|
CREST Syndrome
CREST syndrome, also known as the limited cutaneous form of systemic sclerosis (lcSSc), is a multisystem connective tissue disorder. The acronym "CREST" refers to the five main features: calcinosis, Raynaud's phenomenon, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasia. CREST syndrome is associated with detectable antibodies against centromeres (a component of the cell nucleus), and usually spares the kidneys (a feature more common in the related condition systemic scleroderma). If the lungs are involved, it is usually in the form of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Signs and symptoms Calcinosis CREST causes thickening and tightening of the skin with deposition of calcific nodules ("calcinosis"). Raynaud's phenomenon Raynaud's phenomenon is frequently the first manifestation of CREST/lcSSc, preceding other symptoms by years. Stress and cold temperature induce an exaggerated vasoconstriction of the small arteries, arterioles, and thermoregulatory vessels of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheumatology
Rheumatology (Greek ''ῥεῦμα'', ''rheûma'', flowing current) is a branch of medicine devoted to the diagnosis and management of disorders whose common feature is inflammation in the bones, muscles, joints, and internal organs. Rheumatology covers more than 100 different complex diseases, collectively known as rheumatic diseases, which includes many forms of arthritis as well as lupus and Sjögren syndrome, Sjögren's syndrome. Physician, Doctors who have undergone formal training in rheumatology are called rheumatologists. Many of these diseases are now known to be disorders of the immune system, and rheumatology has significant overlap with immunology, the branch of medicine that studies the immune system. Rheumatologist A rheumatologist is a physician who specializes in the field of medical sub-specialty called rheumatology. A rheumatologist holds a board certification after specialized training. In the United States, training in this field requires four years unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telangiectasias
Telangiectasias, also known as spider veins, are small dilated blood vessels that can occur near the surface of the skin or mucous membranes, measuring between 0.5 and 1 millimeter in diameter. These dilated blood vessels can develop anywhere on the body, but are commonly seen on the face around the nose, cheeks and chin. Dilated blood vessels can also develop on the legs, although when they occur on the legs, they often have underlying venous reflux or "hidden varicose veins" (see Venous hypertension section below). When found on the legs, they are found specifically on the upper thigh, below the knee joint and around the ankles. Many patients with spider veins seek the assistance of physicians who specialize in vein care or peripheral vascular disease. These physicians are called vascular surgeons or phlebologists. More recently, interventional radiologists have started treating venous problems. Some telangiectasias are due to developmental abnormalities that can closely mim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Connective Tissue Disorders
Systemic fundamental to a predominant social, economic, or political practice. This refers to: In medicine In medicine, ''systemic'' means affecting the whole body, or at least multiple organ systems. It is in contrast with ''topical'' or ''local''. *Systemic administration, a route of administration of medication so that the entire body is affected *Systemic circulation, carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the body and then returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart *Systemic disease, an illness that affects multiple organs, systems or tissues, or the entire body *Systemic effect, an adverse effect of an exposure that affects the body as a whole, rather than one part *Systemic inflammatory response syndrome, an inflammatory state affecting the whole body, frequently in response to infection *Systemic lupus erythematosus, a chronic autoimmune connective tissue disease that can affect any part of the body *Systemic scleroderma, also known as systemic sclerosis, a systemic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue Diseases
A connective tissue disease (collagenosis) is any disease that has the connective tissues of the body as a target of pathology. Connective tissue is any type of biological tissue with an extensive extracellular matrix that supports, binds together, and protects organs. These tissues form a framework, or matrix, for the body, and are composed of two major structural protein molecules: collagen and elastin. There are many different types of collagen protein in each of the body's tissues. Elastin has the capability of stretching and returning to its original length—like a spring or rubber band. Elastin is the major component of ligaments (tissues that attach bone to bone) and skin. In patients with connective tissue disease, it is common for collagen and elastin to become injured by inflammation (ICT). Many connective tissue diseases feature abnormal immune system activity with inflammation in tissues as a result of an immune system that is directed against one's own body tissu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scleroderma
Scleroderma is a group of autoimmune diseases that may result in changes to the skin, blood vessels, muscles, and internal organs. The disease can be either localized to the skin or involve other organs, as well. Symptoms may include areas of thickened skin, stiffness, feeling tired, and poor blood flow to the fingers or toes with cold exposure. One form of the condition, known as CREST syndrome, classically results in calcium deposits, Raynaud's syndrome, esophageal problems, thickening of the skin of the fingers and toes, and areas of small, dilated blood vessels. The cause is unknown, but it may be due to an abnormal immune response. Risk factors include family history, certain genetic factors, and exposure to silica. The underlying mechanism involves the abnormal growth of connective tissue, which is believed to be the result of the immune system attacking healthy tissues. Diagnosis is based on symptoms, supported by a skin biopsy or blood tests. While no cure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johns Hopkins School Of Medicine
The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine (JHUSOM) is the medical school of Johns Hopkins University, a private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1893, the School of Medicine shares a campus with the Johns Hopkins Hospital and Johns Hopkins Children's Center, established in 1889. It has consistently ranked among the top medical schools in the United States in terms of the number/amount of research grants/funding awarded by the National Institutes of Health, among other measures. History The founding physicians (the "Four Doctors") of the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine included pathologist William Henry Welch (1850–1934), the first dean of the school and a mentor to generations of research scientists; a Canadian, internist Sir William Osler (1849–1919), regarded as the ''Father of Modern Medicine'', having been perhaps the most influential physician of the late 19th and early 20th centuries as author of ''The Principles and Practice of Medicine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Biliary Cholangitis
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), previously known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is an autoimmune disease of the liver. It results from a slow, progressive destruction of the small bile ducts of the liver, causing bile and other toxins to build up in the liver, a condition called cholestasis. Further slow damage to the liver tissue can lead to scarring, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis. Common symptoms are tiredness, itching, and in more advanced cases, jaundice. In early cases, the only changes may be those seen in blood tests. PBC is a relatively rare disease, affecting up to one in 3,000–4,000 people. It is much more common in women, with a sex ratio of at least 9:1 female to male. The condition has been recognised since at least 1851, and was named "primary biliary cirrhosis" in 1949. Because cirrhosis is a feature only of advanced disease, a change of its name to "primary biliary cholangitis" was proposed by patient advocacy groups in 2014. Signs and symptoms P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunosuppresive Drug
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system. Classification Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified into five groups: * glucocorticoids * cytostatics * antibodies * drugs acting on immunophilins * other drugs Glucocorticoids In pharmacologic (supraphysiologic) doses, glucocorticoids, such as prednisone, dexamethasone, and hydrocortisone are used to suppress various allergic, inflammatory, and autoimmune disorders. They are also administered as posttransplantory immunosuppressants to prevent the acute transplant rejection and graft-versus-host disease. Nevertheless, they do not prevent an infection and also inhibit later reparative processes. Immunosuppressive mechanism Glucocorticoids suppress cell-mediated immunity. They act by inhibiting genes that code for the cytokines Interleukin 1 (IL-1), IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
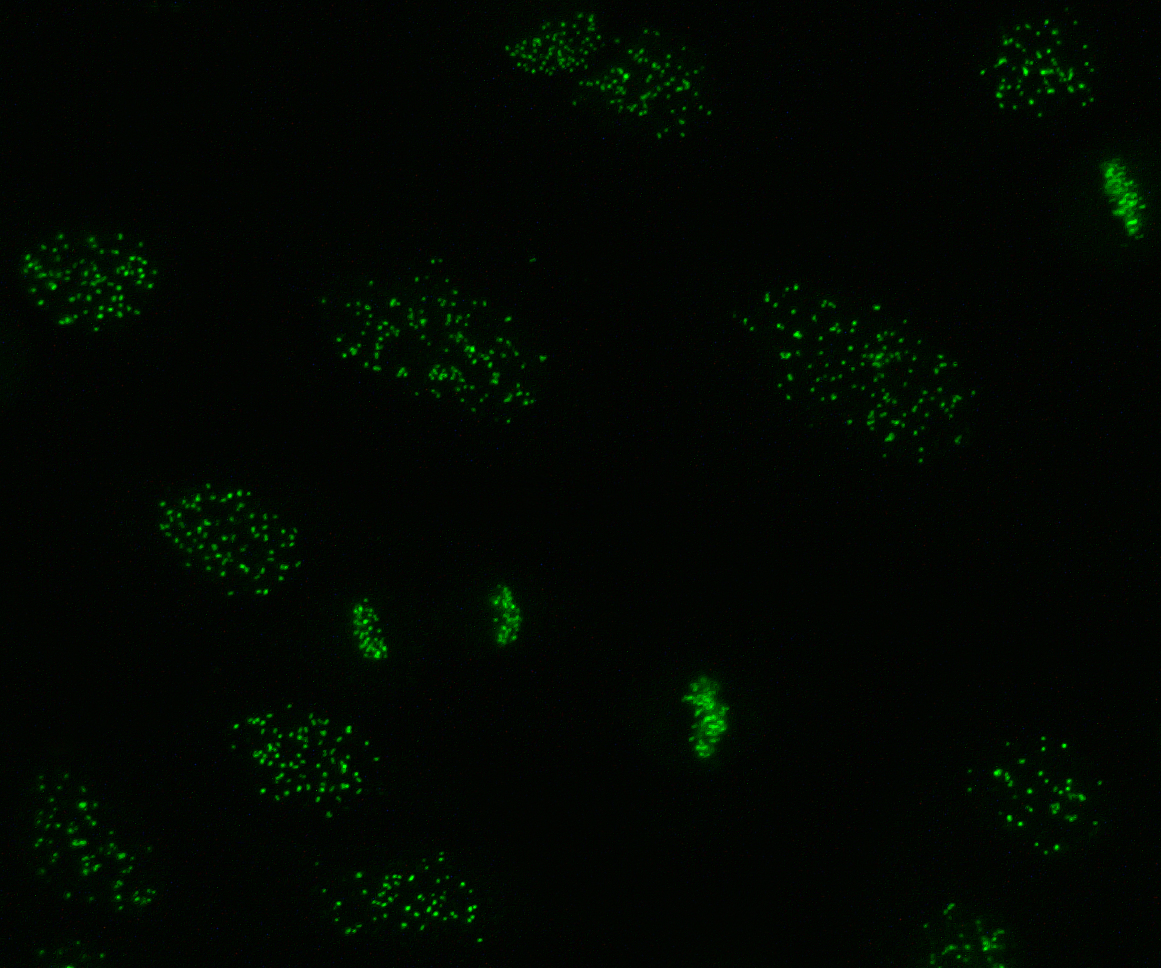
Anti-centromere Antibodies
Anti-centromere antibodies (ACAs; often styled solid, anticentromere) are autoantibodies specific to centromere and kinetochore function. They occur in some autoimmune diseases, frequently in limited systemic scleroderma (formerly called CREST syndrome), and occasionally in the diffuse form of scleroderma Scleroderma is a group of autoimmune diseases that may result in changes to the skin, blood vessels, muscles, and internal organs. The disease can be either localized to the skin or involve other organs, as well. Symptoms may include areas o .... They are rare in other rheumatic conditions and in healthy persons. Anti-centromere antibodies are found in approximately 60% of patients with limited systemic scleroderma and in 15% of those with the diffuse form of scleroderma. The specificity of this test is >98%. Thus, a positive anti-centromere antibody finding is strongly suggestive of limited systemic scleroderma. Anti-centromere antibodies present early in the course o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-nuclear Antibody
Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs, also known as antinuclear factor or ANF) are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the cell nucleus. In normal individuals, the immune system produces antibodies to foreign proteins (antigens) but not to human proteins (autoantigens). In some cases, antibodies to human antigens are produced. There are many subtypes of ANAs such as anti-Ro antibodies, anti-La antibodies, anti-Sm antibodies, anti-nRNP antibodies, anti-Scl-70 antibodies, anti-dsDNA antibodies, anti-histone antibodies, antibodies to nuclear pore complexes, anti-centromere antibodies and anti-sp100 antibodies. Each of these antibody subtypes binds to different proteins or protein complexes within the nucleus. They are found in many disorders including autoimmunity, cancer and infection, with different prevalences of antibodies depending on the condition. This allows the use of ANAs in the diagnosis of some autoimmune disorders, including systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-centromere Antibodies
Anti-centromere antibodies (ACAs; often styled solid, anticentromere) are autoantibodies specific to centromere and kinetochore function. They occur in some autoimmune diseases, frequently in limited systemic scleroderma (formerly called CREST syndrome), and occasionally in the diffuse form of scleroderma Scleroderma is a group of autoimmune diseases that may result in changes to the skin, blood vessels, muscles, and internal organs. The disease can be either localized to the skin or involve other organs, as well. Symptoms may include areas o .... They are rare in other rheumatic conditions and in healthy persons. Anti-centromere antibodies are found in approximately 60% of patients with limited systemic scleroderma and in 15% of those with the diffuse form of scleroderma. The specificity of this test is >98%. Thus, a positive anti-centromere antibody finding is strongly suggestive of limited systemic scleroderma. Anti-centromere antibodies present early in the course o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |