|
CSF Tap Test
The CSF tap test, sometimes lumbar tap test or Miller Fisher Test, is a medical test that is used to decide whether shunting of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) would be helpful in a patient with suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH). The test involves removing 30-50 ml of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) through a lumbar puncture, after which motor and cognitive function is clinically reassessed. The name "Fisher test" is after C. Miller Fisher Charles Miller Fisher (December 5, 1913, Waterloo, Ontario – April 14, 2012, Albany, New York) was a Canadian neurologist whose notable contributions include the first detailed descriptions of lacunar strokes, the identification of transient ..., a Canadian neurologist working in Boston, Massachusetts, who described the test. Clinical improvement showed a high predictive value for subsequent success with shunting. A "negative" test has a very low predictive accuracy, as many patients may improve after a shunt in spite of lack of improveme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates. CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations. There is about 125 mL of CSF at any one time, and about 500 mL is generated every day. CSF acts as a shock absorber, cushion or buffer, providing basic mechanical and immunological protection to the brain inside the skull. CSF also serves a vital function in the cerebral autoregulation of cerebral blood flow. CSF occupies the subarachnoid space (between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater) and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord. It fills the ventricles of the brain, cisterns, and sulci, as well as the central canal of the spinal cord. There is also a connection from the subarachnoid space to the bony labyrinth of the inner ear via the perilymphat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
Normal-pressure hydrocephalus (NPH), also called malresorptive hydrocephalus, is a form of communicating hydrocephalus in which excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs in the ventricles, and with normal or slightly elevated cerebrospinal fluid pressure. As the fluid builds up, it causes the ventricles to enlarge and the pressure inside the head to increase, compressing surrounding brain tissue and leading to neurological complications. The disease presents in a classic triad of symptoms, which are memory impairment, urinary frequency, and balance problems/ gait deviations (note: this diagnosis method is obsolete). The disease was first described by Salomón Hakim and Adams in 1965. The treatment is surgical placement of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt to drain excess CSF into the lining of the abdomen where the CSF will eventually be absorbed. NPH is often misdiagnosed as other conditions including Meniere's disease due to balance problems, Parkinson's disease (due to gait) or Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
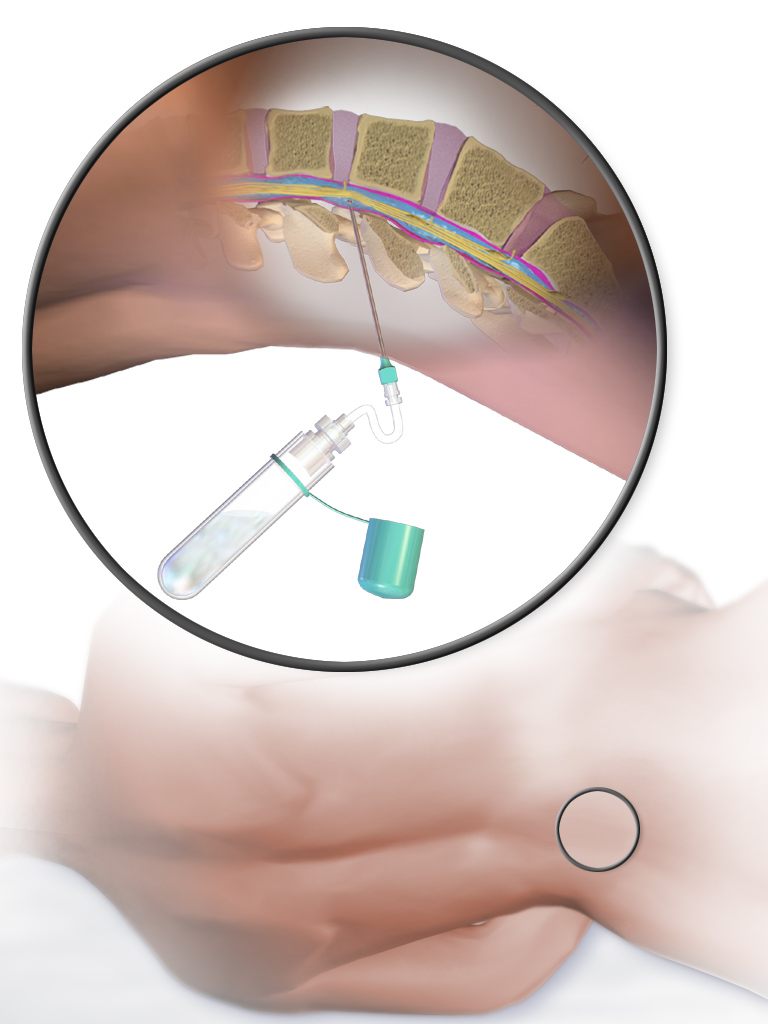
Lumbar Puncture
Lumbar puncture (LP), also known as a spinal tap, is a medical procedure in which a needle is inserted into the spinal canal, most commonly to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for diagnostic testing. The main reason for a lumbar puncture is to help diagnose diseases of the central nervous system, including the brain and spine. Examples of these conditions include meningitis and subarachnoid hemorrhage. It may also be used therapeutically in some conditions. Increased intracranial pressure (pressure in the skull) is a contraindication, due to risk of brain matter being compressed and pushed toward the spine. Sometimes, lumbar puncture cannot be performed safely (for example due to a bleeding diathesis, severe bleeding tendency). It is regarded as a safe procedure, but post-dural-puncture headache is a common side effect if a small atraumatic needle is not used. The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia using a aseptic technique, sterile technique. A hypodermic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Shunt
A cerebral shunt is a device permanently implanted inside the head and body to drain excess fluid away from the brain. They are commonly used to treat hydrocephalus, the swelling of the brain due to excess buildup of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). If left unchecked, the excess CSF can lead to an increase in intracranial pressure (ICP), which can cause intracranial hematoma, cerebral edema, crushed brain tissue or herniation. The drainage provided by a shunt can alleviate or prevent these problems in patients with hydrocephalus or related diseases. Shunts come in a variety of forms, but most of them consist of a valve housing connected to a catheter, the lower end of which is usually placed in the peritoneal cavity. The main differences between shunts are usually in the materials used to construct them, the types of valve (if any) used, and whether the valve is programmable or not. Description Valves types Shunt location The location of the shunt is determined by the neurosurg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Tests
A medical test is a medical procedure performed to detect, diagnose, or monitor diseases, disease processes, susceptibility, or to determine a course of treatment. Medical tests such as, physical and visual exams, diagnostic imaging, genetic testing, chemical and cellular analysis, relating to clinical chemistry and molecular diagnostics, are typically performed in a medical setting. Types of tests By purpose Medical tests can be classified by their purposes, the most common of which are diagnosis, screening and evaluation. Diagnostic A diagnostic test is a procedure performed to confirm or determine the presence of disease in an individual suspected of having a disease, usually following the report of symptoms, or based on other medical test results. This includes posthumous diagnosis. Examples of such tests are: * Using nuclear medicine to examine a patient suspected of having a lymphoma. * Measuring the blood sugar in a person suspected of having diabetes mellitus after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |