|
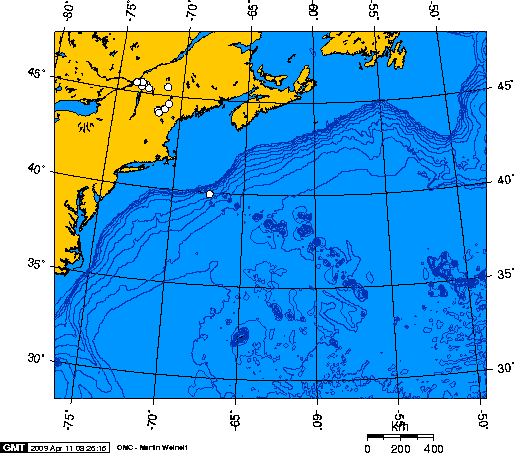
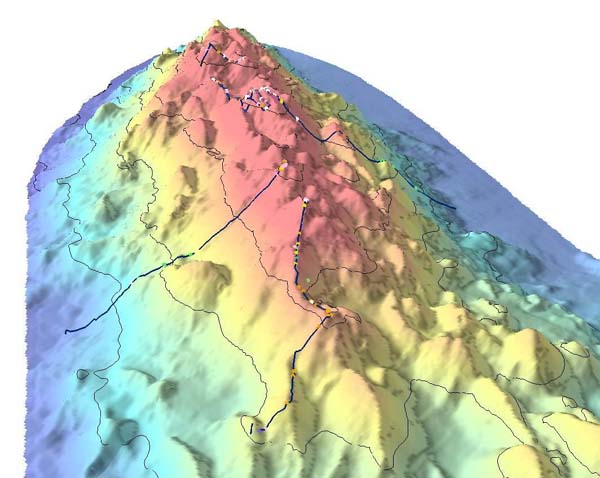
Caloosahatchee Seamount
The Caloosahatchee Seamount is a seamount in the northern Atlantic Ocean. It is part of the Corner Rise Seamounts, which was active about 75 million years ago. It was formed when the North American Plate moved over the New England hotspot The New England hotspot, also referred to as the Great Meteor hotspot and sometimes the Monteregian hotspot, is a volcanic hotspot in the North Atlantic Ocean. It created the Monteregian Hills intrusions in Montreal and Montérégie, the White ..., also known as the Great Meteor Hotspot. The Great Meteor Hotspot also formed various kimberlite fields in Canada, the Monteregian Hills, the White Mountains, the New England Seamounts, and the Seewarte Seamounts, which are the newest volcanoes produced by the New England Hotspot. References Seamounts of the Atlantic Ocean Hotspot volcanoes {{marine-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N. Scientific explorations of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corner Rise Seamounts
The Corner Rise Seamounts are a chain of extinct submarine volcanoes in the northern Atlantic Ocean east of the New England Seamounts. Both it and the New England Seamounts were formed when the North American Plate moved over the Great Meteor hotspot 75 million years ago. It is the shallowest seamount in New England, with some of its nineteen highest peaks only 800–900 m deep. Like most seamounts, they attract fish. Over 175 species have been found there, including splendid alfonsino, black cardinal fish, black scabbardfish, and wreckfish. Trawl fishing during the 1970s and 1980s resulted in approximately 20,000 tons of fish being harvested. As a result, the seamounts were closed to demersal fishing (collecting fish near the bottom of the ocean, as opposed to pelagic fishing, collecting fish near the surface) beginning 1 January 1997. The original ban was supposed to be lifted 31 December 2010, but was extended until 31 December 2020. Almost a decade into the ban, a 2005 Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seamount
A seamount is a large geologic landform that rises from the ocean floor that does not reach to the water's surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from the seafloor to in height. They are defined by oceanographers as independent features that rise to at least above the seafloor, characteristically of conical form.IHO, 2008. Standardization of Undersea Feature Names: Guidelines Proposal form Terminology, 4th ed. International Hydrographic Organization and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission, Monaco. The peaks are often found hundreds to thousands of meters below the surface, and are therefore considered to be within the deep sea. During their evolution over geologic time, the largest seamounts may reach the sea surface where wave action erodes the summit to form a flat surface. After they have subsided and sunk below the sea surface such flat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American Plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Cuba, the Bahamas, extreme northeastern Asia, and parts of Iceland and the Azores. With an area of , it is the Earth's second largest tectonic plate, behind the Pacific Plate (which borders the plate to the west). It extends eastward to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and westward to the Chersky Range in eastern Siberia. The plate includes both continental and oceanic crust. The interior of the main continental landmass includes an extensive granitic core called a craton. Along most of the edges of this craton are fragments of crustal material called terranes, which are accreted to the craton by tectonic actions over a long span of time. It is thought that much of North America west of the Rocky Mountains is composed of such terranes. Boundaries The southern boundary with the Cocos Plate to the west and the Caribbean Plate to the east is a transform fault, represented by the Swan Islands Transform Fault unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New England Hotspot
The New England hotspot, also referred to as the Great Meteor hotspot and sometimes the Monteregian hotspot, is a volcanic hotspot in the North Atlantic Ocean. It created the Monteregian Hills intrusions in Montreal and Montérégie, the White Mountains intrusions in New Hampshire, the New England and Corner Rise seamounts off the coast of North America, and the Seewarte Seamounts east of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge on the African Plate, the latter of which include its most recent eruptive center, the Great Meteor Seamount. The New England, Great Meteor, or Monteregian hotspot track has been used to estimate the movement of the North American Plate away from the African Plate from the early Cretaceous period to the present using the fixed hotspot reference frame. Geologic history The geologic history of the New England hotspot is the subject of much debate among geoscientists. The conventional opinion is that volcanic activity associated with the hotspot results from movement o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seamounts Of The Atlantic Ocean
A seamount is a large geologic landform that rises from the ocean floor that does not reach to the water's surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet or cliff, cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from volcano#Extinct, extinct volcanoes that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from the seafloor to in height. They are defined by oceanography, oceanographers as independent features that rise to at least above the seafloor, characteristically of conical form.IHO, 2008. Standardization of Undersea Feature Names: Guidelines Proposal form Terminology, 4th ed. International Hydrographic Organization and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission, Monaco. The peaks are often found hundreds to thousands of meters below the surface, and are therefore considered to be within the deep sea. During their evolution over geologic time, the largest seamounts may reach the sea surface where wave action erodes the summit to form a flat surface. After they have subsided and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |