|
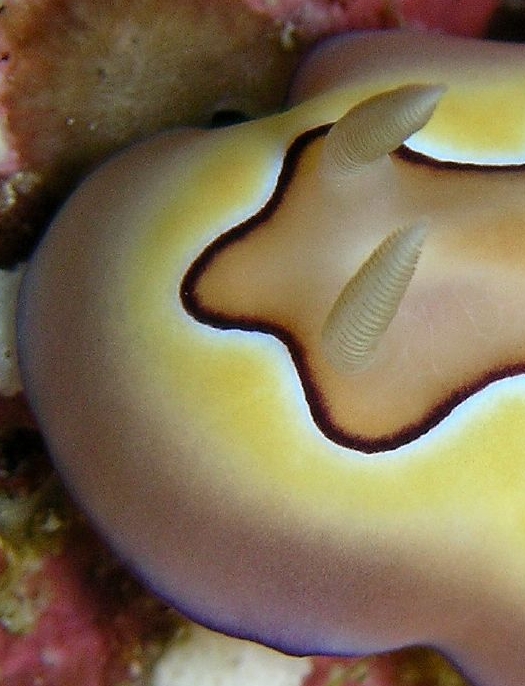
Cadlina Rumia
''Cadlina rumia'' is a species of sea slug or dorid nudibranch, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Cadlinidae.Rudman W. B. (1984). "The Chromodorididae (Opisthobranchia: Mollusca) of the Indo-West Pacific: a review of the genera". ''Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society'' 81(2/3): 115-273. page: 243 Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=532477 on 2012-02-29. Distribution Distribution of ''Cadlina rumia'' is amphiatlantic (occurring in Western Atlantic and in Eastern Atlantic). Distribution in Western Atlantic includes: Florida, Belize, Panama, Venezuela, Bahamas, Dominican Republic, Jamaica, Puerto Rico, Curaçao, St. Maarten/St. Martin, St. Lucia, St. Vincent & the Grenadines, Grenada, Brazil and Panama. This is the only species of ''Cadlina'' in the tropical western Atlantic. Distribution in Eastern Atlantic includes: ... Description Its body is oval and flat, covered with numerous small tubercle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Gustav Gotthelf Marcus
Ernst Gustav Gotthelf Marcus (8 June 1893 – 30 June 1968) was a German zoologist, former occupant of the chair of zoology at the University of São Paulo from 1936 to 1963, and co-founder of the Oceanographic Institute of the University of São Paulo. Life Marcus was born in Berlin in a Jewish family, the son of Georg Marcus, a jurist, and Regina Schwartz. As a child, he lived near the Berlin Zoo, where he observed all kinds of animals, and collected beetles. He studied at the Kaiser Friedrich Gymnasium and later entered the Friedrich Wilhelm University to study zoology. He began his doctoral studies in the Entomology Department at the Berlin Museum and, in 1914, he published his first zoological work. However, his studies were later delayed due to World War I, where he fought as a soldier, and his second work, a thesis on Coleoptera, was published only in 1919, when he received his doctorate. After graduation, he continued to work at the museum and was assigned to the Bryozoa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
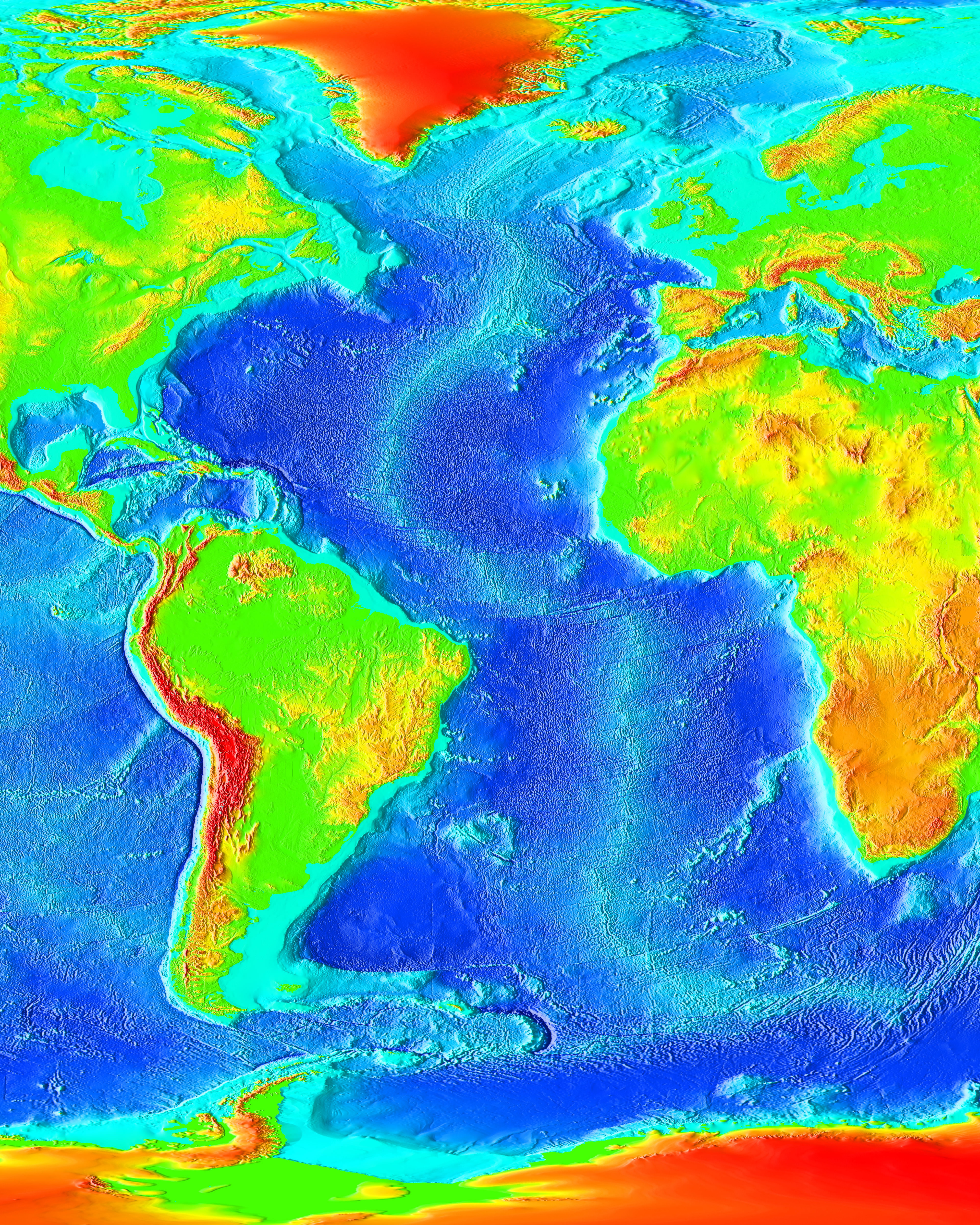
Eastern Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N. Scientific explorations of the Atlantic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scopalina
''Scopalina'' is a genus of sponges belonging to the family Scopalinidae. The genus has almost cosmopolitan distribution In biogeography, cosmopolitan distribution is the term for the range of a taxon that extends across all or most of the world in appropriate habitats. Such a taxon, usually a species, is said to exhibit cosmopolitanism or cosmopolitism. The ext .... Species: *'' Scopalina agoga'' *'' Scopalina australiensis'' *'' Scopalina azurea'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q4116937 Heteroscleromorpha Sponge genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callyspongia
''Callyspongia'' is a genus of demosponges Demosponges (Demospongiae) are the most diverse class in the phylum Porifera. They include 76.2% of all species of sponges with nearly 8,800 species worldwide (World Porifera Database). They are sponges with a soft body that covers a hard, ... in the family Callyspongiidae. Species The following species are recognised in the genus ''Callyspongia'': Subgenus ''Callyspongia (Callyspongia)'' Duchassaing & Michelotti, 1864 Subgenus ''Callyspongia (Cavochalina)'' Carter, 1885 Subgenus ''Callyspongia (Cladochalina)'' Schmidt, 1870 Subgenus ''Callyspongia (Euplacella)'' Lendenfeld, 1887 Subgenus ''Callyspongia (Toxochalina)'' Ridley, 1884 Subgenus unassigned References Callyspongiidae Sponge genera {{Demospongiae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haliclona
''Haliclona'' is a genus of demosponges in the family Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ... Chalinidae. Species The following species are recognised in the genus ''Haliclona'': ;Subgenus Haliclona (Flagellia) Van Soest, 2017 * '' Haliclona (Flagellia) amirantensis'' Van Soest, 2017 * '' Haliclona (Flagellia) anataria'' (Lévi & Lévi, 1983) * '' Haliclona (Flagellia) edaphus'' De Laubenfels, 1930 * '' Haliclona (Flagellia) flagellifera'' (Ridley & Dendy, 1886) * '' Haliclona (Flagellia) hajdui'' Van Soest, 2017 * '' Haliclona (Flagellia) hamata'' (Thiele, 1903) * '' Haliclona (Flagellia) hentscheli'' Van Soest, 2017 * '' Haliclona (Flagellia) hiberniae'' Van Soest, 2017 * '' Haliclona (Flagellia) indonesiae'' Van Soest, 2017 * '' Haliclona (Flagellia) porosa'' (Fri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysidea Etheria
''Dysidea etheria'', commonly known as the ethereal sponge or heavenly sponge, is a species of lobate sponge within the class Demospongiae. This marine sponge is known for its light blue color and can be found in the Caribbean as well as off the coasts of Florida and Georgia.Diaz M.C. (2011) Mangrove and coral reef sponge faunas: untold stories about shallow water Porifera in the Caribbean. In: Maldonado M., Turon X., Becerro M., Jesús Uriz M. (eds) Ancient Animals, New Challenges. Developments in Hydrobiology, vol 219. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-4688-6_15 Like all other poriferans, ''D. etheria'' is capable of both sexual and asexual reproduction. The use of spicule collection as well as chemical defenses allows D. etheria to protect itself against predators such as the zebra doris and the orange knobby star. ''D. etheria'' is also known as a host species of the invasive brittle star ''Ophiothela mirabilis.'' Lastly, various molecular biology stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spongivorous
A spongivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating animals of the phylum Porifera, commonly called sea sponges, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their diet, spongivore animals like the hawksbill turtle have developed sharp, narrow bird-like beak that allows them to reach within crevices on the reef to obtain sponges. Examples The hawksbill turtle is one of the few animals known to feed primarily on sponges. It is the only known spongivorous reptile. Sponges of various select species constitute up to 95% of the diets of Caribbean hawksbill turtle populations. '' Pomacanthus imperator'', the emperor angelfish; http://www.esajournals.org/doi/abs/10.1890/0012-9658(1998)079%5B1740:AIBSOA%5D2.0.CO;2 '' Lactophrys bicaudalis'', the spotted trunkfish; and '' Stephanolepis hispidus,'' the filefish are known spongivorous coral reef fish. The rock beauty ''Holocanthus tricolor'' is also spongivorous, with sponges making up 96% of their diet. Cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sponges
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. Sponges have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the evolutionary tree from the last common ancestor of all animals, making them the sister group of all other animals. Etymology The term ''sponge'' derives from the Ancient Greek word ( 'sponge'). Overview Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicellular, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinophores
A rhinophore is one of a pair of chemosensory club-shaped, rod-shaped or ear-like structures which are the most prominent part of the external head anatomy in sea slugs, marine gastropod opisthobranch mollusks such as the nudibranchs, sea hares (Aplysiomorpha), and sap-sucking sea slugs (Sacoglossa). Etymology The name relates to the rhinophore's function as an organ of "smell". ''Rhino-'' means nose from Ancient Greek ῥίς ''rhis'' and from its genitive ῥινός ''rhinos''. "Phore" means "to bear" from New Latin ''-phorus'' and from Greek -phoros (φορος) "bearing", a derivative of ''phérein'' (φέρειν). Function Rhinophores are scent or taste receptors, also known as chemosensory organs situated on the dorsal surface of the head. They are primarily used for distance chemoreception and rheoreception (response to water current). The "scents" detected by rhinophores are chemicals dissolved in the sea water. The fine structure and hairs of the rhinophore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N. Scientific explorations of the Atlantic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |