|
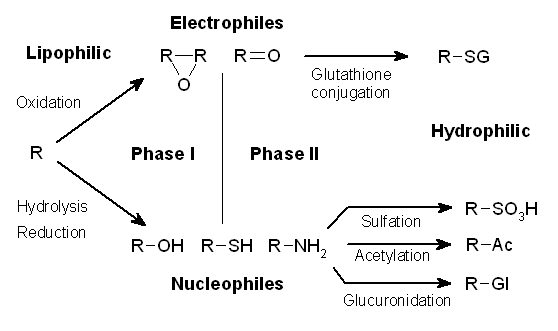
CYP26B1
Cytochrome P450 26B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CYP26B1'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases that catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and the synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. The enzyme encoded by this gene is involved in the specific inactivation of all-trans-retinoic acid to hydroxylated forms, such as 4-oxo-, 4-OH-, and 18-OH-all-trans-retinoic acid. In a developing mouse embryo, CYP26B1 is expressed in the distal tip of the forming limb bud with an abundance in the apical ectodermal ridge. In a knockout mouse model, mice manifest with severe limb malformations and die after birth due to respiratory distress. However, if the expression of CYP26B1 is conditionally deleted only prior to E9.5, the limbs are not as severely truncated and more digits are visible. Research suggests that this difference is attributable to the timing of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a Protein superfamily, superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance (pharmacology), clearance of various compounds, as well as for hormone synthesis and breakdown. In 1963, Ronald W. Estabrook, Estabrook, David Y. Cooper, Cooper, and Otto Rosenthal, Rosenthal described the role of CYP as a catalyst in steroid hormone synthesis and drug metabolism. In plants, these proteins are important for the biosynthesis of secondary metabolite, defensive compounds, fatty acids, and hormones. CYP enzymes have been identified in all kingdom (biology), kingdoms of life: animals, plants, fungus, fungi, protists, bacteria, and archaea, as well as in viruses. However, they are not omnipresent; for example, they have not been found in ''Escherichia coli''. , more than 300,000 distinct CYP proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Superfamily
A protein superfamily is the largest grouping (clade) of proteins for which common ancestry can be inferred (see homology (biology), homology). Usually this common ancestry is inferred from structural alignment and mechanistic similarity, even if no sequence similarity is evident. Sequence homology can then be deduced even if not apparent (due to low sequence similarity). Superfamilies typically contain several protein families which show sequence similarity within each family. The term ''protein clan'' is commonly used for protease and glycosyl hydrolases superfamilies based on the MEROPS and CAZy classification systems. Identification Superfamilies of proteins are identified using a number of methods. Closely related members can be identified by different methods to those needed to group the most evolutionarily divergent members. Sequence similarity Historically, the similarity of different amino acid sequences has been the most common method of inferring Sequence homology, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzymes
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' Chemical specificity, specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monooxygenase
Monooxygenases are enzymes that incorporate one hydroxyl group (−OH) into substrates in many metabolic pathways. In this reaction, the two atoms of dioxygen are reduced to one hydroxyl group and one H2O molecule by the concomitant oxidation of NAD(P)H. One important subset of the monooxygenases, the cytochrome P450 omega hydroxylases, is used by cells to metabolize arachidonic acid (i.e. eicosatetraenoic acid) to the cell signaling molecules, 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid or to reduce or totally inactivate the activate signaling molecules for example by hydroxylating leukotriene B4 to 20-hydroxy-leukotriene B5, 5-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid to 5,20-dihydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid, 5-oxo-eicosatetraenoic acid to 5-oxo-20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid, 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid to 12,20-dihydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid, and epoxyeicosatrienoic acids to 20-hydroxy-epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. Classification They are classified as oxidoreductase enzymes that catalyzes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Metabolism
Drug metabolism is the metabolic breakdown of drugs by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. More generally, xenobiotic metabolism (from the Greek xenos "stranger" and biotic "related to living beings") is the set of metabolic pathways that modify the chemical structure of xenobiotics, which are compounds foreign to an organism's normal biochemistry, such as any drug or poison. These pathways are a form of biotransformation present in all major groups of organisms and are considered to be of ancient origin. These reactions often act to detoxify poisonous compounds (although in some cases the intermediates in xenobiotic metabolism can themselves cause toxic effects). The study of drug metabolism is called pharmacokinetics. The metabolism of pharmaceutical drugs is an important aspect of pharmacology and medicine. For example, the rate of metabolism determines the duration and intensity of a drug's pharmacologic action. Drug metabolism also affects mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membranes. When chemically isolated, it is a yellowish crystalline solid. Cholesterol also serves as a precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, bile acid and vitamin D. Cholesterol is the principal sterol synthesized by all animals. In vertebrates, hepatic cells typically produce the greatest amounts. It is absent among prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), although there are some exceptions, such as '' Mycoplasma'', which require cholesterol for growth. François Poulletier de la Salle first identified cholesterol in solid form in gallstones in 1769. However, it was not until 1815 that chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul named the compound "cholesterine". Etymology The word "cholesterol" comes from the Ancient Greek ''chole-'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroids
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Hundreds of steroids are found in plants, animals and fungi. All steroids are manufactured in cells from the sterols lanosterol (opisthokonts) or cycloartenol (plants). Lanosterol and cycloartenol are derived from the cyclization of the triterpene squalene. The steroid core structure is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in four " fused" rings: three six-member cyclohexane rings (rings A, B and C in the first illustration) and one five-member cyclopentane ring (the D ring). Steroids vary by the functional groups attached to this four-ring core and by the oxidation state of the rings. Sterols are forms of steroids with a hydroxy group at position three and a skeleton derived from cholestane. '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipids
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology. Lipids may be broadly defined as hydrophobic or amphiphilic small molecules; the amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such as vesicles, multilamellar/unilamellar liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment. Biological lipids originate entirely or in part from two distinct types of biochemical subunits or "building-blocks": ketoacyl and isoprene groups. Using this approach, lipids may be divided into eight categories: fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, saccharolipids, and polyketides (derived from condensati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tretinoin
Tretinoin, also known as all-''trans'' retinoic acid (ATRA), is a medication used for the treatment of acne and acute promyelocytic leukemia. For acne, it is applied to the skin as a cream, gel or ointment. For leukemia, it is taken by mouth for up to three months. Topical tretinoin is also the most extensively investigated retinoid therapy for photoaging. Common side effects when used as a cream are limited to the skin and include skin redness, peeling, and sun sensitivity. When used by mouth, side effects include shortness of breath, headache, numbness, depression, skin dryness, itchiness, hair loss, vomiting, muscle pains, and vision changes. Other severe side effects include high white blood cell counts and blood clots. Use during pregnancy is contraindicated due to the risk of birth defects. It is in the retinoid family of medications. Tretinoin was patented in 1957, and approved for medical use in 1962. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical Ectodermal Ridge
The apical ectodermal ridge (AER) is a structure that forms from the ectodermal cells at the distal end of each limb bud and acts as a major signaling center to ensure proper development of a limb. After the limb bud induces AER formation, the AER and limb mesenchyme—including the zone of polarizing activity (ZPA)—continue to communicate with each other to direct further limb development. The position of the limb bud, and hence the AER, is specified by the expression boundaries of Hox genes in the embryonic trunk. At these positions, the induction of cell outgrowth is thought to be mediated by a positive feedback loop of fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) between the intermediate mesoderm, the lateral plate mesoderm and the surface ectoderm. FGF8 in the intermediate mesoderm signals to the lateral mesoderm, restricting the expression of FGF10 through intermediate Wnt signals. Then, FGF10 in the lateral plate mesoderm signals to the surface ectoderm to create the AER, which ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |