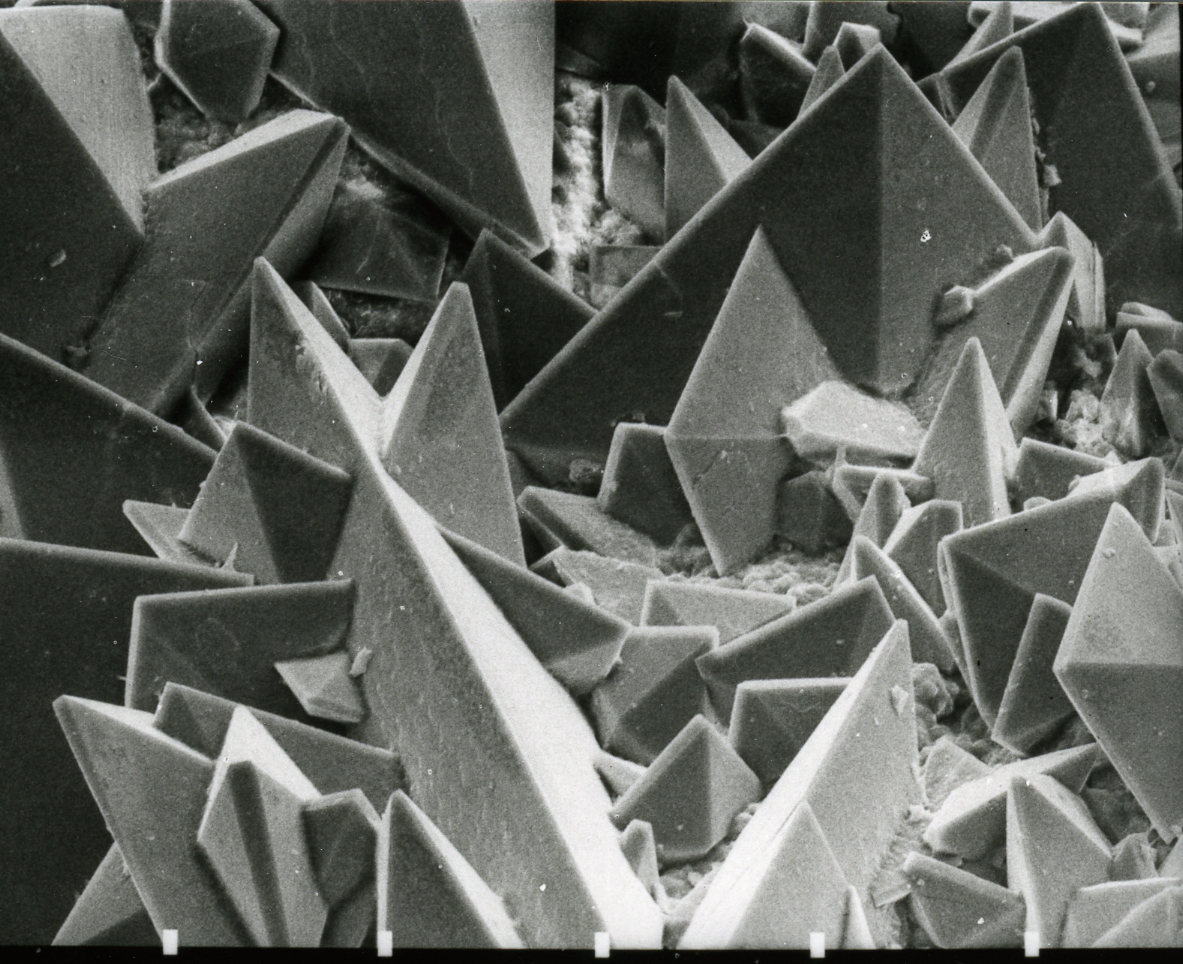
Calcium Oxalate
Calcium oxalate (in archaic terminology, oxalate of lime) is a calcium salt of oxalic acid with the chemical formula . It forms hydrates , where ''n'' varies from 1 to 3. Anhydrous and all hydrated forms are colorless or white. The monohydrate occurs naturally as the mineral whewellite, forming envelope-shaped crystals, known in plants as raphides. The two rarer hydrates are dihydrate , which occurs naturally as the mineral weddellite, and trihydrate , which occurs naturally as the mineral caoxite, are also recognized. Some foods have high quantities of calcium oxalates and can produce sores and numbing on ingestion and may even be fatal. Tribes with diets that depend highly on fruits and vegetables high in calcium oxalate, such as in Micronesia, reduce the level of it by boiling and cooking them. They are a constituent in 76% of human kidney stones. Calcium oxalate is also found in beerstone, a scale that forms on containers used in breweries. Occurrence Many plants accumu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oily acid"). Types of fatty acids Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsaturati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_male_in_flight.jpg)