|
CSF Glucose
CSF glucose or glycorrhachia is a measurement used to determine the concentration of glucose in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Normal values in humans The glucose level in CSF is proportional to the blood glucose level and corresponds to 60-70% of the concentration in blood. Therefore, normal CSF glucose levels lie between 2.5 and 4.4 mmol/L (45–80 mg/dL). Abnormalities in CSF glucose concentration Low CSF glucose levels Hypoglycorrhachia (low CSF glucose levels) can be caused by CNS infections, inflammatory conditions, subarachnoid hemorrhage, hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), impaired glucose transport (e.g. GLUT1 deficiency syndrome), increased CNS glycolytic activity and metastatic carcinoma. CSF glucose levels can be useful in distinguishing among causes of meningitis as more than 50% of patients with bacterial meningitis have decreased CSF glucose levels while patients with viral meningitis usually have normal CSF glucose levels. Decrease in glucose levels during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MCnc
In chemistry, the mass concentration (or ) is defined as the mass of a constituent divided by the volume of the mixture . :\rho_i = \frac For a pure chemical the mass concentration equals its density (mass divided by volume); thus the mass concentration of a component in a mixture can be called the density of a component in a mixture. This explains the usage of (the lower case Greek letter rho), the symbol most often used for density. Definition and properties The volume in the definition refers to the volume of the solution, ''not'' the volume of the solvent. One litre of a solution usually contains either slightly more or slightly less than 1 litre of solvent because the process of dissolution causes volume of liquid to increase or decrease. Sometimes the mass concentration is called titre. Notation The notation common with mass density underlines the connection between the two quantities (the mass concentration being the mass density of a component in the solution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastatic Carcinoma
Metastatic carcinoma is cancer that is able to grow at sites distant from the primary site of origin; thus, dissemination to the skin may occur with any malignant neoplasm, and these infiltrates may result from direct invasion of the skin from underlying tumors, may extend by lymphatic or hematogenous spread, or may be introduced by therapeutic procedures.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. . The most common malignancy found in bone is metastatic carcinoma. See also *Skin lesion *Metastasis Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then ... * Carcinoma References {{Dermal-growth-stub Dermal and subcutaneous growths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSF/serum Glucose Ratio
The CSF/serum glucose ratio, also known as CSF/Blood glucose ratio, is a measurement used to compare CSF glucose CSF glucose or glycorrhachia is a measurement used to determine the concentration of glucose in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Normal values in humans The glucose level in CSF is proportional to the blood glucose level and corresponds to 60-70% of th ... and blood sugar. Because many bacteria metabolize glucose, and because the blood brain barrier minimizes transversal, the ratio can be useful in determining whether there is a bacterial infection in the CSF. The normal ratio is 0.6. It is used to distinguish between bacterial and viral meningitis, as it is often lowered in bacterial meningitis and normal in viral meningitis. References Neurology CSF tests {{med-diagnostic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Sugar
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blood of a 70 kg (154 lb) human at all times. The body tightly regulates blood glucose levels as a part of metabolic homeostasis. Glucose is stored in skeletal muscle and liver cells in the form of glycogen; in fasting individuals, blood glucose is maintained at a constant level at the expense of glycogen stores in the liver and skeletal muscle. In humans, a blood glucose level of 4 grams, or about a teaspoon, is critical for normal function in a number of tissues, and the human brain consumes approximately 60% of blood glucose in fasting, sedentary individuals. A persistent elevation in blood glucose leads to glucose toxicity, which contributes to cell dysfunction and the pathology grouped together as complications of diabetes. Gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose circulates in the blood plasma. This is generally a blood sugar level higher than 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL), but symptoms may not start to become noticeable until even higher values such as 13.9–16.7 mmol/L (~250–300 mg/dL). A subject with a consistent range between ~5.6 and ~7 mmol/L (100–126 mg/dL) ( American Diabetes Association guidelines) is considered slightly hyperglycemic, and above 7 mmol/L (126 mg/dL) is generally held to have diabetes. For diabetics, glucose levels that are considered to be too hyperglycemic can vary from person to person, mainly due to the person's renal threshold of glucose and overall glucose tolerance. On average, however, chronic levels above 10–12 mmol/L (180–216 mg/dL) can produce noticeable organ damage over time. Signs and symptoms The degree of hyperglycemia can change over time depending on the metabolic cause, for example, impaired gluco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New England Journal Of Medicine
''The New England Journal of Medicine'' (''NEJM'') is a weekly medical journal published by the Massachusetts Medical Society. It is among the most prestigious peer-reviewed medical journals as well as the oldest continuously published one. History In September 1811, John Collins Warren, a Boston physician, along with James Jackson, submitted a formal prospectus to establish the ''New England Journal of Medicine and Surgery and Collateral Branches of Science'' as a medical and philosophical journal. Subsequently, the first issue of the ''New England Journal of Medicine and Surgery and the Collateral Branches of Medical Science'' was published in January 1812. The journal was published quarterly. In 1823, another publication, the ''Boston Medical Intelligencer'', appeared under the editorship of Jerome V. C. Smith. The editors of the ''New England Journal of Medicine and Surgery and the Collateral Branches of Medical Science'' purchased the weekly ''Intelligencer'' for $600 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Meningitis
Viral meningitis, also known as aseptic meningitis, is a type of meningitis due to a viral infection. It results in inflammation of the meninges (the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord). Symptoms commonly include headache, fever, photophobia, sensitivity to light and neck stiffness. Viruses are the most common cause of aseptic meningitis. Most cases of viral meningitis are caused by enteroviruses (common stomach viruses). However, other viruses can also cause viral meningitis, such as West Nile virus, Mumps virus, mumps, Measles virus, measles, Herpes simplex virus, herpes simplex types I and II, Varicella zoster virus, varicella and lymphocytic choriomeningitis (LCM) virus. Based on clinical symptoms, viral meningitis cannot be reliably differentiated from bacterial meningitis, although viral meningitis typically follows a more benign clinical course. Viral meningitis has no evidence of bacteria present in cerebral spinal fluid (CSF). Therefore, lumbar puncture with C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion or altered consciousness, nausea, vomiting, and an inability to tolerate light or loud noises. Young children often exhibit only nonspecific symptoms, such as irritability, drowsiness, or poor feeding. A non-blanching rash (a rash that does not fade when a glass is rolled over it) may also be present. The inflammation may be caused by infection with viruses, bacteria or other microorganisms. Non-infectious causes include malignancy (cancer), subarachnoid haemorrhage, chronic inflammatory disease (sarcoidosis) and certain drugs. Meningitis can be life-threatening because of the inflammation's proximity to the brain and spinal cord; therefore, the condition is classified as a medical emergency. A lumbar puncture, in which a needle is inse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
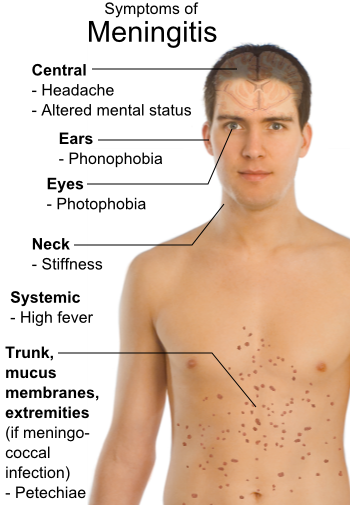
Meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion or altered consciousness, nausea, vomiting, and an inability to tolerate light or loud noises. Young children often exhibit only nonspecific symptoms, such as irritability, drowsiness, or poor feeding. A non-blanching rash (a rash that does not fade when a glass is rolled over it) may also be present. The inflammation may be caused by infection with viruses, bacteria or other microorganisms. Non-infectious causes include malignancy (cancer), subarachnoid haemorrhage, chronic inflammatory disease (sarcoidosis) and certain drugs. Meningitis can be life-threatening because of the inflammation's proximity to the brain and spinal cord; therefore, the condition is classified as a medical emergency. A lumbar puncture, in which a needle is inserte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvate (). The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes. Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that does not require oxygen (In anaerobic conditions pyruvate is converted to lactic acid). The wide occurrence of glycolysis in other species indicates that it is an ancient metabolic pathway. Indeed, the reactions that make up glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur in the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes, catalyzed by metal. In most organisms, glycolysis occurs in the liquid part of cells, the cytosol. The most common type of glycolysis is the ''Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP) pathway'', which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCnc
Molar concentration (also called molarity, amount concentration or substance concentration) is a measure of the concentration of a chemical species, in particular of a solute in a solution, in terms of amount of substance per unit volume of solution. In chemistry, the most commonly used unit for molarity is the number of moles per liter, having the unit symbol mol/L or mol/ dm3 in SI unit. A solution with a concentration of 1 mol/L is said to be 1 molar, commonly designated as 1 M. Definition Molar concentration or molarity is most commonly expressed in units of moles of solute per litre of solution. For use in broader applications, it is defined as amount of substance of solute per unit volume of solution, or per unit volume available to the species, represented by lowercase c: :c = \frac = \frac = \frac. Here, n is the amount of the solute in moles, N is the number of constituent particles present in volume V (in litres) of the solution, and N_\text is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |