|
CRH3
The CRH3 Hexie (simplified Chinese: 和谐号; traditional Chinese: 和諧號; pinyin: Héxié Hào; literally: "Harmony") is a version of the Siemens Velaro high-speed train used in China on the Beijing–Tianjin intercity railway line, Wuhan-Guangzhou Passenger Dedicated Line, Zhengzhou-Xi'an Passenger Dedicated Line and the Shanghai–Nanjing intercity railway. It is capable of service speed of as the very similar Velaro E used in Spain, but, similarly to the Sapsan, it is wider to take advantage of a more generous structure gauge and thus be able to fit in more seats in a 2+3 layout. Variants In November 2005, the Ministry of Railways ordered 60 Velaro trains for use on the Beijing–Tianjin intercity railway line. On 27 July 2006, the joint project office was opened at Tangshan. CRH3C Prototypes The first three trains were built in Germany by Siemens, and these imported trains were labelled CRH3A (CRH3-002A, CRH3-003A and CRH3-004A), different than the CRH3A-5218 de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRH3 Entering And Leaving Shaoguan Station
The CRH3 Hexie (simplified Chinese: 和谐号; traditional Chinese: 和諧號; pinyin: Héxié Hào; literally: "Harmony") is a version of the Siemens Velaro high-speed train used in China on the Beijing–Tianjin intercity railway line, Wuhan-Guangzhou Passenger Dedicated Line, Zhengzhou-Xi'an Passenger Dedicated Line and the Shanghai–Nanjing intercity railway. It is capable of service speed of as the very similar Velaro E used in Spain, but, similarly to the Sapsan, it is wider to take advantage of a more generous structure gauge and thus be able to fit in more seats in a 2+3 layout. Variants In November 2005, the Ministry of Railways ordered 60 Velaro trains for use on the Beijing–Tianjin intercity railway line. On 27 July 2006, the joint project office was opened at Tangshan. CRH3C Prototypes The first three trains were built in Germany by Siemens, and these imported trains were labelled CRH3A (CRH3-002A, CRH3-003A and CRH3-004A), different than the CRH3A-5218 de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexie (train)
Hexie (), also known as the CRH series EMU, is an umbrella term for the multiple unit High-speed rail, high-speed and Higher-speed rail, higher-speed trains operated by China Railway under the China Railway High-speed brand. All series of Hexie are based on foreign-developed technology and later manufactured locally in China through technology transfer licenses, with the ultimate goal of China acquiring the know-how and capability to produce high-speed rail trains. The Harmony series does not belong to any single platform, instead encompassing all high-speed trains in China with roots in foreign technology, specifically CRH1, CRH2, CRH3 and CRH5. Although later variants of Hexie such as CRH380A were designed by Chinese companies, they are still classified as CRH due to incorporation of foreign technology. History In 2007, China's Ministry of Railways (China), Ministry of Railways drafted a plan for China's future high-speed network. Bombardier Transportation, Kawasaki Heavy Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siemens Velaro
Siemens Velaro is a family of high-speed electric multiple unit trains built by Siemens and used in Germany, Belgium, France, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Spain, China, Russia, and Turkey. The Velaro is based on the ICE 3M/F high-speed trains manufactured by Siemens for the Deutsche Bahn (DB). The Deutsche Bahn were the first to order Siemens high-speed trains; it ordered 13 of these units in 1994, the Nederlandse Spoorwegen (NS) 4 units. The trains were delivered in 1999 for service. The trains were labeled and marketed as the Velaro by their manufacturer, Siemens. Siemens developed its Siemens Velaro based on the ICE 3M/F. Spain's RENFE was the first to order Velaro trains, known as Velaro E, for their AVE network. China ordered wider versions for the Beijing-Tianjin high-speed rail (China Railways CRH3) and Russia for the Moscow–Saint Petersburg and the Saint Petersburg–Nizhny Novgorod routes ( Velaro RUS/Сапсан). Since December 2013, the latest generation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuhan–Guangzhou High-speed Railway
The Wuhan–Guangzhou high-speed railway, also called the Wuguang high-speed railway and short for Beijing–Guangzhou–Shenzhen–Hong Kong high-speed railway, Wuhan–Guangzhou section, is a high-speed rail line, operated by China Railway High-speed (CRH), connecting Wuhan and Guangzhou, the provincial capitals of Hubei and Guangdong, respectively. It was the world's fastest train service, initially using coupled CRH2C and CRH3C trains which averages in non-stop commercial service. The line is part of the 2230-km long Beijing–Guangzhou–Shenzhen–Hong Kong high-speed railway. Since the railway line opened ten years ago, it has transported 500 million passengers and provided over 500000 train services. Rolling stock When the line opened, the trains had a maximum in-service speed of according to Chinese sources. Each train consists of two eight-car electric multiple units coupled together to make a 16-car train. The passenger capacity of the train is about 1114 (CRH3C� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanghai–Nanjing Intercity Railway
The Shanghai–Nanjing intercity railway or Huning intercity railway () is a -long high-speed rail line between Shanghai and Nanjing, the capital of Jiangsu province. and are shorthand Chinese names for Shanghai and Nanjing, respectively. The Huning intercity high-speed railway largely follows the route of the preexisting Nanjing-Shanghai section of the conventional Beijing–Shanghai railway and the Beijing–Shanghai high-speed railway. Construction of this high-speed railway began in July 2008. The line went into test operations in early April 2010, and opened for full service on July 1, 2010. The line has a design speed of . The journey time between the two cities has been shortened from 120 minutes to 73 minutes on nonstop trains. According to the arrangements of related departments, 120 pairs of trains are operating on the line, and the time interval between services is 5 minutes at the shortest. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-speed Rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail system that runs significantly faster than traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated tracks. While there is no single standard that applies worldwide, lines built to handle speeds above or upgraded lines in excess of are widely considered to be high-speed. The first high-speed rail system, the Tōkaidō Shinkansen, began operations in Japan in 1964 and was widely known as the bullet train. High-speed trains mostly operate on standard gauge tracks of continuously welded rail on grade-separated rights of way with large radii. However, certain regions with wider legacy railways, including Russia and Uzbekistan, have sought to develop a high speed railway network in Russian gauge. There are no narrow gauge high-speed trains; the fastest is the Cape gauge Spirit of Queensland at . Many countries have developed, or are currently building, high-speed rail infrastructure to connect major citie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
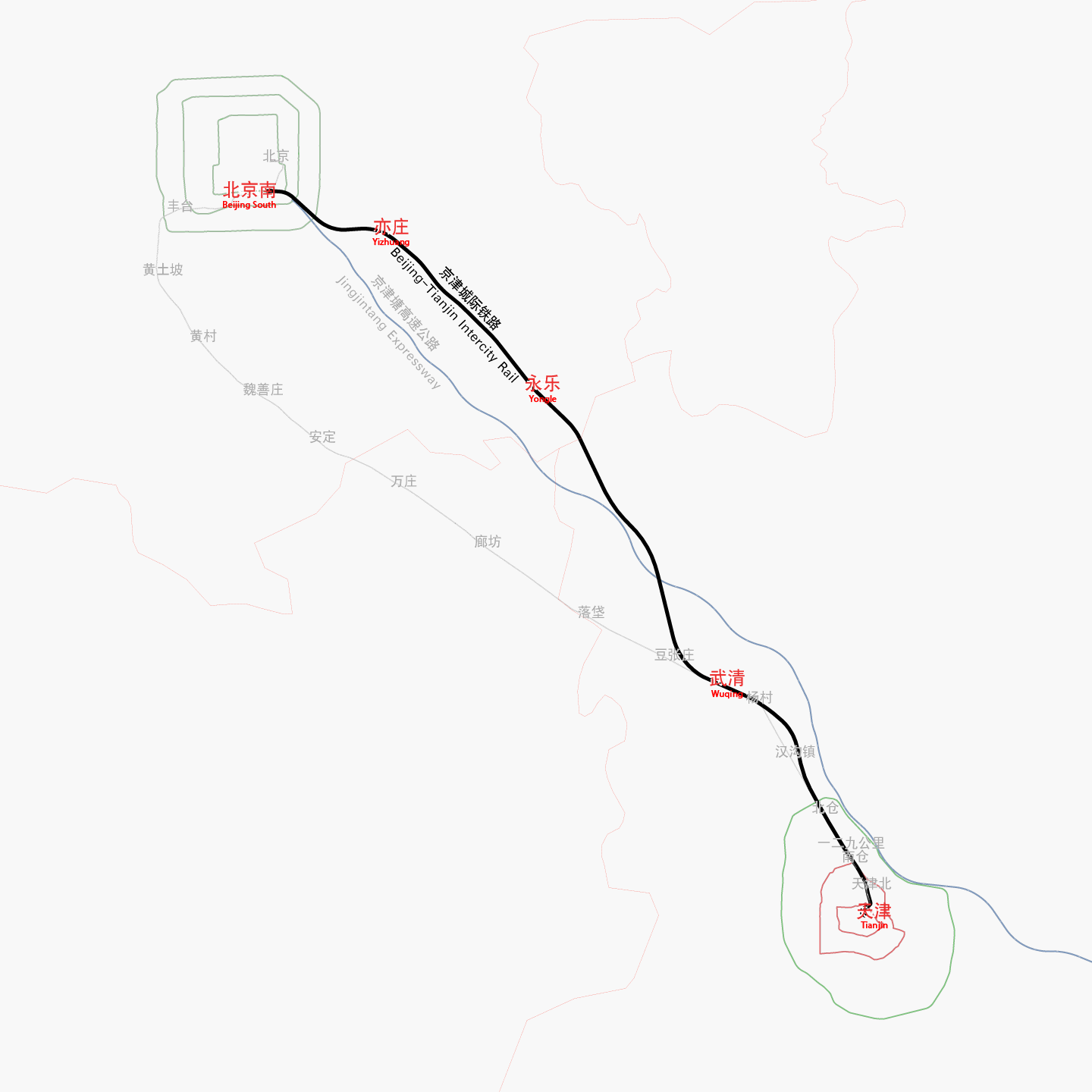
Beijing–Tianjin Intercity Railway
The Beijing–Tianjin intercity railway () is a Chinese high-speed railway that runs 117 km line (72.7 statute miles) between Beijing and Tianjin. Designed for passenger traffic only, the Chinese government built the line to accommodate trains traveling at a maximum speed of , and currently carries CRH high-speed trains running speeds up to since August 2018. When the line opened on August 1, 2008, it set the record for the fastest conventional train service in the world by top speed, and reduced travel time between the two largest cities in northern China from 70 to 30 minutes. A second phase of construction extended this line from Tianjin to Yujiapu railway station in the Binhai New Area was opened on September 20, 2015. The line is projected to approach operating capacity in the first half of 2016. Anticipating this, a second parallel line, the Beijing–Binhai intercity railway, commenced construction on December 29, 2015. It will run from Beijing Sub-Center railway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Changsha South Railway Station
Changsha South railway station () is a metro station and a railway station Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prep ... of Wuguang Passenger Railway and Hukun Passenger Railway. The station is located in :zh:黎托街道, Lituo Subdistrict, Yuhua District, Changsha, Yuhua District, Changsha, Hunan, People's Republic of China, China. It is a hub and the connecting point of Beijing–Guangzhou–Shenzhen–Hong Kong High-Speed Railway, Shanghai–Kunming High-Speed Railway and the proposed Xiamen-Changsha-Chongqing High-Speed Railway. The station was opened on 26 December 2009. It is a transportation center of high-speed railways, metro lines Line 2 (Changsha Metro), 2 & Line 4 (Changsha Metro), 4, Changsha Maglev, maglev, buses and coaches, which seamlessly connect downtown, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tangshan Railway Vehicle
CRRC Tangshan Co., Ltd., is a manufacturer of rolling stock located in Tangshan, Hebei province, People's Republic of China. While Datong built mainline steam locomotives until 1988, Tangshan built steam for industrial use until 1999, becoming the last works in the world to build steam for non-tourist use. History The predecessor of the subsidiary, Tangshan Locomotive and Rolling Stock Works was founded before the establishment of the People's Republic of China in 1949. It was nationalized and remaining as an entity of the Ministry of Railways until 2002, when it was a manufacturing facility of (LORIC). In 2002, LORIC was split into CNR Group and CSR Group, which Tangshan works belonged to the former due to geographical location. CNR Group and CSR Group also belonged to newly established State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission, another department of the State Council. Due to the initial public offering of China CNR, the assets of the works was injected to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICE 3
ICE 3, or Intercity-Express 3, is a family of high-speed electric multiple unit trains operated by Deutsche Bahn. It includes classes 403, 406, 407 and 408, which are known as ICE 3, ICE 3M, New ICE 3 and ICE 3neo respectively. Three multisystem trains, known as ICE International, are owned by Nederlandse Spoorwegen (NS, Dutch Railways). Based on the ICE 3M/F, Siemens developed its Siemens Velaro train family with versions used in Germany, Belgium, France, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Spain, China, Russia and Turkey. Class 403 The design goal of the ICE 3 (Class 403) was to create a higher-powered, lighter train than its predecessors. This was achieved by distributing its 16 traction motors underneath the whole train. The train is licensed for and has reached on trial runs. On regular Intercity-Express services they run at up to , the maximum design speed of German high-speed lines. Because the train does not have power cars, the whole length of the train is availa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRRC Changchun Railway Vehicles
CRRC Changchun Railway Vehicles Co., Ltd. () is a Chinese rolling stock manufacturer and a division of the CRRC. While the CRV emerged in 2002, the company's roots date back to the establishment of the Changchun Car Company in 1954. The company became a division of CNR Corporation before its merger with CSR to form the present CRRC. It has produced a variety of rolling stock for customers in China and abroad, including locomotives, passenger cars, multiple units, rapid transit and light rail vehicles. It has established technology transfer partnerships with several foreign railcar manufacturers, including Bombardier Transportation, Alstom, and Siemens Mobility. Joint Ventures In 2004 Alstom won the first high speed train contract in China, supporting CRRC to build 60 CRH5 high speed trains. In November 2016, CRRC won Melbourne suburban train contract for Evolution Rail as Public Private Partnership with Downer Group, Plenary Group. Changchun Bombardier Railway Vehicles Co. Ltd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siemens Mobility
Siemens Mobility GmbH is a separately-managed company of Siemens, arising from a corporate restructuring effective 1 August 2018. With its global headquarters in Munich, Siemens Mobility has four core business units: Mobility Management, dedicated to rail technology and intelligent traffic systems, Railway Electrification, Rolling Stock, and Customer Services. History Innovations from the late 19th century, such as the world's first electric train, when Siemens & Halske unveiled a train in which power was supplied through the rails, and the world's first electric tram, with the implementation of 2.5-kilometer-long electric tramway located in Berlin, built at the company's own expense, cemented the use of electric power in transportation systems. In the following years, inventions such as the first electric trolleybus, mine locomotives, and the first underground railway in continental Europe (in Budapest), set the path from trams and subways to today's high-speed trains. Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |