|
Calcinosis Cutis
Calcinosis cutis is a type of calcinosis wherein calcium deposits form in the skin. A variety of factors can result in this condition. The most common source is dystrophic calcification, which occurs in soft tissue as a response to injury. In addition, calcinosis is seen in Limited Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis, also known as CREST syndrome (the "C" in CREST). In dogs, calcinosis cutis is found in young, large breed dogs and is thought to occur after a traumatic injury. Causes Calcinosis may result from a variety of causes such as: *Trauma to the region *Inflammation (bug bites, acne) *Varicose veins *Infections * Tumors (malignant or benign) *Diseases of connective tissue *Hypercalcemia *Hyperphosphatemia Calcinosis cutis is associated with systemic sclerosis. Diagnosis Types Calcinosis cutis may be divided into the following types: * Dystrophic calcinosis cutis * Metastatic calcinosis cutis * Iatrogenic calcinosis cutis * Traumatic calcinosis cutis * Idiopathic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to as ''photomicroscopy''. At a basic level, photomicroscopy may be performed simply by connecting a camera to a microscope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iatrogenic Calcinosis Cutis
Calcinosis cutis is a type of calcinosis wherein calcium deposits form in the skin. A variety of factors can result in this condition. The most common source is dystrophic calcification, which occurs in soft tissue as a response to injury. In addition, calcinosis is seen in Limited Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis, also known as CREST syndrome (the "C" in CREST). In dogs, calcinosis cutis is found in young, large breed dogs and is thought to occur after a traumatic injury. Causes Calcinosis may result from a variety of causes such as: *Trauma to the region *Inflammation (bug bites, acne) *Varicose veins *Infections *Tumors (malignant or benign) *Diseases of connective tissue * Hypercalcemia *Hyperphosphatemia Calcinosis cutis is associated with systemic sclerosis. Diagnosis Types Calcinosis cutis may be divided into the following types: * Dystrophic calcinosis cutis * Metastatic calcinosis cutis * Iatrogenic calcinosis cutis * Traumatic calcinosis cutis * Idiopathic ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcinosis
Calcinosis is the formation of calcium deposits in any soft tissue. It is a rare condition that has many different causes. These range from infection and injury to systemic diseases like kidney failure. Types Dystrophic calcification The most common type of calcinosis is dystrophic calcification. This type of calcification can occur as a response to any soft tissue damage, including that involved in implantation of medical devices. Metastatic calcification Metastatic calcification involves a systemic calcium excess imbalance, which can be caused by hypercalcemia, kidney failure, milk-alkali syndrome, lack or excess of other minerals, or other causes. Tumoral calcinosis The cause of the rare condition of tumoral calcinosis is not entirely understood. It is generally characterized by large, globular calcifications near joints. See also * Calcification * Calcinosis cutis * Dermatomyositis * Fahr's syndrome Primary Indiana familial brain calcification Initial Posting: Apri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία '' -logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments (as "cell blocks"). Collection of tissues Histopathological examination of tissues starts with surgery, biopsy, or autopsy. The tissue is removed from the body or plant, and then, often following expert dissection in the fresh state, placed in a fixative which stabilizes the tissues to prevent decay. The most common fixative is 10% neutral buffered formalin (corresponding to 3.7% w/v formaldehyde in neutral buffered water, such as phosphat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
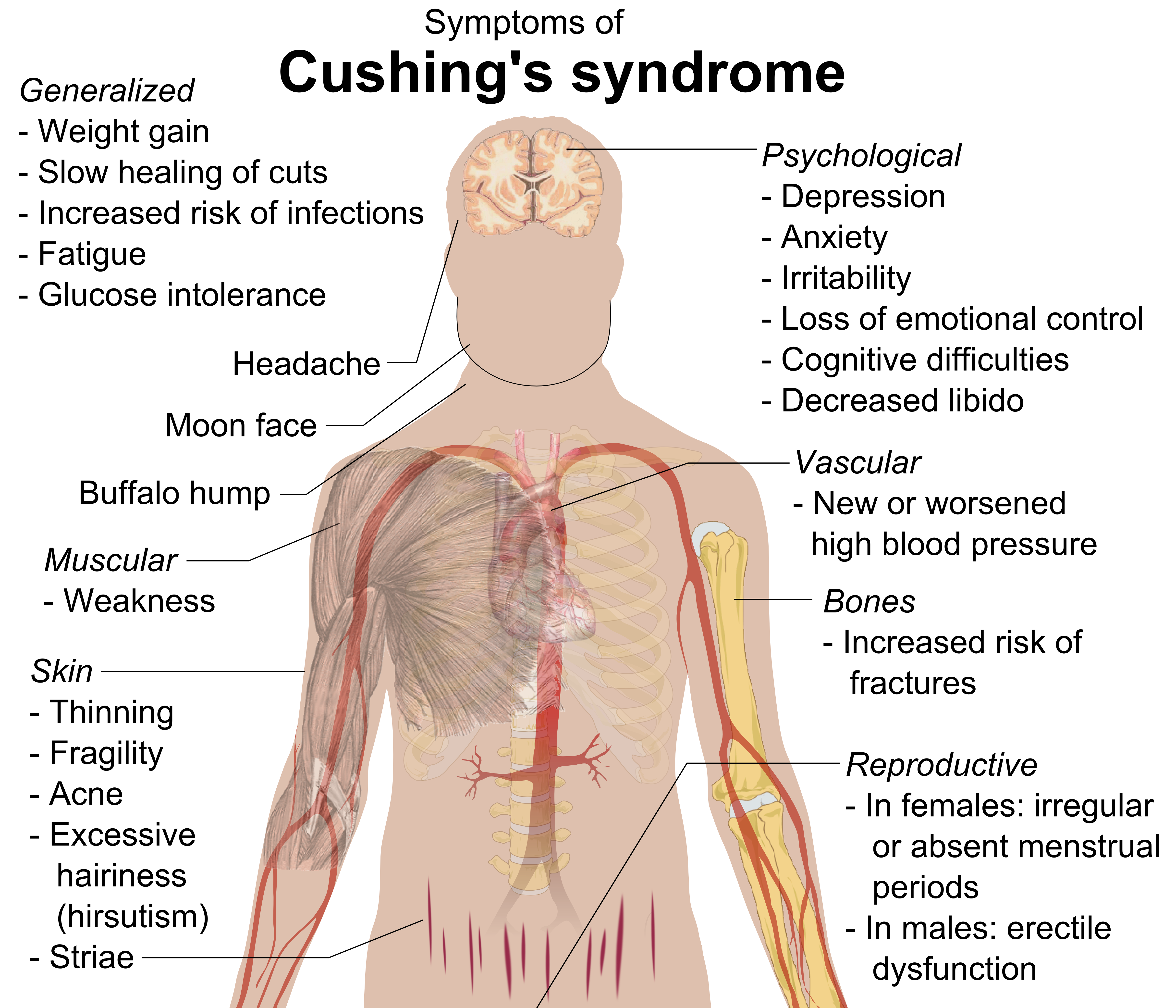
Cushing's Syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, a round red face, a fat lump between the shoulders, weak muscles, weak bones, acne, and fragile skin that heals poorly. Women may have more hair and irregular menstruation. Occasionally there may be changes in mood, headaches, and a chronic feeling of tiredness. Cushing's syndrome is caused by either excessive cortisol-like medication, such as prednisone, or a tumor that either produces or results in the production of excessive cortisol by the adrenal glands. Cases due to a pituitary adenoma are known as Cushing's disease, which is the second most common cause of Cushing's syndrome after medication. A number of other tumors, often referred to as ectopic due to their placement outside the pituitary, may also cause Cushing's. Some of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
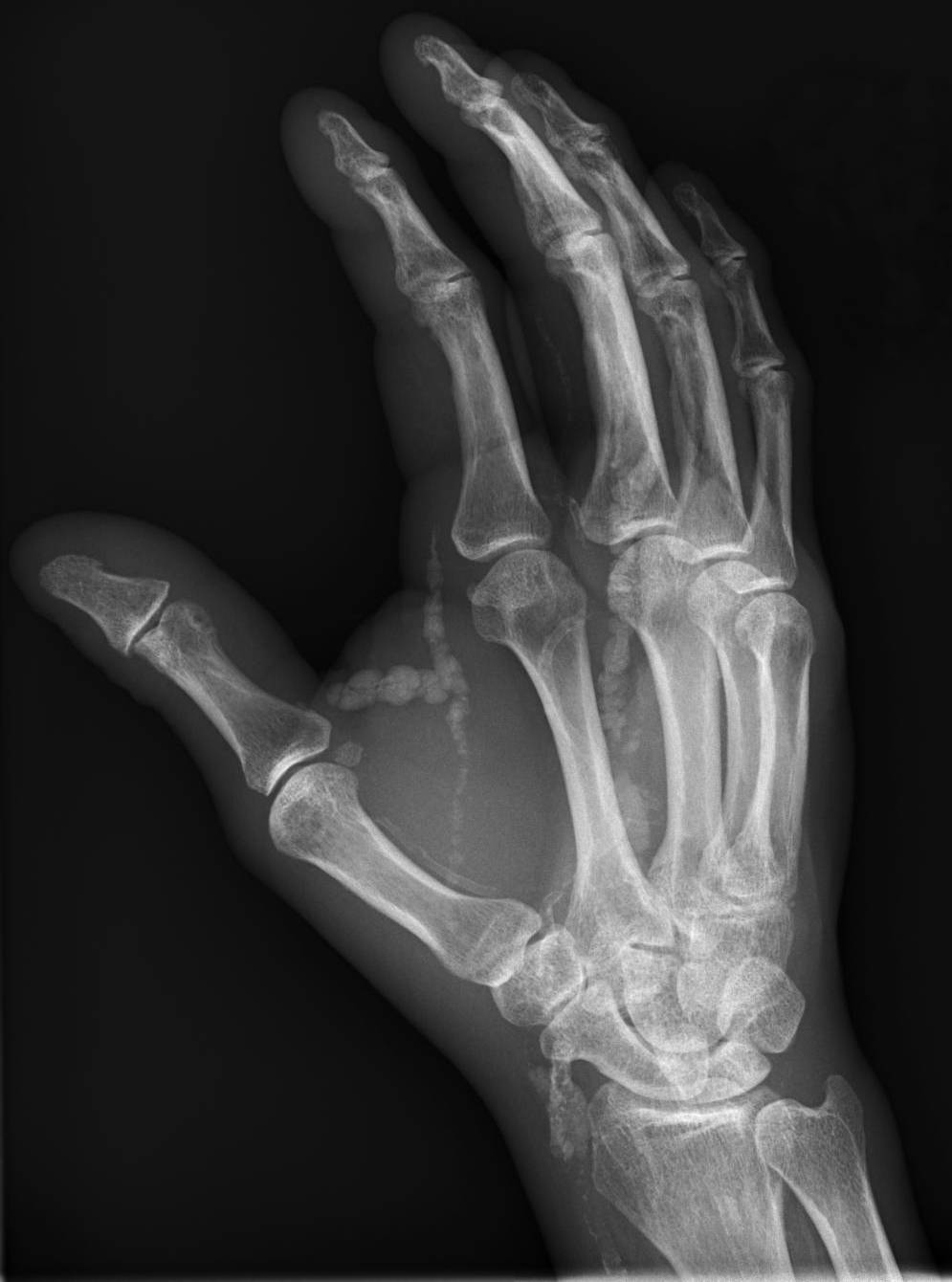
Osteoma Cutis
Osteoma cutis is a cutaneous condition characterized by the presence of bone within the skin in the absence of a preexisting or associated lesion. See also * Calcinosis cutis * Skin lesion * List of cutaneous conditions Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier agai ... References External links Skin conditions resulting from errors in metabolism {{Cutaneous-condition-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumoral Calcinosis
Tumoral calcinosis is a rare condition in which there is calcium deposition in the soft tissue in periarticular location, around joints, outside the joint capsule. They are frequently (0.5–3%) seen in patients undergoing renal dialysis. Clinically also known as hyperphosphatemic familial tumoral calcinosis (HFTC), is often caused by genetic mutations in genes that regulate phosphate physiology in the body (leading to too much phosphate (hyperphosphatemia)). Best described genes that harbour mutations in humans are FGF-23, Klotho (KL), or GALNT3. A zebrafish animal model with reduced GALNT3 expression also showed HFTC-like phenotype, indicating an evolutionary conserved mechanism that is involved in developing tumoral calcinosis. Clinical features The name indicates calcinosis (calcium deposition) which resembles tumor (like a new growth). They are not true neoplasms – they don't have dividing cells. They are just deposition of inorganic calcium with serum exudate. Childr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subepidermal Calcified Nodule
Subepidermal calcified nodule is a type of Calcinosis cutis. It's a cutaneous condition characterized by calcification of the skin resulting from the deposition of calcium and phosphorus, occurring most frequently as one or a few skin lesions on the scalp or face of children. Lesions may also appear on the ear and eyelid. See also * Ectopic calcification * Calcinosis cutis * Skin lesion A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of th ... * List of cutaneous conditions References Skin conditions resulting from errors in metabolism {{Cutaneous-condition-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idiopathic Scrotal Calcinosis
Idiopathic scrotal calcinosis is a cutaneous condition characterized by calcification of the skin resulting from the deposition of calcium and phosphorus occurring on the scrotum. However, the levels of calcium and phosphate in the blood are normal. Idiopathic scrotal calcinosis typically affects young males, with an onset between adolescence and early adulthood. The scrotal calcinosis appears, without any symptoms, as yellowish nodules that range in size from 1 mm to several centimeters. Without known links to other lesions or systemic pre-conditions, scrotal calcinosis was considered idiopathic. It is not related to calcium phosphate imbalance or renal insufficiency. By 2010, studies supported that epidermoid cysts are believed to be caused by dystrophic calcification. This process involves subclinical inflammation, rupture, calcification, and cyst wall obliteration. Presentation * Single or multiple hard, marble-like nodules of varying size affecting scrotal skin. * No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idiopathic Calcinosis Cutis
An idiopathic disease is any disease with an unknown cause or mechanism of apparent spontaneous origin. From Greek ἴδιος ''idios'' "one's own" and πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", ''idiopathy'' means approximately "a disease of its own kind". For some medical conditions, one or more causes are somewhat understood, but in a certain percentage of people with the condition, the cause may not be readily apparent or characterized. In these cases, the origin of the condition is said to be idiopathic. With some other medical conditions, the root cause for a large percentage of all cases have not been established—for example, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis or ankylosing spondylitis; the majority of these cases are deemed idiopathic. Medical advances and this term Advances in medical science improve the understanding of causes of diseases and the classification of diseases; thus, regarding any particular condition or disease, as more root causes are discovered and as events t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traumatic Calcinosis Cutis
Calcinosis cutis is a type of calcinosis wherein calcium deposits form in the skin. A variety of factors can result in this condition. The most common source is dystrophic calcification, which occurs in soft tissue as a response to injury. In addition, calcinosis is seen in Limited Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis, also known as CREST syndrome (the "C" in CREST). In dogs, calcinosis cutis is found in young, large breed dogs and is thought to occur after a traumatic injury. Causes Calcinosis may result from a variety of causes such as: *Trauma to the region *Inflammation (bug bites, acne) *Varicose veins *Infections *Tumors (malignant or benign) *Diseases of connective tissue * Hypercalcemia *Hyperphosphatemia Calcinosis cutis is associated with systemic sclerosis. Diagnosis Types Calcinosis cutis may be divided into the following types: * Dystrophic calcinosis cutis * Metastatic calcinosis cutis * Iatrogenic calcinosis cutis * Traumatic calcinosis cutis * Idiopathic calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastatic Calcinosis Cutis
Calcinosis cutis is a type of calcinosis wherein calcium deposits form in the skin. A variety of factors can result in this condition. The most common source is dystrophic calcification, which occurs in soft tissue as a response to injury. In addition, calcinosis is seen in Limited Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis, also known as CREST syndrome (the "C" in CREST). In dogs, calcinosis cutis is found in young, large breed dogs and is thought to occur after a traumatic injury. Causes Calcinosis may result from a variety of causes such as: *Trauma to the region *Inflammation (bug bites, acne) *Varicose veins *Infections *Tumors (malignant or benign) *Diseases of connective tissue * Hypercalcemia *Hyperphosphatemia Calcinosis cutis is associated with systemic sclerosis. Diagnosis Types Calcinosis cutis may be divided into the following types: * Dystrophic calcinosis cutis * Metastatic calcinosis cutis * Iatrogenic calcinosis cutis * Traumatic calcinosis cutis * Idiopathic calci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |