|
Cable Fault Location
Cable fault location is the process of locating periodic faults, such as insulation faults in cables. In this process, mobile shock discharge generators are among the devices used. Cable faults Cable faults are damage to cables which effect a resistance in the cable. If allowed to persist, this can lead to a voltage breakdown. There are different types of cable faults, which must first be classified before they can be located. The insulation of the cable plays a significant role in this. While paper-impregnated cables are particularly susceptible to external chemical and thermal influences, in high-voltage PE or XLPE cables the polyethylene insulation of the conductor is affected, leading to partial breakdowns and cracks that “eat away” the insulation. Screening faults A contact between conductor and screen generates a varying resistance. Phase faults The contact between multiple conductors generates a varying resistance. Sheath faults Sheath faults are damage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Cable
An electrical cable is an assembly of one or more wires running side by side or bundled, which is used to carry electric current. One or more electrical cables and their corresponding connectors may be formed into a ''cable assembly'', which is not necessarily suitable for connecting two devices but can be a partial product (e.g. to be soldered onto a printed circuit board with a connector mounted to the housing). Cable assemblies can also take the form of a cable tree or cable harness, used to connect many terminals together. Etymology The original meaning of ''cable'' in the electrical wiring sense was for submarine telegraph cables that were armoured with iron or steel wires. Early attempts to lay submarine cables without armouring failed because they were too easily damaged. The armouring in these early days (mid-19th century) was implemented in separate factories to the factories making the cable cores. These companies were specialists in manufacturing wire rope of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time-domain Reflectometer
A time-domain reflectometer (TDR) is an electronic instrument used to determine the characteristics of electrical lines by observing reflected waveforms. It can be used to characterize and locate faults in metallic cables (for example, twisted pair wire or coaxial cable). It can also be used to locate discontinuities in a connector, printed circuit board, or any other electrical path. Description A TDR measures reflections along a conductor. In order to measure those reflections, the TDR will transmit an incident signal onto the conductor and listen for its reflections. If the conductor is of a uniform impedance and is properly terminated, then there will be no reflections and the remaining incident signal will be absorbed at the far-end by the termination. Instead, if there are impedance variations, then some of the incident signal will be reflected back to the source. A TDR is similar in principle to radar. The impedance of the discontinuity can be determined from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Technology
Energy development is the field of activities focused on obtaining sources of energy from natural resources. These activities include production of renewable, nuclear, and fossil fuel derived sources of energy, and for the recovery and reuse of energy that would otherwise be wasted. Energy conservation and efficiency measures reduce the demand for energy development, and can have benefits to society with improvements to environmental issues. Societies use energy for transportation, manufacturing, illumination, heating and air conditioning, and communication, for industrial, commercial, and domestic purposes. Energy resources may be classified as primary resources, where the resource can be used in substantially its original form, or as secondary resources, where the energy source must be converted into a more conveniently usable form. Non-renewable resources are significantly depleted by human use, whereas renewable resources are produced by ongoing processes that can sustai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burner Device
Burner may refer to: * Gas burner, coal burner or oil burner, a mechanical device that burns a gas or liquid fuel in a controlled manner ** Laboratory gas burners: *** Bunsen burner *** Meker–Fisher burner *** Teclu burner ** Hot-air balloon device, a device to inflate a hot air balloon * Burner (rocket stage) * Burner (Burning Man), an active participant in the annual Burning Man festival and the surrounding community * ''Burner'' (Breadwinner album), 1994 * ''Burner'' (Odd Nosdam album), 2005 * Burner (comics), a fictional mutant character in the Marvel Comics Universe * Burner or stinger (medicine), a minor neurological injury suffered mostly by athletes participating in contact sports * Burner, a CD/DVD/Blu-ray recording tool; see Optical disc drive * Prepaid mobile phone used temporarily so that the user cannot be traced * Burner (mobile application) for cell phone privacy * Raleigh Burner, a 500 bc BMX bike manufactured by Rudolph Company * Slang for a linear amplifier f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Null Detector
A galvanometer is an electromechanical measuring instrument for electric current. Early galvanometers were uncalibrated, but improved versions, called ammeters, were calibrated and could measure the flow of current more precisely. A galvanometer works by deflecting a pointer in response to an electric current flowing through a coil in a constant magnetic field. Galvanometers can be thought of as a kind of actuator. Galvanometers came from the observation, first noted by Hans Christian Ørsted in 1820, that a magnetic compass's needle deflects when near a wire having electric current. They were the first instruments used to detect and measure small amounts of current. André-Marie Ampère, who gave mathematical expression to Ørsted's discovery, named the instrument after the Italian electricity researcher Luigi Galvani, who in 1791 discovered the principle of the frog galvanoscope – that electric current would make the legs of a dead frog jerk. Galvanometers have been ess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
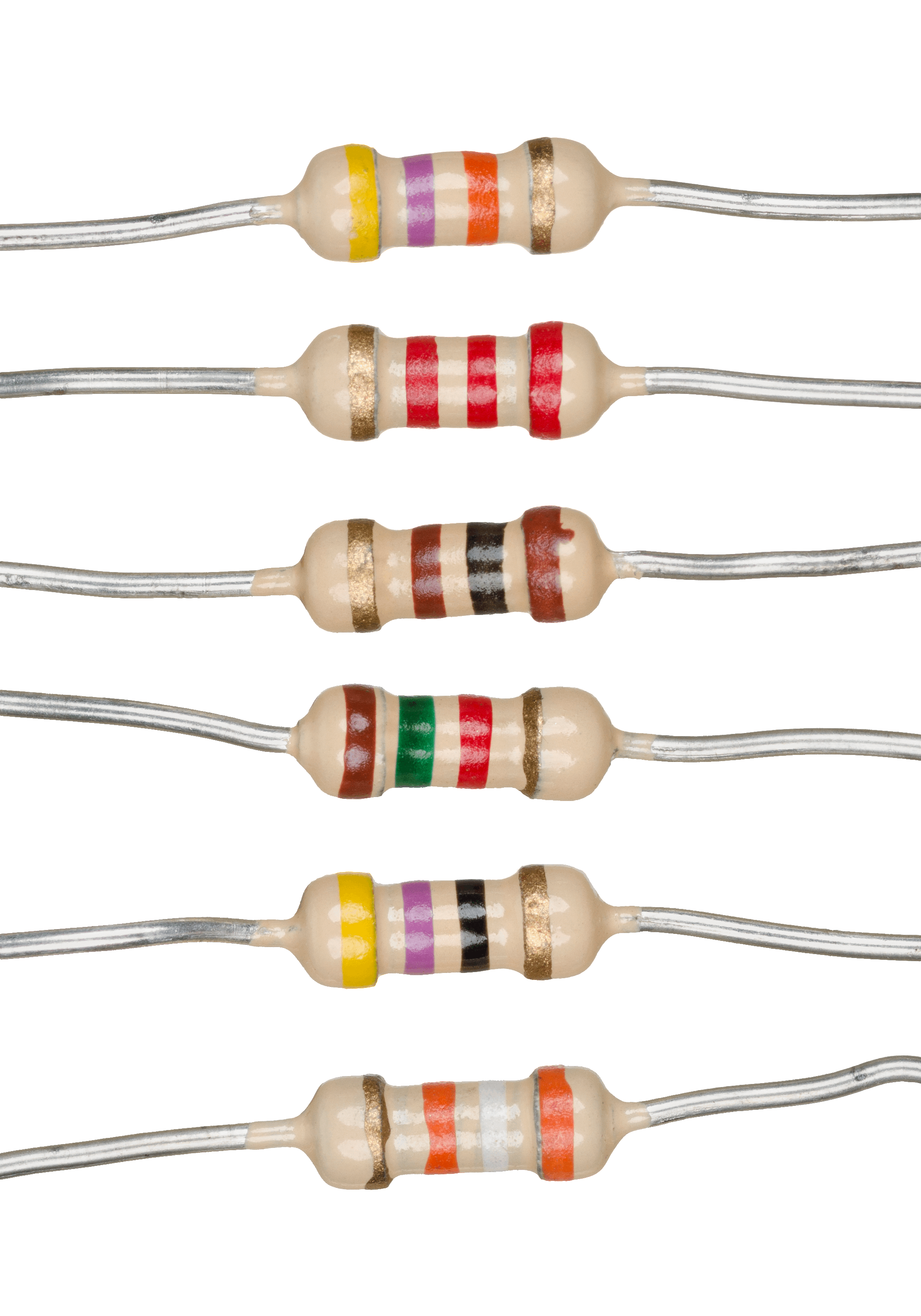
Resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Practical resistors as discrete components can be composed of various compounds and forms. Resisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murray Loop Bridge
The Murray loop bridge is a bridge circuit used for locating faults in underground or underwater Electrical cable, cables. It has been used for more than 100 yearsLatimer Clark, Robert Sabine ''Electrical tables and formulæ: for use of telegraph inspectors and operators'', E. & F.N. Spon, 1871 pp. 41-44 but is being replaced by the more precise Time-domain reflectometer. One end of the faulted cable is connected through a pair of resistors to the voltage source. Also a null detector is connected. The other end of the cable is shorted. The bridge is brought to balance by changing the values of ''RB1'' and ''RB2'', which is achieved when: \frac = \frac which is equivalent to: R_x = (R_g + R_y) \cdot \frac The value of resistance ''Rx'' is proportional the length ''Lx'', thus the location of the fault can be calculated: L_x = 2 \cdot L \cdot \frac where ''L'' is the total length of the cable under test - a value proportional to ''Rg''. The method assumes a single fault exis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Arc
An electric arc, or arc discharge, is an electrical breakdown of a gas that produces a prolonged electrical discharge. The electric current, current through a normally Electrical conductance, nonconductive medium such as air produces a plasma (physics), plasma; the plasma may produce visible light. An arc discharge is characterized by a lower voltage than a glow discharge and relies on thermionic emission of electrons from the electrodes supporting the arc. An archaic term is voltaic arc, as used in the phrase "voltaic arc lamp". Techniques for arc suppression can be used to reduce the duration or likelihood of arc formation. In the late 19th century, Arc lamp, electric arc lighting was in wide use for Street light#Arc lamps, public lighting. Some low-pressure electric arcs are used in many applications. For example, fluorescent lamp, fluorescent tubes, mercury, sodium, and metal-halide lamps are used for lighting; xenon arc lamps have been used for movie projectors. Electric a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shock Discharge Generator
Shock may refer to: Common uses Collective noun *Shock, a historic commercial term for a group of 60, see English numerals#Special names * Stook, or shock of grain, stacked sheaves Healthcare * Shock (circulatory), circulatory medical emergency ** Cardiogenic shock, resulting from dysfunction of the heart ** Distributive shock, resulting from an abnormal distribution of blood flow *** Septic shock, a result of severe infection *** Toxic shock syndrome, a specific type of severe infection *** Anaphylactic shock ** Hemorrhagic shock, from a large volume of blood loss ** Neurogenic shock, due to a high spinal cord injury disrupting the sympathetic nervous system * Cold shock response of organisms to sudden cold, especially cold water * Electric shock ** Defibrillation, electric shock to restore heart rhythm ** Electroconvulsive therapy or shock treatment, psychiatric treatment * Hydrostatic shock, from ballistic impact * Insulin shock or diabetic hypoglycemia, from too much in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Impedance
In electrical engineering, impedance is the opposition to alternating current presented by the combined effect of resistance and reactance in a circuit. Quantitatively, the impedance of a two-terminal circuit element is the ratio of the complex representation of the sinusoidal voltage between its terminals, to the complex representation of the current flowing through it. In general, it depends upon the frequency of the sinusoidal voltage. Impedance extends the concept of resistance to alternating current (AC) circuits, and possesses both magnitude and phase, unlike resistance, which has only magnitude. Impedance can be represented as a complex number, with the same units as resistance, for which the SI unit is the ohm (). Its symbol is usually , and it may be represented by writing its magnitude and phase in the polar form . However, Cartesian complex number representation is often more powerful for circuit analysis purposes. The notion of impedance is useful for perf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |