|
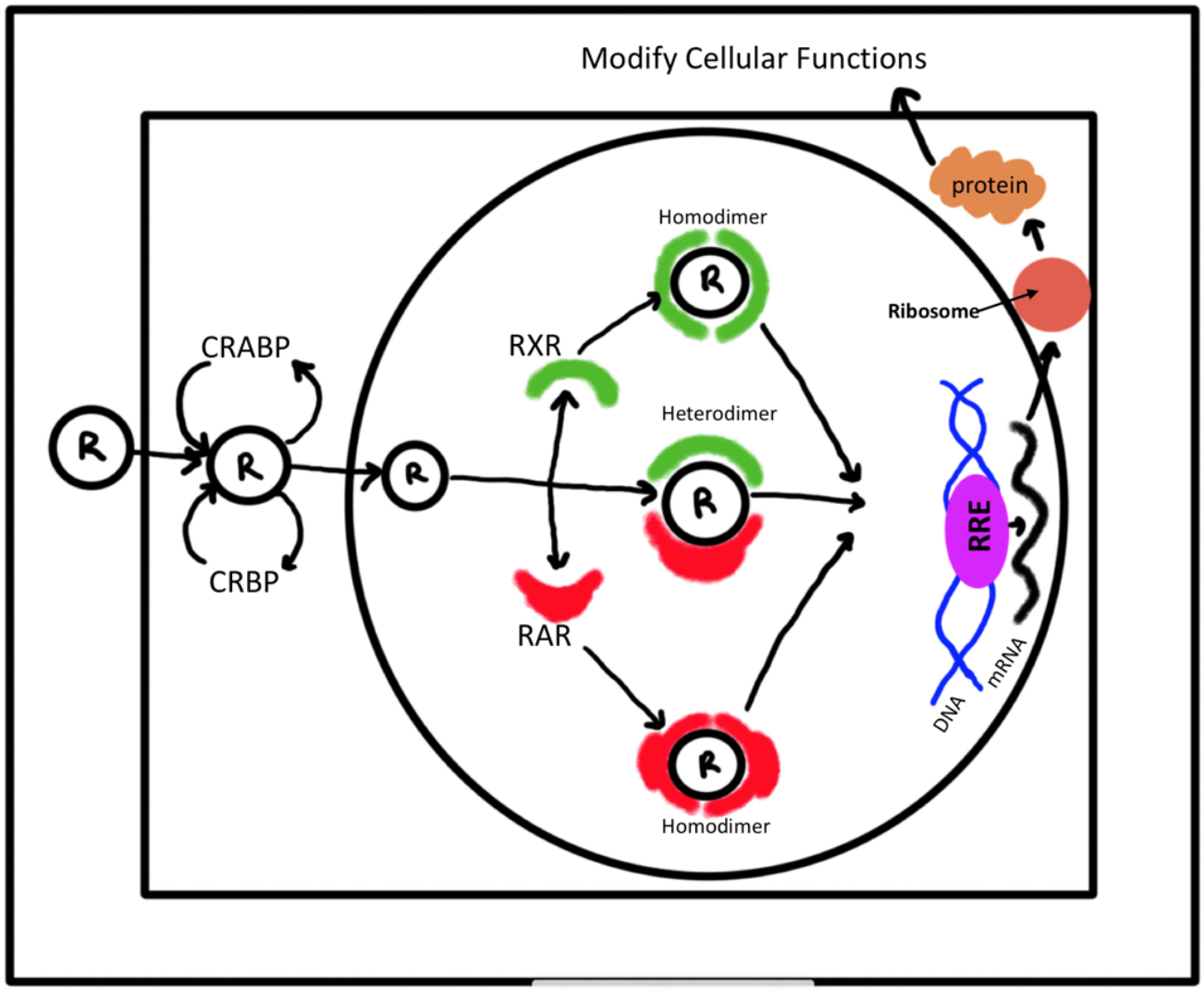
CRABP1
Cellular retinoic acid-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CRABP1'' gene. CRABP1 is assumed to play an important role in retinoic acid-mediated differentiation and proliferation processes. It is structurally similar to the cellular retinol-binding proteins, but binds only retinoic acid. CRABP1 is constitutively expressed and is believed to have different functions in the cell than the related CRABP2. Function CRABP1 binds to retinoid acid and helps to transport it into the nucleus (Figure 1). Both CRABP1 and CRABP2 perform this activity. The retinoic acid molecule is then released and further bound to retinoic acid receptor (RAR) and the retinoid X receptor (RXR) as homodimers or heterodimers. This complex then further binds to retinoic acid response elements (RARE) on DNA that regulates transcription of retinoid acid dependent null genes. The domains for the nuclear localization and the retinoic acid binding are shown in Figure 3. CRABP1 has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRABP2
Cellular retinoic acid-binding protein 2 is a cytoplasmic binding protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CRABP2'' gene. CRABP2 is structurally similar to CRABP1, but CRABP2 has a lower affinity for retinoic acid (RA). CRABP2 is associated with cells that produce large amounts of retinoic acid and may play a role in mediating the effects of retinoic acid in the cell. Function A number of specific carrier proteins for members of the vitamin A family have been discovered. Retinoic acid is an active metabolite of vitamin A (retinol). Cellular retinoic acid binding proteins (CRABP) are low molecular weight proteins whose precise function remains largely unknown. The inducibility of the CRABP2 gene suggests that this isoform is important in retinoic acid-mediated regulation of human skin growth, differentiation and development. CRABP2 is involved in the metabolism and transportation of retinoic acid from the cytosol to the RARs (retinoic acid receptors) located in the nucleus. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinoic Acid
Retinoic acid (used simplified here for all-''trans''-retinoic acid) is a metabolite of vitamin A1 (all-''trans''-retinol) that mediates the functions of vitamin A1 required for growth and development. All-''trans''-retinoic acid is required in chordate animals, which includes all higher animals from fish to humans. During early embryonic development, all-''trans''-retinoic acid generated in a specific region of the embryo helps determine position along the embryonic anterior/posterior axis by serving as an intercellular signaling molecule that guides development of the posterior portion of the embryo. It acts through Hox genes, which ultimately control anterior/posterior patterning in early developmental stages. All-''trans''-retinoic acid (ATRA) is the major occurring retinoic acid, while isomers like 13-''cis''- and 9-''cis''-retinoic acid are also present in much lower levels. The key role of all-''trans''-retinoic acid in embryonic development mediates the high teratogenici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinoid Transfer By CRABP1
The retinoids are a class of chemical compounds that are vitamers of vitamin A or are chemically related to it. Retinoids have found use in medicine where they regulate epithelial cell growth. Retinoids have many important functions throughout the body including roles in vision, regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation, growth of bone tissue, immune function, and activation of tumor suppressor genes. Research is also being done into their ability to treat skin cancers. Currently, alitretinoin (9-''cis''-retinoic acid) may be used topically to help treat skin lesions from Kaposi's sarcoma, and tretinoin (all-''trans''- retinoic acid) is used to treat acute promyelocytic leukemia. Types There are four generations of retinoids: * First generation include retinol, retinal, tretinoin ( retinoic acid), isotretinoin, and alitretinoin * Second generation include etretinate and its metabolite acitretin * Third generation include adapalene, bexarotene, and tazarotene * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Effects Of CRABP1
Cellular may refer to: * Cellular automaton, a model in discrete mathematics *Cell biology, the evaluation of cells work and more * ''Cellular'' (film), a 2004 movie * Cellular frequencies, assigned to networks operating in cellular RF bands * Cellular manufacturing *Cellular network, cellular radio networks *U.S. Cellular Field, also known as "The Cell", a baseball stadium in Chicago * U.S. Cellular Arena, an arena in Milwaukee, Wisconsin Terms such as cellular organization, cellular structure, cellular system, and so on may refer to: *Cell biology, the evaluation of how cells work and more * Cellular communication networks, systems for allowing communication through mobile phones and other mobile devices * Cellular organizational structures, methods of human organization in social groups * Clandestine cell organizations, entities organized to commit crimes, acts of terror, or other malicious activities See also *Cell (other) Cell most often refers to: * Cell (biolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domains Of CRABP1
Domain may refer to: Mathematics *Domain of a function, the set of input values for which the (total) function is defined **Domain of definition of a partial function ** Natural domain of a partial function **Domain of holomorphy of a function *Domain (mathematical analysis), an open connected set *Domain of discourse, the set of entities over which logic variables may range * Domain of an algebraic structure, the set on which the algebraic structure is defined * Domain theory, the study of certain subsets of continuous lattices that provided the first denotational semantics of the lambda calculus * Domain (ring theory), a nontrivial ring without left or right zero divisors ** Integral domain, a non-trivial commutative ring without zero divisors ***Atomic domain, an integral domain in which every non-zero non-unit is a finite product of irreducible elements *** Bézout domain, an integral domain in which the sum of two principal ideals is again a principal ideal ***Euclidean domain, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinoic Acid Receptor
The retinoic acid receptor (RAR) is a type of nuclear receptor which can also act as a ligand-activated transcription factor that is activated by both all-trans retinoic acid and 9-cis retinoic acid the retinoid active derivatives of Vitamin A . They are typically found within the nucleus. There are three retinoic acid receptors (RAR), RAR-alpha, RAR-beta, and RAR-gamma, encoded by the , , genes, respectively. Within each RAR subtype there are various isoforms differing in their N-terminal region A. Multiple splice variants have been identified in human RARs: four for , five for , and two for . As with other type II nuclear receptors, RAR heterodimerizes with RXR and in the absence of ligand, the RAR/RXR dimer binds to hormone response elements known as retinoic acid response elements (RAREs) complexed with corepressor protein. Binding of agonist ligands to RAR results in dissociation of corepressor and recruitment of coactivator protein that, in turn, promotes transcript ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinoid X Receptor
The retinoid X receptor (RXR) is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by 9-cis retinoic acid, which is discussed controversially to be of endogenous relevance, and 9-''cis''-13,14-dihydroretinoic acid, which is likely to be the major endogenous mammalian RXR-selective agonist. In a novel review publication, this 9-''cis''-13,14-dihydroretinoic acid was shown to be a metabolite not originating from the known vitamin A (vitamin A1) pathway and its nutritional precursors all-''trans''-retinol ( vitamin A (vitamin A1) or all-''trans''- beta-carotene (provitamin A (provitamin A1)). An independent pathway for generating this endogenous RXR-ligand 9-''cis''-13,14-dihydroretinoic acid from 9-''cis''-13,14-dihydroretinol present in food source and named vitamin A5 or alternatively via provitamin A5 has been suggested as the first novel vitamin identified since 1948, cobalamin / vitamin B12. There are three retinoic X receptors (RXR): RXR-alpha, RXR-beta, and RXR-gamma, en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinases
In molecular biology, extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) or classical MAP kinases are widely expressed protein kinase intracellular signalling molecules that are involved in functions including the regulation of meiosis, mitosis, and postmitotic functions in differentiated cells. Many different stimuli, including growth factors, cytokines, virus infection, ligands for heterotrimeric G protein-coupled receptors, transforming agents, and carcinogens, activate the ERK pathway. The term, "extracellular signal-regulated kinases", is sometimes used as a synonym for mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), but has more recently been adopted for a specific subset of the mammalian MAPK family. In the MAPK/ERK pathway, Ras activates c-Raf, followed by mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (abbreviated as MKK, MEK, or MAP2K) and then MAPK1/2 (below). Ras is typically activated by growth hormones through receptor tyrosine kinases and GRB2/ SOS, but may also receive other s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morris Water Navigation Task
The Morris water navigation task, also known as the Morris water maze (not to be confused with '' water maze''), is a behavioral procedure mostly used with rodents. It is widely used in behavioral neuroscience to study spatial learning and memory. It enables learning, memory, and spatial working to be studied with great accuracy, and can also be used to assess damage to particular cortical regions of the brain. It is used by neuroscientists to measure the effect of neurocognitive disorders on spatial learning and possible neural treatments, to test the effect of lesions to the brain in areas concerned with memory, and to study how age influences cognitive function and spatial learning. The task is also used as a tool to study drug-abuse, neural systems, neurotransmitters, and brain development. Overview The basic procedure for the Morris water navigation task is that the rat is placed in a large circular pool and is required to find an invisible or visible platform that all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |