|
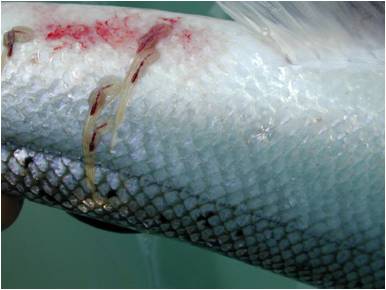
Caligus Musaicus
''Caligus musaicus'' is a sea louse species that parasitises the European flounder (''Platichthys flesus''); it was discovered off Portugal. References Siphonostomatoida Crustaceans of the Atlantic Ocean Crustaceans described in 2010 {{copepod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Louse
Sea lice (singular: sea louse) are copepods (small crustaceans) of the family Caligidae within the order Siphonostomatoida. They are marine ectoparasites (external parasites) that feed on the mucus, epidermal tissue, and blood of host fish. The roughly 559 species in 37 genera include around 162 ''Lepeophtheirus'' and 268 ''Caligus'' species. The genera ''Lepeophtheirus'' and ''Caligus'' parasitize marine fish, in particular those species that have been recorded on farmed salmon. ''Lepeophtheirus salmonis'' and various ''Caligus'' species are adapted to salt water and are major ectoparasites of farmed and wild Atlantic salmon. Several antiparasitic drugs have been developed for control purposes. ''L. salmonis'' is the best understood in the areas of its biology and interactions with its salmon host. ''Caligus rogercresseyi'' has become a major parasite of concern on salmon farms in Chile. Studies are under way to gain a better understanding of the parasite and the host-parasit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), Disease vector, vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropreda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
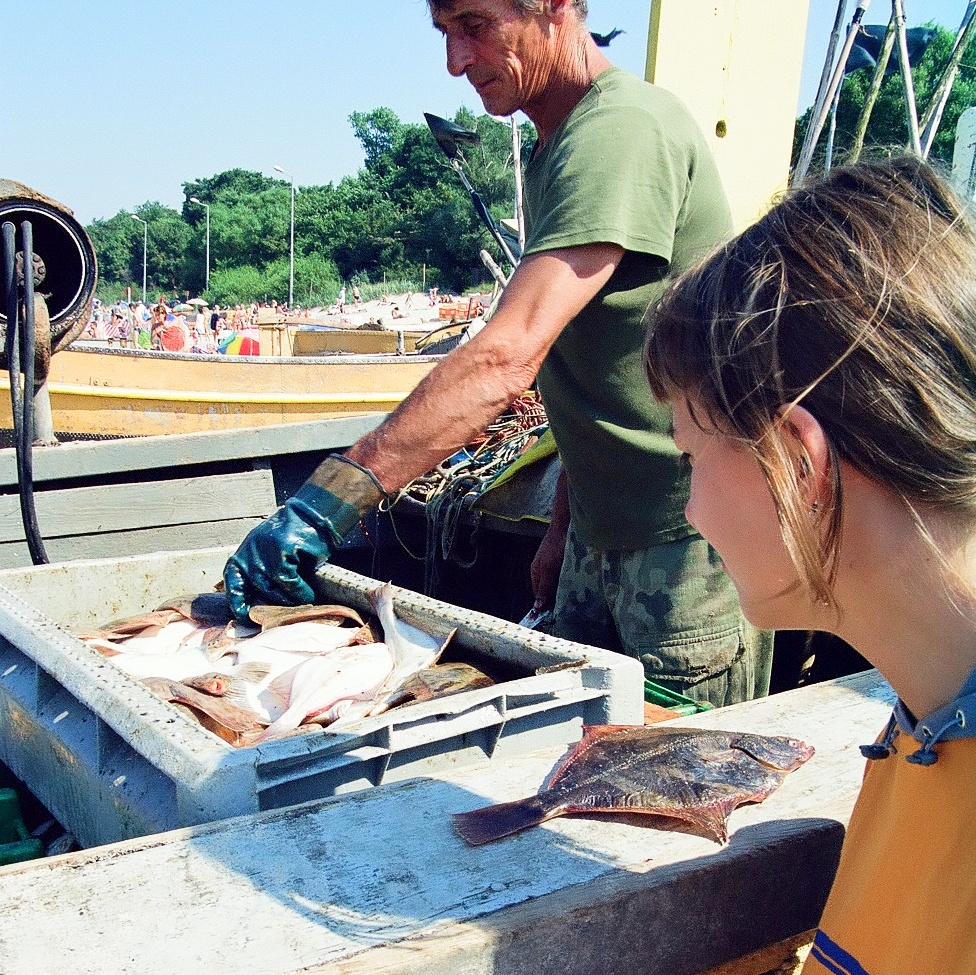
European Flounder
The European flounder (''Platichthys flesus'') is a flatfish of European coastal waters from the White Sea in the north to the Mediterranean and the Black Sea in the south. It has been introduced into the United States and Canada accidentally through transport in ballast water. It is caught and used for human consumption. The European flounder is oval in shape and is usually right-eyed. It normally grows about 30 cm in length, although lengths of up to 60 cm have been recorded. The upper surface is usually dull brown or olive in colour with reddish spots and brown blotches and this fish can change colour to suit its background, providing an effective camouflage. The underside is pearly-white, giving the fish one of its common names, the white fluke. The lateral line features rows of small tubercles, as do the bases of the dorsal and anal fins. Description The European flounder is a flatfish with an oval-shaped body with a width about half its length. The maximum recor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of the Azores and Madeira. It features the westernmost point in continental Europe, and its Iberian portion is bordered to the west and south by the Atlantic Ocean and to the north and east by Spain, the sole country to have a land border with Portugal. Its two archipelagos form two autonomous regions with their own regional governments. Lisbon is the capital and largest city by population. Portugal is the oldest continuously existing nation state on the Iberian Peninsula and one of the oldest in Europe, its territory having been continuously settled, invaded and fought over since prehistoric times. It was inhabited by pre-Celtic and Celtic peoples who had contact with Phoenicians and Ancient Greek traders, it was ruled by the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustaceana
''Crustaceana'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal specialising in carcinology. It was established in 1960 and is published monthly by Brill Publishers. The journal is abstracted and indexed by BIOSIS Previews, the Science Citation Index, The Zoological Record, and GeoRef. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2011 impact factor of 0.464. The journal is edited by J.C. von Vaupel Klein. It charges an unspecified publication fee from authors of all regular papers, and an optional open access fee of USD 1830.CrustaceanaInstructions for Authors Brill Publishers Brill Academic Publishers (known as E. J. Brill, Koninklijke Brill, Brill ()) is a Dutch international academic publisher founded in 1683 in Leiden, Netherlands. With offices in Leiden, Boston, Paderborn and Singapore, Brill today publishes 27 ... References External links * *{{Official website, http://www.brill.nl/crustaceana Carcinology journals Publications established in 1960 Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siphonostomatoida
Siphonostomatoida is an order of copepods, containing around 75% of all the copepods that parasitise fishes. Their success has been linked to their possession of siphon-like mandibles and of a "frontal filament" to aid attachment to their hosts. Most are marine, but a few live in fresh water. There are 40 recognised families: * Archidactylinidae Izawa, 1996 *Artotrogidae Brady, 1880 *Asterocheridae Giesbrecht, 1899 *Brychiopontiidae Humes, 1974 *Caligidae Burmeister, 1835 * Calverocheridae Stock, 1968 *Cancerillidae Giesbrecht, 1897 *Codobidae Boxshall & Ohtsuka, 2001 *Coralliomyzontidae Humes & Stock, 1991 * Dichelesthiidae Milne-Edwards, 1840 *Dichelinidae Boxshall & Ohtsuka, 2001 *Dinopontiidae Murnane, 1967 *Dirivultidae Humes & Dojiri, 1980 *Dissonidae Yamaguti, 1963 *Ecbathyriontidae Humes, 1987 *Entomolepididae Brady, 1899 *Eudactylinidae C. B. Wilson, 1932 * Hatschekiidae Kabata, 1979 * Hyponeoidae Heegaard, 1962 * Kroyeriidae Kabata, 1979 * Lernaeopodidae Milne-Edwards, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustaceans Of The Atlantic Ocean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |