|
Cadralazine
Cadralazine is an antihypertensive of the hydrazinophthalazine chemical class Chemical classification systems attempt to classify elements or compounds according to certain chemical functional or structural properties. Whereas the structural properties are largely intrinsic, functional properties and the derived classi .... References Secondary alcohols Carbamates Hydrazides Pyridazines Ethyl esters {{antihypertensive-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridazines
Pyridazine is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound with the molecular formula . It contains a six-membered Ring (chemistry), ring with two adjacent nitrogen atoms. It is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 208 °C. It is Structural isomer, isomeric with two other diazine () rings, pyrimidine and pyrazine. Occurrence Pyridazines are rare in nature, possibly reflecting the scarcity of naturally occurring hydrazines, common building blocks for the synthesis of these heterocycles. The pyridazine structure is a popular pharmacophore which is found within a number of herbicides such as credazine, pyridafol and pyridate. It is also found within the structure of several drugs such as cefozopran, cadralazine, minaprine, pipofezine, and hydralazine. Synthesis In the course of his classic investigation on the Fischer indole synthesis, Emil Fischer prepared the first pyridazine via the condensation of phenylhydrazine and levulinic acid. The parent heterocycle was first pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antihypertensive
Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure). Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke, heart failure, kidney failure and myocardial infarction. Evidence suggests that a reduction of blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34% and of ischaemic heart disease by 21%. It can reduce the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. There are many classes of antihypertensives, which lower blood pressure by different means. Among the most important and most widely used medications are thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors), angiotensin II receptor blockers or antagonists (ARBs), and beta blockers. Which type of medication to use initially for hypertension has been the subject of several large studies and resulting national guidelines. The fundamental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazinophthalazine
Hydrazinophthalazines are a class of antihypertensive drugs characterized by a phthalazine ring system with a hydrazine group attached. The most notable member of this class is hydralazine, a medication used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure. Hydrazinophthalazines act as direct-acting smooth muscle relaxants, primarily affecting resistance arterioles to cause vasodilation. This pharmacological action results in decreased peripheral resistance and lowered blood pressure. While hydralazine is the most well-known compound in this class, other related drugs such as dihydralazine also belong to the hydrazinophthalazine family and exhibit similar antihypertensive properties. These compounds have been in clinical use since the mid-20th century, with hydralazine being discovered in the 1940s and approved by the FDA in 1953. Examples include: *Hydralazine * Dihydralazine *Cadralazine * Endralazine Chemically, the latter two aren't phthalazines; but they are classified as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Class
Chemical classification systems attempt to classify elements or compounds according to certain chemical functional or structural properties. Whereas the structural properties are largely intrinsic, functional properties and the derived classifications depend to a certain degree on the type of chemical interaction partners on which the function is exerted. Sometimes other criteria like purely physical ones (e.g. molecular weight) or – on the other hand – functional properties above the chemical level are also used for building chemical taxonomies. Some systems mix the various levels, resulting in hierarchies where the domains are slightly confused, for example having structural and functional aspects end up on the same level. Whereas chemical function is closely dependent on chemical structure, the situation becomes more involved when e.g. pharmacological function is integrated, because the QSAR can usually not be directly computed from structural qualities. Physico-ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol (), is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol, to complex, like sugar alcohols and cholesterol. The presence of an OH group strongly modifies the properties of hydrocarbons, conferring hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. The OH group provides a site at which many reactions can occur. History The flammable nature of the exhalations of wine was already known to ancient natural philosophers such as Aristotle (384–322 BCE), Theophrastus (–287 BCE), and Pliny the Elder (23/24–79 CE). However, this did not immediately lead to the isolation of alcohol, even despite the development of more advanced distillation techniques in second- and third-century Roman Egypt. An important recognition, first found in one of the writings attributed to Jābir ibn Ḥayyān (ninth century CE), was that by adding salt to boiling win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
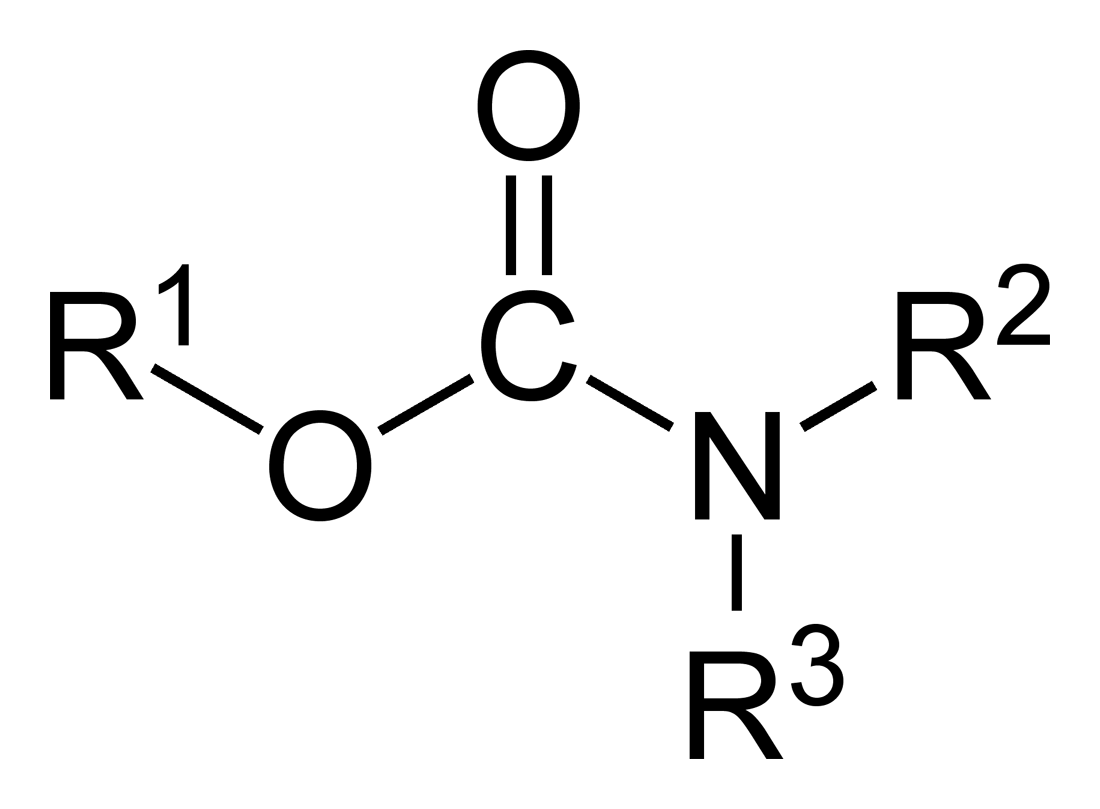
Carbamates
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose repeat units are joined by carbamate like groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. See for clarification. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters and salts are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbonate is not. Adding a calcium salt to an ammonium carbamate/carbonate solution will precipitate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |