|
Cahokia Monks Mound HRoe 2008
The Cahokia Mounds State Historic Site ( 11 MS 2) is the site of a pre-Columbian Native American city (which existed 1050–1350 CE) directly across the Mississippi River from modern St. Louis, Missouri. This historic park lies in south-western Illinois between East St. Louis and Collinsville. The park covers , or about , and contains about 80 manmade mounds, but the ancient city was much larger. At its apex around 1100 CE, the city covered about and included about 120 earthworks in a wide range of sizes, shapes, and functions."Nomination – Cahokia Mounds State Historic Site, Illinois" ''US World Heritage Sites'', National Park Service, accessed 2012-05-03 Cahokia was the largest and most influential urban settlement of the |
Monks Mound
Monks Mound is the largest Pre-Columbian earthwork in the Americas and the largest pyramid north of Mesoamerica. The beginning of its construction dates from 900–955 CE. Located at the Cahokia Mounds UNESCO World Heritage Site near Collinsville, Illinois, the mound size was calculated in 1988 as about 100 feet (30 m) high, 955 feet (291 m) long including the access ramp at the southern end, and 775 feet (236 m) wide. This makes Monks Mound roughly the same size at its base as the Great Pyramid of Giza (13.1 acres / 5.3 hectares). The perimeter of its base is larger than the Pyramid of the Sun at Teotihuacan. As a platform mound, the earthwork supported a wooden structure on the summit. Unlike Egyptian pyramids which were built of stone, the platform mound was constructed almost entirely of layers of basket-transported soil and clay. Because of this construction and its flattened top, over the years, it has retained rainwater within the structure. This has caused slumping, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology and represents a part of the archaeological record. Sites may range from those with few or no remains visible above ground, to buildings and other structures still in use. Beyond this, the definition and geographical extent of a "site" can vary widely, depending on the period studied and the theoretical approach of the archaeologist. Geographical extent It is almost invariably difficult to delimit a site. It is sometimes taken to indicate a settlement of some sort although the archaeologist must also define the limits of human activity around the settlement. Any episode of deposition such as a hoard or burial can form a site as well. Development-led archaeology undertaken as cultural resources management has the disadvantage (or the ben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel K
Daniel is a masculine given name and a surname of Hebrew origin. It means "God is my judge"Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 68. (cf. Gabriel—"God is my strength"), and derives from two early biblical figures, primary among them Daniel from the Book of Daniel. It is a common given name for males, and is also used as a surname. It is also the basis for various derived given names and surnames. Background The name evolved into over 100 different spellings in countries around the world. Nicknames (Dan, Danny) are common in both English and Hebrew; "Dan" may also be a complete given name rather than a nickname. The name "Daniil" (Даниил) is common in Russia. Feminine versions (Danielle, Danièle, Daniela, Daniella, Dani, Danitza) are prevalent as well. It has been particularly well-used in Ireland. The Dutch names "Daan" and "Daniël" are also variations of Daniel. A related surname developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illiniwek
The Illinois Confederation, also referred to as the Illiniwek or Illini, were made up of 12 to 13 tribes who lived in the Mississippi River Valley. Eventually member tribes occupied an area reaching from Lake Michicigao (Michigan) to Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, and Arkansas. The five main tribes were the Cahokia, Kaskaskia, Michigamea, Peoria, and Tamaroa. The name of the confederation was derived from the transliteration by French explorers of to ''Illinois'', more in keeping with the sounds of their own language. The tribes are estimated to have had tens of thousands of members, before the advancement of European contact in the 17th century that inhibited their growth and resulted in a marked decline in population. The Illinois, like many Native American groups, sustained themselves through agriculture, hunting, and fishing. A partially nomadic group, the Illinois often lived in longhouses and wigwams, according to the season and resources that were available to them in the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cahokia Tribe
__NOTOC__ The Cahokia ( mia, kahokiaki) were an Algonquian-speaking Native American tribe and member of the Illinois Confederation; their territory was in what is now the Midwestern United States in North America. As a member of the Illinois Confederation, the Cahokia were likely similar to other Illinois groups in culture, economy, and technology. At the time of European contact with the Illini, the peoples were located in what would later be organized as the states of Illinois, Iowa, Missouri, and Arkansas. After coming upon a complex of monumental earthwork mounds in southern Illinois, the Europeans named the site after the historic Cahokia tribe, then present in the vicinity. But scholars do not believe the tribe was related to the builders of Cahokia Mounds; the site had been abandoned by Native Americans for centuries. French missionaries built two missions as part of their proselytizing of the Cahokia: the Tamaroa/Cahokia mission in 1699 CE and the River L’Abbė m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
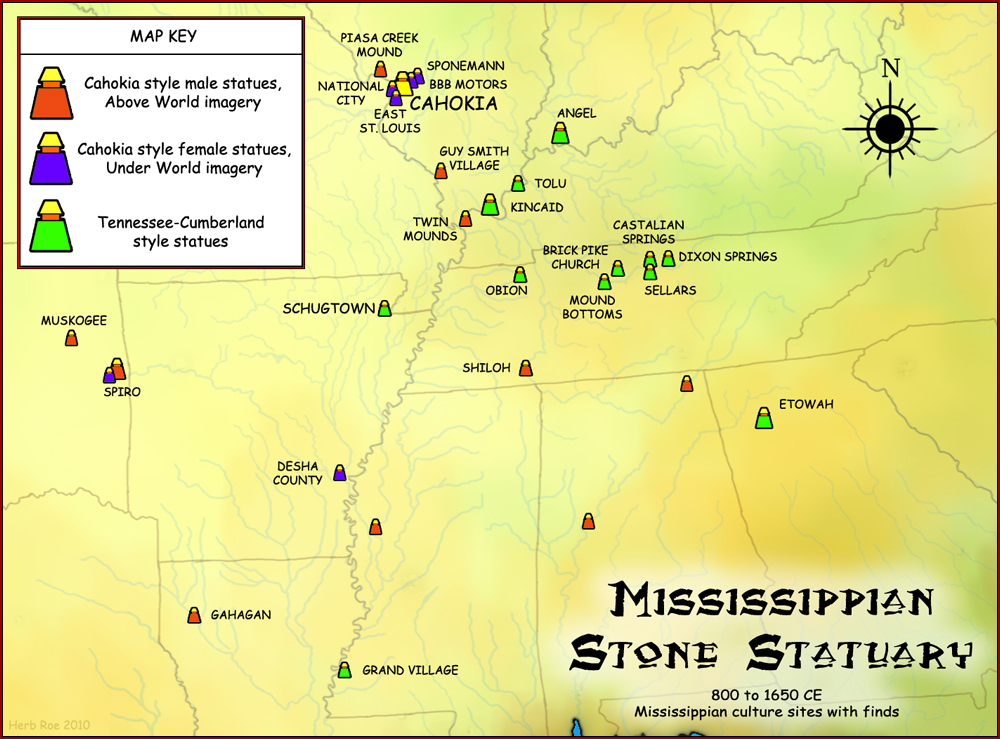
Mississippian Stone Statuary
The Mississippian stone statuary are artifacts of polished stone in the shape of human figurines made by members of the Mississippian culture (800 to 1600 CE) and found in archaeological sites in the American Midwest and Southeast. Two distinct styles exist; the first is a style of carved flint clay found over a wide geographical area but believed to be from the American Bottom area and manufactured at the Cahokia site specifically; the second is a variety of carved and polished locally available stone primarily found in the Tennessee-Cumberland region and northern Georgia (although there are lone outliers of this style in other regions). Early European explorers reported seeing stone and wooden statues in native temples, but the first documented modern discovery was made in 1790 in Kentucky, and given as a gift to Thomas Jefferson. History Archaeologists have divided what is known about Mississippian culture religious practices into three major "cult" manifestations. The '' Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Woodland Period
In the classification of archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 BCE to European contact in the eastern part of North America, with some archaeologists distinguishing the Mississippian period, from 1000 CE to European contact as a separate period. The term "Woodland Period" was introduced in the 1930s as a generic term for prehistoric sites falling between the Archaic hunter-gatherers and the agriculturalist Mississippian cultures. The Eastern Woodlands cultural region covers what is now eastern Canada south of the Subarctic region, the Eastern United States, along to the Gulf of Mexico. This period is variously considered a developmental stage, a time period, a suite of technological adaptations or "traits", and a "family tree" of cultures related to earlier Archaic cultures. It can be characterized as a chronological and cultural manifestation without any massive changes in a shor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Archaic Period
In the classification of the archaeological cultures of North America, the Archaic period in North America, taken to last from around 8000 to 1000 BC in the sequence of North American pre-Columbian cultural stages, is a period defined by the ''archaic stage'' of cultural development. The Archaic stage is characterized by subsistence economies supported through the exploitation of nuts, seeds, and shellfish. As its ending is defined by the adoption of sedentary farming, this date can vary significantly across the Americas. The rest of the Americas also have an Archaic Period. Classifications This classification system was first proposed by Gordon Willey and Philip Phillips in the widely accepted 1958 book ''Method and Theory in American Archaeology''. In the organization of the system, the Archaic period followed the Lithic stage and is superseded by the Formative stage. # The Lithic stage # The Archaic stage # The Formative stage # The Classic stage # The Post-Classic stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippian Cultures HRoe 2010
Mississippian may refer to: *Mississippian (geology), a subperiod of the Carboniferous period in the geologic timescale, roughly 360 to 325 million years ago *Mississippian culture, a culture of Native American mound-builders from 900 to 1500 AD *Mississippian Railway, a short line railroad *A native of Mississippi Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ... See also * Mississippi (other) {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USA Today
''USA Today'' (stylized in all uppercase) is an American daily middle-market newspaper and news broadcasting company. Founded by Al Neuharth on September 15, 1982, the newspaper operates from Gannett's corporate headquarters in Tysons, Virginia. Its newspaper is printed at 37 sites across the United States and at five additional sites internationally. The paper's dynamic design influenced the style of local, regional, and national newspapers worldwide through its use of concise reports, colorized images, Infographic, informational graphics, and inclusion of popular culture stories, among other distinct features. With an average print circulation of 159,233 as of 2022, a digital-only subscriber base of 504,000 as of 2019, and an approximate daily readership of 2.6 million, ''USA Today'' is ranked as the first by circulation on the list of newspapers in the United States. It has been shown to maintain a generally center-left audience, in regards to political persuasion. ''US ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Institute Of Architects
The American Institute of Architects (AIA) is a professional organization for architects in the United States. Headquartered in Washington, D.C., the AIA offers education, government advocacy, community redevelopment, and public outreach to support the architecture profession and improve its public image. The AIA also works with other members of the design and construction community to help coordinate the building industry. The AIA is currently headed by Lakisha Ann Woods, CAE, as EVP/Chief Executive Officer and Dan Hart, FAIA, as 2022 AIA President. History The American Institute of Architects was founded in New York City in 1857 by a group of 13 architects to "promote the scientific and practical perfection of its members" and "elevate the standing of the profession." This initial group included Cornell University Architecture Professor Charles Babcock, Henry W. Cleaveland, Henry Dudley, Leopold Eidlitz, Edward Gardiner, Richard Morris Hunt, Detlef Lienau, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of World Heritage Sites In The United States
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) World Heritage Sites are places of importance to cultural or natural heritage as described in the UNESCO World Heritage Convention, established in 1972. Cultural heritage consists of monuments (such as architectural works, monumental sculptures, or inscriptions), groups of buildings, and sites (including archaeological sites). Natural features (consisting of physical and biological formations), geological and physiographical formations (including habitats of threatened species of animals and plants), and natural sites which are important from the point of view of science, conservation, or natural beauty, are defined as natural heritage. The United States accepted the convention on December 7, 1973. , there are 24 World Heritage Sites in the United States, with a further 19 on the tentative list. The first sites in the United States added to the list were Mesa Verde National Park and Yellowstone Nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)