|
CXCL8
Interleukin 8 (IL-8 or chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 8, CXCL8) is a chemokine produced by macrophages and other cell types such as epithelial cells, airway smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells. Endothelial cells store IL-8 in their storage vesicles, the Weibel–Palade bodies. In humans, the interleukin-8 protein is encoded by the ''CXCL8'' gene. IL-8 is initially produced as a precursor peptide of 99 amino acids which then undergoes cleavage to create several active IL-8 isoforms. In culture, a 72 amino acid peptide is the major form secreted by macrophages. There are many receptors on the surface membrane capable of binding IL-8; the most frequently studied types are the G protein-coupled serpentine receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2. Expression and affinity for IL-8 differs between the two receptors (CXCR1 > CXCR2). Through a chain of biochemical reactions, IL-8 is secreted and is an important mediator of the immune reaction in the innate immune system response. Function IL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemokine
Chemokines (), or chemotactic cytokines, are a family of small cytokines or signaling proteins secreted by cells that induce directional movement of leukocytes, as well as other cell types, including endothelial and epithelial cells. In addition to playing a major role in the activation of host immune responses, chemokines are important for biological processes, including morphogenesis and wound healing, as well as in the pathogenesis of diseases like cancers. Cytokine proteins are classified as chemokines according to behavior and structural characteristics. In addition to being known for mediating chemotaxis, chemokines are all approximately 8–10 kilodaltons in mass and have four cysteine residues in conserved locations that are key to forming their 3-dimensional shape. These proteins have historically been known under several other names including the ''SIS family of cytokines'', ''SIG family of cytokines'', ''SCY family of cytokines'', ''Platelet factor-4 superfamily'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophages
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. This self-protection method can be contrasted with that employed by Natural killer cell, Natural Killer cells. This process of engulfment and digestion is called phagocytosis; it acts to defend the host against infection and injury. Macrophages are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adapti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein-coupled Receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. They are coupled with G proteins. They pass through the cell membrane seven times in the form of six loops (three extracellular loops interacting with ligand molecules, three intracellular loops interacting with G proteins, an N-terminal extracellular region and a C-terminal intracellular region) of amino acid residues, which is why they are sometimes referred to as seven-transmembrane receptors. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 2.5 Generic (CC BY 2.5) licence/ref> Ligands can bind either to the extracellular N-terminus and loops (e.g. glutamate receptors) or to the binding site wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 8 Receptor, Alpha
Interleukin 8 receptor, alpha is a chemokine receptor. This name and the corresponding gene symbol IL8RA have been replaced by the HGNC approved name C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 1 and the approved symbol CXCR1. It has also been designated as CD181 (cluster of differentiation 181). The IUPHAR Committee on Receptor Nomenclature and Drug Classification use the HGNC recommended name, CXCR1. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the G-protein-coupled receptor family. This protein is a receptor for interleukin 8 (IL8). It binds to IL8 with high affinity, and transduces the signal through a G-protein-activated second messenger system. Knockout studies in mice suggested that this protein inhibits embryonic oligodendrocyte precursor migration in developing spinal cord. IL8RA, IL8RB, which encodes another high affinity IL8 receptor, and IL8RBP, a pseudogene of IL8RB, form a gene cluster in a region mapped to chromosome 2q33-q36. Stimulation of CXCR1 in neutrophil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toll-like Receptor
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. They are single-pass membrane protein, single-spanning receptor (biochemistry), receptors usually expressed on sentinel cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells, that recognize structurally conserved molecules derived from Microorganism, microbes. Once these microbes have reached physical barriers such as the skin or intestinal tract mucosa, they are recognized by TLRs, which activate immune cell responses. The TLRs include TLR1, TLR2, TLR3, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9, TLR10, TLR11, TLR12, and TLR13. Humans lack genes for TLR11, TLR12 and TLR13 and mice lack a functional gene for TLR10. The receptors TLR1, TLR2, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6, and TLR10 are located on the cell membrane, whereas TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9 are located in Intracellular receptor, intracellular Vesicle (biology and chemistry), vesicles (because they are sensors of nucleic acids). TLRs received their name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
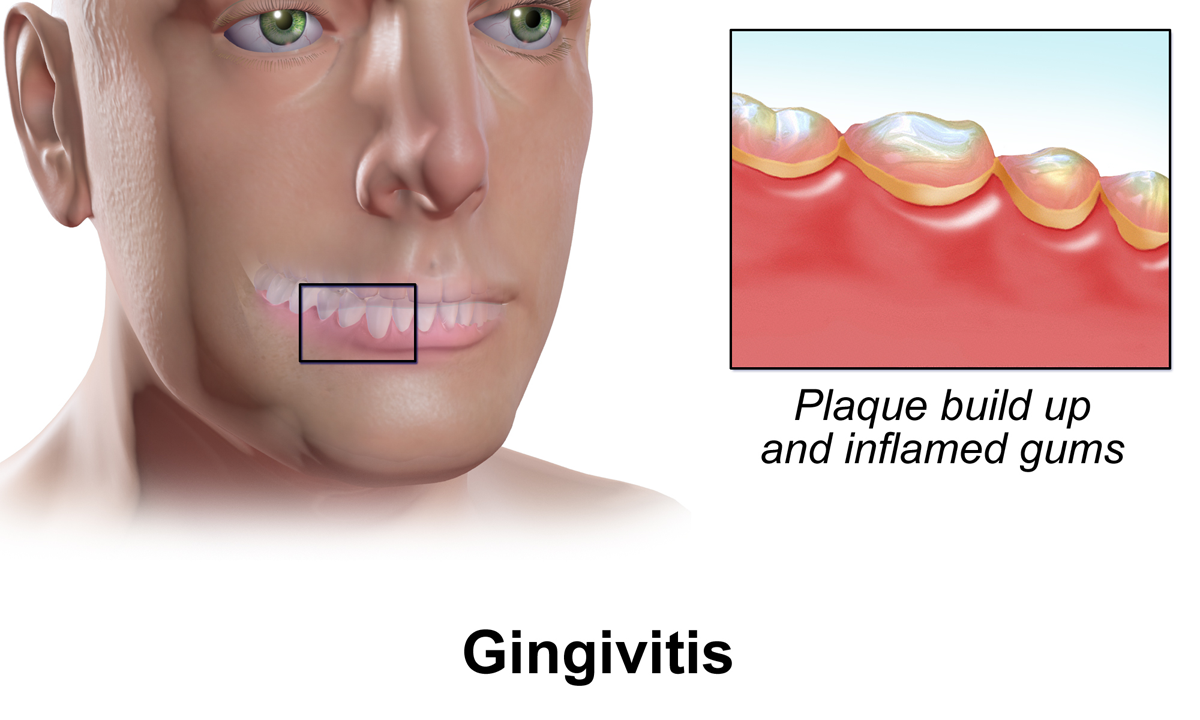
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a non-destructive disease that causes inflammation of the gums; ulitis is an alternative term. The most common form of gingivitis, and the most common form of periodontal disease overall, is in response to bacterial biofilms (also called plaque) that are attached to tooth surfaces, termed ''plaque-induced gingivitis''. Most forms of gingivitis are plaque-induced. While some cases of gingivitis never progress to periodontitis, periodontitis is always preceded by gingivitis. Gingivitis is reversible with good oral hygiene; however, without treatment, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, in which the inflammation of the gums results in tissue destruction and bone resorption around the teeth. Periodontitis can ultimately lead to tooth loss. Signs and symptoms The symptoms of gingivitis are somewhat non-specific and manifest in the gum tissue as the classic signs of inflammation: *Swollen gums *Bright red gums *Gums that are tender or painful to the touch *B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahymena
''Tetrahymena'' is a genus of free-living ciliates, examples of unicellular eukaryotes. The genus Tetrahymena is the most widely studied member of its phylum. It can produce, store and react with different types of hormones. ''Tetrahymena'' cells can recognize both related and hostile cells. They can also switch from commensalistic to pathogenic modes of survival. They are common in freshwater lakes, ponds, and streams. ''Tetrahymena'' species used as model organisms in biomedical research are '' T. thermophila'' and '' T. pyriformis''. ''T. thermophila'': a model organism in experimental biology As a ciliated protozoan, ''Tetrahymena thermophila'' exhibits nuclear dimorphism: two types of cell nuclei. They have a bigger, non-germline macronucleus and a small, germline micronucleus in each cell at the same time and these two carry out different functions with distinct cytological and biological properties. This unique versatility allows scientists to use ''Tetrahyme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratinocyte
Keratinocytes are the primary type of cell found in the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. In humans, they constitute 90% of epidermal skin cells. Basal cells in the basal layer (''stratum basale'') of the skin are sometimes referred to as basal keratinocytes. Keratinocytes form a barrier against environmental damage by heat, UV radiation, water loss, pathogenic bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses. A number of structural proteins, enzymes, lipids, and antimicrobial peptides contribute to maintain the important barrier function of the skin. Keratinocytes differentiate from epidermal stem cells in the lower part of the epidermis and migrate towards the surface, finally becoming corneocytes and eventually being shed, which happens every 40 to 56 days in humans. Function The primary function of keratinocytes is the formation of a barrier against environmental damage by heat, UV radiation, dehydration, pathogenic bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses. Pathoge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mast Cell
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a part of the immune and neuroimmune systems. Mast cells were discovered by Friedrich von Recklinghausen and later rediscovered by Paul Ehrlich in 1877. Although best known for their role in allergy and anaphylaxis, mast cells play an important protective role as well, being intimately involved in wound healing, angiogenesis, immune tolerance, defense against pathogens, and vascular permeability in brain tumors. The mast cell is very similar in both appearance and function to the basophil, another type of white blood cell. Although mast cells were once thought to be tissue-resident basophils, it has been shown that the two cells develop from different hematopoietic lineages and thus cannot be the same cells. Structure Mast cells ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrophils
Neutrophils are a type of phagocytic white blood cell and part of innate immunity. More specifically, they form the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. Their functions vary in different animals. They are also known as neutrocytes, heterophils or polymorphonuclear leukocytes. They are formed from stem cells in the bone marrow and differentiated into subpopulations of neutrophil-killers and neutrophil-cagers. They are short-lived (between 5 and 135 hours, see ) and highly mobile, as they can enter parts of tissue where other cells/molecules cannot. Neutrophils may be subdivided into segmented neutrophils and banded neutrophils (or bands). They form part of the polymorphonuclear cells family (PMNs) together with basophils and eosinophils. The name ''neutrophil'' derives from staining characteristics on hematoxylin and eosin ( H&E) histological or cytological preparations. Whereas basophilic white blood cells stain dark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |