|
Cahto
The Cahto (also spelled Kato, especially in anthropological and linguistic contexts) are an indigenous Californian group of Native Americans. Today most descendants are enrolled as the federally recognized tribe, the Cahto Indian Tribe of the Laytonville Rancheria, and a small group of Cahto are enrolled in the Round Valley Indian Tribes of the Round Valley Reservation. Name ''Cahto (Kato)'' means loosely "People of the Lake" or "Lake People," and may derive from the Northern Pomo word for "lake", which referred to an important Cahto village site, called Djilbi. Therefore the Cahto are sometimes referred to as the ''Kaipomo'' or Kato people. The Cahto (Kato) called themselves Tlokyhan, or "Grass People." Today they use Kooʾyoohaangn or Cahto Tribe as tribal designation. Reservation The tribe controls the Laytonville Rancheria (), also known as the Cahto Rancheria, a federal Indian reservation of Cahto and Pomo people. The rancheria is large and located west of Laytonville ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cahto Flag
The Cahto (also spelled Kato, especially in anthropological and linguistic contexts) are an indigenous Californian group of Native Americans. Today most descendants are enrolled as the federally recognized tribe, the Cahto Indian Tribe of the Laytonville Rancheria, and a small group of Cahto are enrolled in the Round Valley Indian Tribes of the Round Valley Reservation. Name ''Cahto (Kato)'' means loosely "People of the Lake" or "Lake People," and may derive from the Northern Pomo word for "lake", which referred to an important Cahto village site, called Djilbi. Therefore the Cahto are sometimes referred to as the ''Kaipomo'' or Kato people. The Cahto (Kato) called themselves Tlokyhan, or "Grass People." Today they use Kooʾyoohaangn or Cahto Tribe as tribal designation. Reservation The tribe controls the Laytonville Rancheria (), also known as the Cahto Rancheria, a federal Indian reservation of Cahto and Pomo people. The rancheria is large and located west of Laytonville i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cahto Language
Cahto (also spelled Kato) is an language death, extinct Athabaskan languages, Athabaskan language that was formerly spoken by the Kato (tribe), Kato people of the Laytonville and Branscomb area at the head of the South Fork Eel River, South Fork of the Eel River. It is one of the four languages belonging to the ''California Athabaskan'' cluster of the Pacific Coast Athabaskan languages. Most Kato speakers were bilingual in Northern Pomo and some also spoke Yuki language, Yuki. Phonology Consonants Cahto has 26 consonant phonemes and 30 phones. Vowels Cahto has 9 vowel phonemes (including the diphthong) and 12 phones. References * University of California Publications in American Archaeology and Ethnography 5(3):65-238. * Goddard, Pliny Earle (1912). ''Elements of the Kato Language.'' University of California Publications in American Archaeology and Ethnography 11(1):1-176. * * Golla, Victor (2011). ''California Indian Languages.'' Berkeley: University of California Press. . E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomo People
The Pomo are an Indigenous people of California. Historical Pomo territory in Northern California was large, bordered by the Pacific Coast to the west, extending inland to Clear Lake, and mainly between Cleone and Duncans Point. One small group, the Northeastern Pomo, lived in the vicinity of present-day Stonyford in Colusa County, separated from the core Pomo area by lands inhabited by Yuki and Wintuan speakers. The name Pomo derives from a conflation of the Pomo words and . It originally meant "those who live at red earth hole" and was once the name of a village in southern Potter Valley near the present-day community of Pomo, California in Mendocino County. It may have referred to local deposits of the red mineral magnesite, used for red beads, or to the reddish earth and clay, such as hematite, mined in the area. In the Northern Pomo dialect, ''-pomo'' or ''-poma'' was used as a suffix after the names of places, to mean a subgroup of people of the place. By 1877, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federally Recognized Tribe
This is a list of federally recognized tribes in the contiguous United States of America. There are also federally recognized Alaska Native tribes. , 574 Indian tribes were legally recognized by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) of the United States.Federal Acknowledgment of the Pamunkey Indian Tribe Of these, 231 are located in Alaska. Description  In the United States, the Indian tribe is a fundamental unit, and the constitution grants
In the United States, the Indian tribe is a fundamental unit, and the constitution grants [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
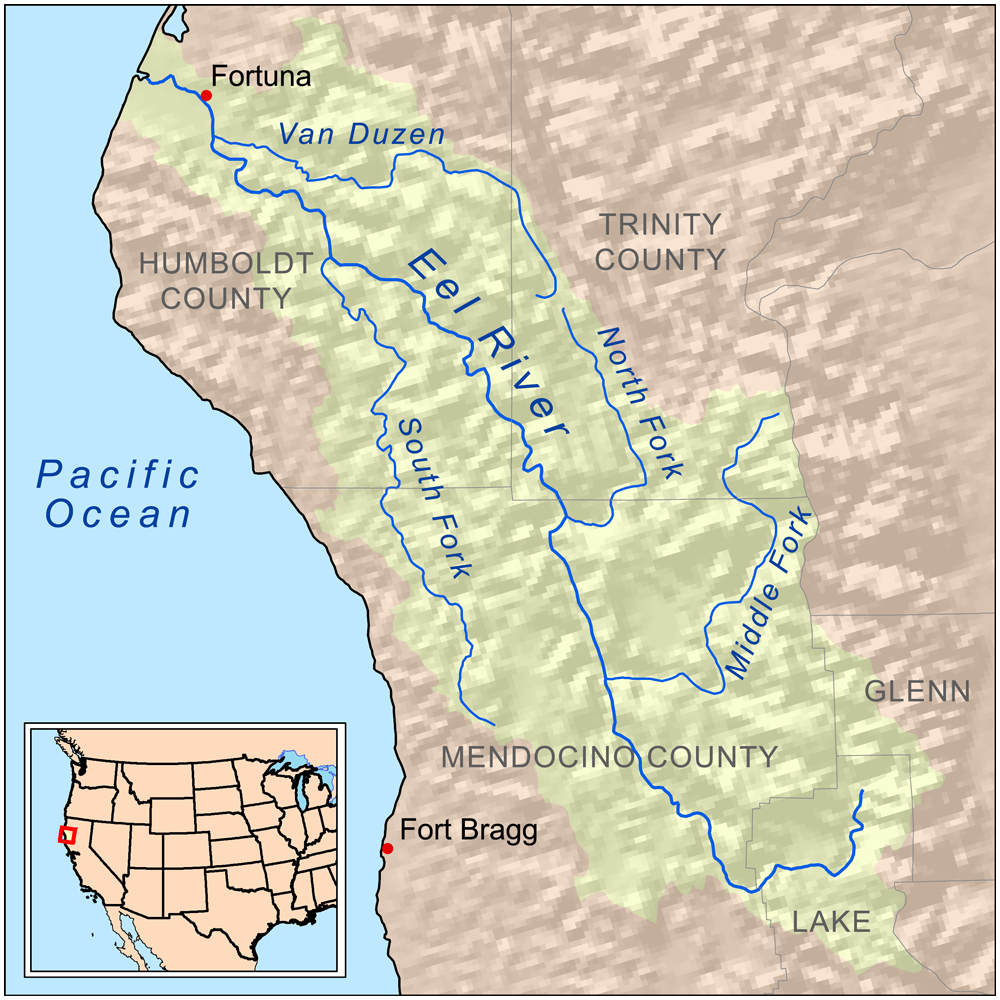
Eel River (California)
The Eel River ( Wiyot: ''Wiya't''; Cahto: ''Taanchow''; Northern Pomo: ''ch'idiyu'') is a major river, about long, of northwestern California. The river and its tributaries form the third largest watershed entirely in California, draining a rugged area of in five counties. The river flows generally northward through the Coast Ranges west of the Sacramento Valley, emptying into the Pacific Ocean about downstream from Fortuna and just south of Humboldt Bay. The river provides groundwater recharge, recreation, and industrial, agricultural and municipal water supply.William M. Brown and John R. RitterSediment transport and Turbidity in the Eel River Basin, 1971, prepared in cooperation with the California Department of Water Resources, 67 pages The Eel River system is among the most dynamic in California because of the region's unstable geology and the influence of major Pacific storms. The discharge is highly variable; average flows in January and February are over 100 tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athabascan Language
Athabaskan (also spelled ''Athabascan'', ''Athapaskan'' or ''Athapascan'', and also known as Dene) is a large family of indigenous languages of North America, located in western North America in three areal language groups: Northern, Pacific Coast and Southern (or Apachean). Kari and Potter (2010:10) place the total territory of the 53 Athabaskan languages at . Chipewyan is spoken over the largest area of any North American native language, while Navajo is spoken by the largest number of people of any native language north of Mexico. ''Athebaskan '' is a version of a Cree name for Lake Athabasca ( crm, Āðapāskāw, script=Latn 'herethere are reeds one after another'), in Canada. Cree is one of the Algonquian languages and therefore not itself an Athabaskan language. The name was assigned by Albert Gallatin in his 1836 (written 1826) classification of the languages of North America. He acknowledged that it was his choice to use that name for the language family and its assoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round Valley Indian Tribes Of The Round Valley Reservation
The Round Valley Indian Reservation is a federally recognized Indian reservation lying primarily in northern Mendocino County, California, United States. A small part of it extends northward into southern Trinity County. The total land area, including off-reservation trust land, is 93.939 km2 (36.270 sq mi). More than two-thirds of this area is off-reservation trust land, including about in the community of Covelo. The total resident population as of the 2000 census was 300 persons, of whom 99 lived in Covelo. History of the Round Valley Natives The Round Valley Indians consists of the Covelo Indian Community. This community is an accumulation of people from several tribes: the Yuki, who were the original inhabitants of Round Valley, Concow Maidu, Little Lake and other Pomo, Nomlaki, Cahto, Wailaki, and Pit River peoples. They were forced onto this remnant of the land formerly occupied by the Yuki tribe. The Round Valley Indian Reservation began in 1856 as the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the most populated subnational entity in North America and the 34th most populous in the world. The Greater Los Angeles area and the San Francisco Bay Area are the nation's second and fifth most populous urban regions respectively, with the former having more than 18.7million residents and the latter having over 9.6million. Sacramento is the state's capital, while Los Angeles is the most populous city in the state and the second most populous city in the country. San Francisco is the second most densely populated major city in the country. Los Angeles County is the country's most populous, while San Bernardino County is the largest county by area in the country. California borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mattole
The Mattole, including the Bear River Indians, are a group of Native Americans in California. Their traditional lands are along the Mattole and Bear Rivers near Cape Mendocino in Humboldt County, California. A notable difference between the Mattole and other indigenous peoples of California is that the men traditionally had facial tattoos (on the forehead), while other local groups traditionally restricted facial tattooing to women. Name The Wailaki name was ''Tul'bush'' ("foreigners"), the Cahto name was ''Diideeʾ-kiiyaahaangn'' ("The North Tribe"). The Bear River Indians called themselves and the Mattole Ni'ekeni'. Language The Mattole spoke the Mattole language, an Athapaskan language that may have been closely related to that of their Eel River neighbors to the east. According to linguist Victor Golla, the last surviving person who could speak the Mattole language died in the 1950s. Territory Historically, the Mattole lived along the Mattole River in the valley of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Californian
The indigenous peoples of California (known as Native Californians) are the indigenous inhabitants who have lived or currently live in the geographic area within the current boundaries of California before and after the arrival of Europeans. With over forty groups seeking to be federally recognized tribes, California has the second-largest Native American population in the United States. The California cultural area does not conform exactly to the state of California's boundaries. Many tribes on the eastern border with Nevada are classified as Great Basin tribes, and some tribes on the Oregon border are classified as Plateau tribes. Tribes in Baja California who do not cross into California are classified as indigenous peoples of Mexico. History Pre-contact Evidence of human occupation of California dates from at least 19,000 years ago. Prior to European contact, indigenous Californians had 500 distinct sub-tribes or groups, each consisting of 50 to 500 individual members. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eel River Athapaskan Peoples
The Eel River Athabaskans include the Wailaki, Lassik, Nongatl, and Sinkyone (Sinkine) groups of Native Americans that traditionally live in present-day Mendocino, Trinity, and Humboldt counties on or near the Eel River and Van Duzen River of northwestern California. These groups speak dialects of the Wailaki language belonging to the Pacific Coast Athabaskan group of the Athapaskan language family which is prominently represented in Alaska, western Canada, and the southwestern U.S. Other related Athapaskan groups neighboring the Eel River Athapaskans included the Hupa- Whilkut-Chilula to the north, the Mattole on the coast to the west, and the Kato to the south. The Whilkut, Nongatl and Lassik were essentially annihilated during the Bald Hills War in the 1860s. Some Wailaki people are registered members of Round Valley Indian Tribes. Tribes Nongatl The Nongatl (Hupa word meaning ″Athapaskan to the south″) lived traditionally in the territory around the Van ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mattole Language
Mattole, or Mattole–Bear River, is an extinct Athabaskan language once spoken by the Mattole and Bear River peoples of northern California. It is one of the four languages belonging to the ''California Athabaskan'' cluster of the Pacific Coast Athabaskan languages. It was found in two locations: in the valley of the Mattole River, immediately south of Cape Mendocino on the coast of northwest California, and a distinct dialect on Bear River, about 10 miles to the north. References * * Goddard, Pliny Earle (1929). "The Bear River Dialect of Athapascan." ''University of California Publications in American Archaeology and Ethnology'' 24 (5):291-334, 1929. * Golla, Victor (2011). ''California Indian Languages''. Berkeley: University of California Press. . * * Yeadon, David, "California’s North Face", National Geographic, vol. 184, no. 1, p. 48-79, July 1993. External links A Survey of the Athabaskan Language MattoleMattole languageoverview at the Survey of Californi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)