|
Caecinia Gens
The gens Caecinia was a plebeian family of Etruscan origin at ancient Rome. Members of this gens are first mentioned in the time of Cicero, and they remained prominent through the first century of the Empire, before fading into obscurity in the time of the Flavian emperors. A family of this name rose to prominence once more at the beginning of the fifth century.''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology'', vol. I, p. 529 (" Caecina"). Origin The Etruscan roots of the Caecinae are indicated by the form of their nomen, which in the masculine form ends in ', typical of Etruscan names. The feminine form, ''Caecinia'', is formed as though the masculine form were ''Caecinius'', which is also encountered, though rarely, in inscriptions. The Caecinae seem either to have derived their name from, or given it to, the river Caecina, which flows by the town of Volaterrae, one of the ancient cities of Etruria. A sepulchre belonging to the Caecinae has been discovered near V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plebeian
In ancient Rome, the plebeians (also called plebs) were the general body of free Roman citizens who were not patricians, as determined by the census, or in other words "commoners". Both classes were hereditary. Etymology The precise origins of the group and the term are unclear, but may be related to the Greek, ''plēthos'', meaning masses. In Latin, the word is a singular collective noun, and its genitive is . Plebeians were not a monolithic social class. Those who resided in the city and were part of the four urban tribes are sometimes called the , while those who lived in the country and were part of the 31 smaller rural tribes are sometimes differentiated by using the label . ( List of Roman tribes) In ancient Rome In the annalistic tradition of Livy and Dionysius, the distinction between patricians and plebeians was as old as Rome itself, instituted by Romulus' appointment of the first hundred senators, whose descendants became the patriciate. Modern hypotheses d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sextus (praenomen)
''Sextus'' () is a Latin ''praenomen'', or personal name, which was common throughout all periods of Roman history. It was used by both patrician and plebeian families, and gave rise to the patronymic ''gentes Sextia'' and '' Sextilia''. The feminine form is ''Sexta''. The name was regularly abbreviated Sex., but occasionally is found abbreviated S. (usually used for the praenomen ''Spurius''), or Sext.''Dictionary of Greek & Roman Biography & Mythology'' ''Sextus'' was about the tenth most-common praenomen for most of Roman history, although it became slightly more common in imperial times, as other praenomina declined in popularity. Many families did not use it, but it was widespread amongst all social classes, and was favored by some families. The name survived the collapse of Roman civil institutions in the 5th and 6th centuries, and has continued in use into modern times. Origin and meaning of the name ''Sextus'' is the Latin word for ''sixth'', and it falls into a class of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aulus Caecina Paetus
Aulus Caecina Paetus (died AD 42) was a Roman senator, who was condemned to death for his role in the revolt of Lucius Arruntius Camillus Scribonianus against the emperor Claudius. He was suffect consul in the ''nundinium'' of September to December 37 with Gaius Caninius Rebilus as his colleague. When the sentence was handed down, it was determined that he would be allowed to kill himself rather than face the emperor's wrath. However, when the time came, Paetus wavered in his resolution to do so. His wife Arria stabbed herself first in order to give him the courage to do this and handed him the dagger saying "''Non dolet, Paete!''" ("It doesn't hurt, Paetus!")Pliny, ''Letters'3.16 Tacitus, ''Annals'16.34 Cassius Diobr>60.16.5–6 Martialbr>1.13.5 Paetus and Arria had several children together. Those who survived to adulthood included: * Gaius Laecanius Bassus Caecina Paetus, suffect consul in 70, and adopted by Gaius Laecanius Bassus; * Caecina Arria, wife of Publius Clodius Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherusci
The Cherusci were a Germanic tribe that inhabited parts of the plains and forests of northwestern Germany in the area of the Weser River and present-day Hanover during the first centuries BC and AD. Roman sources reported they considered themselves kin with other Irmino tribes and claimed common descent from an ancestor called Mannus. During the early Roman Empire under Augustus, the Cherusci first served as allies of Rome and sent sons of their chieftains to receive Roman education and serve in the Roman army as auxiliaries. The Cherusci leader Arminius led a confederation of tribes in the ambush that destroyed three Roman legions in the Teutoburg Forest in AD9. He was subsequently kept from further damaging Rome by disputes with the Marcomanni and reprisal attacks led by Germanicus. After rebel Cherusci killed Arminius in AD21, infighting among the royal family led to the highly Romanized line of his brother Flavus coming to power. Following their defeat by the Chatti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanicus
Germanicus Julius Caesar (24 May 15 BC – 10 October AD 19) was an ancient Roman general, known for his campaigns in Germania. The son of Nero Claudius Drusus and Antonia the Younger, Germanicus was born into an influential branch of the patrician '' gens Claudia''. The agnomen ''Germanicus'' was added to his full name in 9 BC when it was posthumously awarded to his father in honour of his victories in Germania. In AD 4, he was adopted by his paternal uncle Tiberius, who succeeded Augustus as Roman emperor a decade later. As a result, Germanicus became an official member of the ''gens Julia'', another prominent family, to which he was related on his mother's side. His connection to the Julii was further consolidated through a marriage between himself and Agrippina the Elder, a granddaughter of Augustus. He was also the father of Caligula, the maternal grandfather of Nero, and the older brother of Claudius. During the reign of Augustus, Germanicus enjoyed an accelerated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legatus
A ''legatus'' (; anglicised as legate) was a high-ranking Roman military officer in the Roman Army The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval contin ..., equivalent to a modern high-ranking general officer. Initially used to delegate power, the term became formalised under Augustus as the officer in command of a Roman legion, legion. From the times of the Roman Republic, legates received large shares of the military's rewards at the end of a successful campaign. This made the position a lucrative one, so it could often attract even distinguished consuls or other high-ranking political figures within Roman politics (e.g., the Roman consul, consul Lucius Julius Caesar (consul 64 BC), Lucius Julius Caesar volunteered late in the Gallic Wars as a legate under his first cousin, Julius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aulus Caecina Severus (consul 1 BC)
Aulus Caecina Severus was a Roman politician and general who was consul in 1 BC. He was Emperor Augustus' representative in Moesia when the Great Illyrian Revolt broke out. As a result, he spent 4 years in heavy fighting against the Illyrian tribes before the revolt was suppressed by the Romans. In 14 AD he was in charge of several legions on the lower Rhine which mutinied on the death of Augustus. He was recorded as having handled this poorly, with the situation only being salvaged by the intervention of his commander-in-chief, Germanicus. Over the next two years, while campaigning in Germany, Caecina led his legions with skill and verve. At the conclusion of one hard-fought battle he famously routed the army of Arminius, who seven years earlier had destroyed three Roman legions. He was eulogised by the chroniclers for his exploits. On his return to Rome he was awarded triumph honours. Biography Aulus Caecina Severus was descended from a distinguished Volaterran family of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Principate, which is the first phase of the Roman Empire, and Augustus is considered one of the greatest leaders in human history. The reign of Augustus initiated an imperial cult as well as an era associated with imperial peace, the '' Pax Romana'' or '' Pax Augusta''. The Roman world was largely free from large-scale conflict for more than two centuries despite continuous wars of imperial expansion on the empire's frontiers and the year-long civil war known as the " Year of the Four Emperors" over the imperial succession. Originally named Gaius Octavius, he was born into an old and wealthy equestrian branch of the plebeian ''gens'' Octavia. His maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar was assassinated in 44 BC, and Octavius was named in Caes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seneca The Younger
Lucius Annaeus Seneca the Younger (; 65 AD), usually known mononymously as Seneca, was a Stoicism, Stoic philosopher of Ancient Rome, a statesman, dramatist, and, in one work, satirist, from the post-Augustan age of Latin literature. Seneca was born in Kingdom of Córdoba, Córdoba in Hispania, and raised in Rome, where he was trained in rhetoric and philosophy. His father was Seneca the Elder, his elder brother was Lucius Junius Gallio Annaeanus, and his nephew was the poet Lucan. In AD 41, Seneca was exiled to the island of Corsica under emperor Claudius, but was allowed to return in 49 to become a tutor to Nero. When Nero became emperor in 54, Seneca became his advisor and, together with the praetorian prefect Sextus Afranius Burrus, provided competent government for the first five years of Nero's reign. Seneca's influence over Nero declined with time, and in 65 Seneca was forced suicide, forced to take his own life for alleged complicity in the Pisonian conspiracy to Assassin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' Naturalis Historia'' (''Natural History''), which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. His nephew, Pliny the Younger, wrote of him in a letter to the historian Tacitus: Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume work ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus and Suetonius. Tacitus—who many scholars agree had never travelled in Germania—used ''Bella Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
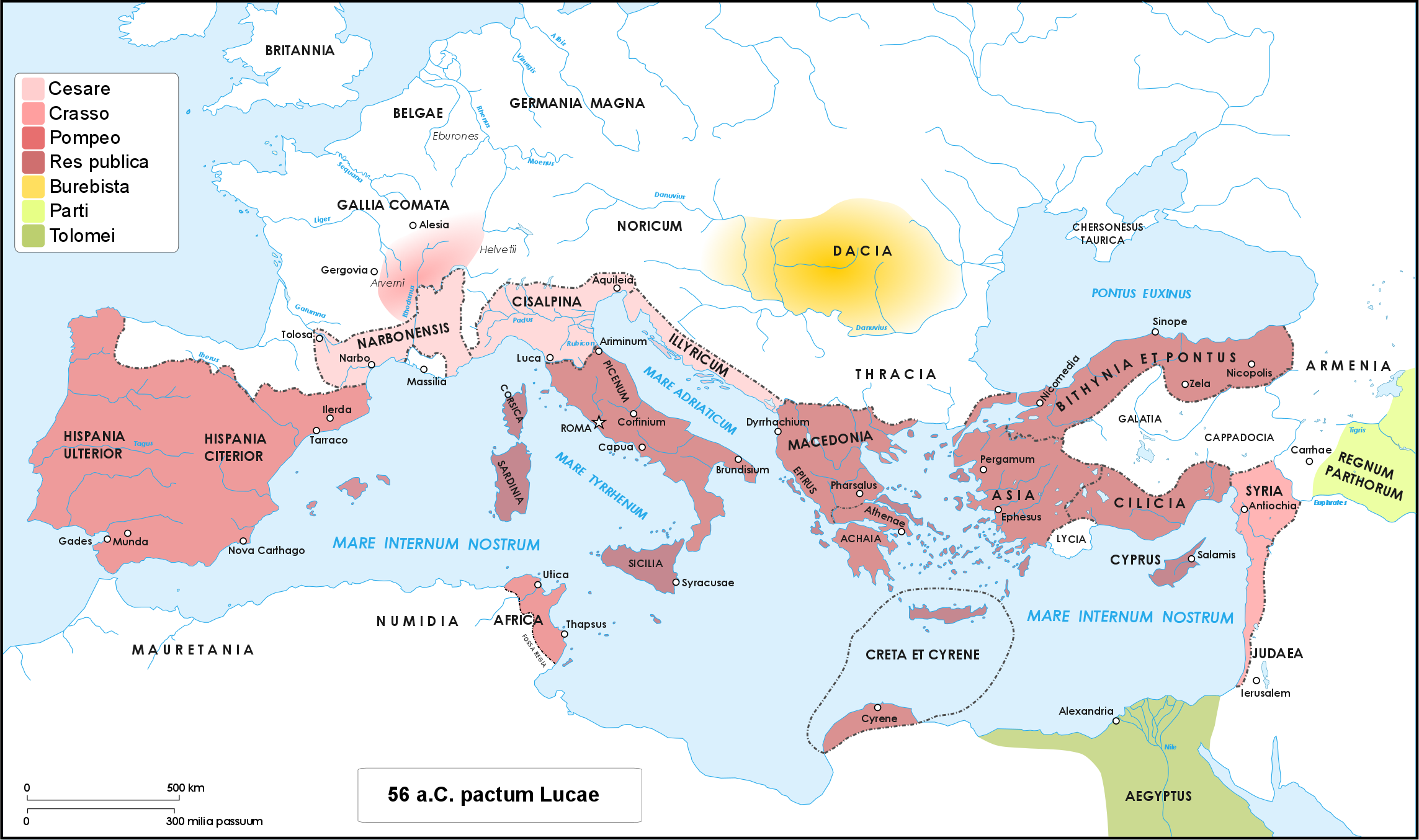
Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was one of the last politico-military conflicts of the Roman Republic before its reorganization into the Roman Empire. It began as a series of political and military confrontations between Gaius Julius Caesar and Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus. Before the war, Caesar had led an invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 49 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down led, however, to the outbreak of civil war. Eventually, Pompey and his allies induced the Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies. Caesar refused and instead marched on Rome. The war was a four-year-long politico-military struggle, fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece, Egypt, Africa, and Hispania. Pompey defeated Caesar in 48 BC at the Battle of Dyrrhachium, but was himself defeated decisively at the Battle of Pharsalus. Many former Pompeians, including Marcus Junius Brutus and Cicero, surrendered after the battle, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and subsequently became dictator from 49 BC until his assassination in 44 BC. He played a critical role in the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Crassus and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass power as were opposed by the within the Roman Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the frequent support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the Gallic Wars, completed by 51 BC, which greatly extended Roman territory. During this time he both invaded Britain and built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |