|
COCH Protein
Cochlin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''COCH'' gene. It is an extracellular matrix (ECM) protein highly abundant in the cochlea and vestibule of the inner ear, constituting the major non-collagen component of the ECM of the inner ear. The protein is highly conserved in human, mouse, and chicken, showing 94% and 79% amino acid identity of human to mouse and chicken sequences, respectively. Structure Cochlin contains three protein domains: an N-terminal LCCL domain, and two copies of Von Willebrand factor type A domains. Function The gene is expressed in spindle-shaped cells located along nerve fibers between the auditory ganglion and sensory epithelium. These cells accompany neurites at the habenula perforata, the opening through which neurites extend to innervate hair cells. This and the pattern of expression of this gene in chicken inner ear paralleled the histologic findings of acidophilic deposits, consistent with mucopolysaccharide ground substance, in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LCCL Domain
In molecular biology, the LCCL domain is a protein domain which has been named after several well-characterised proteins that were found to contain it, namely Limulus clotting factor C, Cochlin (Coch-5b2) and Lgl1 ( CRISPLD2). It is an about 100 amino acids domain whose C-terminal part contains a highly conserved histidine in a conserved motif YxxxSxxCxAAVHxGVI. The LCCL module is thought to be an autonomously folding domain that has been used for the construction of various modular proteins through exon-shuffling. It has been found in various metazoan proteins in association with complement B-type domains, C-type lectin domains, von Willebrand type A domains, CUB domains, discoidin lectin domains or CAP domains. It has been proposed that the LCCL domain could be involved in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding. LCCL exhibits a novel fold. Some proteins known to contain a LCCL domain include Limulus factor C, an LPS endotoxin-sensitive trypsin type serine protease which serve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Von Willebrand Factor Type A Domain
The von Willebrand factor type A (vWA) domain is a protein domain named after its occurrence in von Willebrand factor (vWF), a large multimeric glycoprotein found in blood plasma. Mutant forms of vWF are involved in the aetiology of bleeding disorders. This type A domain is the prototype for a protein superfamily (; see also Pfam clan). The vWA domain is found in various plasma proteins: complement factors B, C2, CR3 and CR4; the integrins (I-domains); collagen types VI, VII, XII and XIV; and other extracellular proteins. Although the majority of vWA-containing proteins are extracellular, the most ancient ones present in all eukaryotes are all intracellular proteins involved in functions such as transcription, DNA repair, ribosomal and membrane transport and the proteasome. A common feature appears to be involvement in multiprotein complexes. Proteins that incorporate vWA domains participate in numerous biological events (e.g. cell adhesion, migration, homing, pattern formation, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurite
A neurite or neuronal process refers to any projection from the cell body of a neuron. This projection can be either an axon or a dendrite. The term is frequently used when speaking of immature or developing neurons, especially of cells in culture, because it can be difficult to tell axons from dendrites before differentiation is complete. Neurite development The development of a neurite requires a complex interplay of both extracellular and intracellular signals. At every given point along a developing neurite, there are receptors detecting both positive and negative growth cues from every direction in the surrounding space. The developing neurite sums together all of these growth signals in order to determine which direction the neurite will ultimately grow towards. While not all of the growth signals are known, several have been identified and characterized. Among the known extracellular growth signals are netrin, a midline chemoattractant, and semaphorin, ephrin and collaps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habenula Perforata
In neuroanatomy, habenula (diminutive of Latin ''habena'' meaning rein) originally denoted the stalk of the pineal gland (pineal habenula; pedunculus of pineal body), but gradually came to refer to a neighboring group of nerve cells with which the pineal gland was believed to be associated, the habenular nucleus. The habenular nucleus is a set of well-conserved structures in all vertebrate animals. Currently, this term refers to this separate cell mass in the caudal portion of the dorsal diencephalon, known as the epithalamus, found in all vertebrates on both sides of the third ventricle. It connects the forebrain and midbrain within the epithalamus. It is embedded in the posterior end of the stria medullaris from which it receives most of its afferent fibers. By way of the fasciculus retroflexus (habenulointerpeduncular tract) it projects to the interpeduncular nucleus and other paramedian cell groups of the midbrain tegmentum. Although they were predominantly studied for their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acidophilic
Acidophiles or acidophilic organisms are those that thrive under highly acidic conditions (usually at pH 5.0 or below). These organisms can be found in different branches of the tree of life, including Archaea, Bacteria,Becker, A.Types of Bacteria Living in Acidic pH" Retrieved 10 May 2017. and Eukarya. Examples A list of these organisms includes: Archaea :* Sulfolobales, an order in the Thermoproteota branch of Archaea :* Thermoplasmatales, an order in the Euryarchaeota branch of Archaea :* ARMAN, in the Euryarchaeota branch of Archaea :* ''Acidianus brierleyi, A. infernus'', facultatively anaerobic thermoacidophilic archaebacteria :* '' Halarchaeum acidiphilum'', acidophilic member of the Halobacteriacaeae :* ''Metallosphaera sedula'', thermoacidophilic Bacteria :* Acidobacteriota, a phylum of Bacteria :* Acidithiobacillales, an order of Pseudomonadota e.g. ''A. ferrooxidans, A. thiooxidans'' :*''Thiobacillus prosperus, T. acidophilus, T. organovorus, T. cuprinus'' :*''Acet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucopolysaccharide
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units (i.e. two-sugar units). The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case of the sulfated glycosaminoglycan keratan, where, in place of the uronic sugar there is a galactose unit. GAGs are found in vertebrates, invertebrates and bacteria. Because GAGs are highly polar molecules and attract water; the body uses them as lubricants or shock absorbers. Mucopolysaccharidoses are a group of metabolic disorders in which abnormal accumulations of glycosaminoglycans occur due to enzyme deficiencies. Production Glycosaminoglycans vary greatly in molecular mass, disaccharide structure, and sulfation. This is because GAG synthesis is not template driven, as are proteins or nucleic acids, but constantly altered by processing enzymes. GAGs are classified into four groups, based on their core disaccharide structures. Hepari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonsyndromic Deafness
Nonsyndromic deafness is hearing loss that is not associated with other signs and symptoms. In contrast, syndromic deafness involves hearing loss that occurs with abnormalities in other parts of the body. Genetic changes are related to the following types of nonsyndromic deafness. * DFNA: nonsyndromic deafness, autosomal dominant * DFNB: nonsyndromic deafness, autosomal recessive * DFNX: nonsyndromic deafness, X-linked * nonsyndromic deafness, mitochondrial Each type is numbered in the order in which it was described. For example, DFNA1 was the first described autosomal dominant type of nonsyndromic deafness. Mitochondrial nonsyndromic deafness involves changes to the small amount of DNA found in mitochondria, the energy-producing centers within cells. Most forms of nonsyndromic deafness are associated with permanent hearing loss caused by damage to structures in the inner ear. The inner ear consists of three parts: a snail-shaped structure called the cochlea that helps process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trabecular Meshwork
The trabecular meshwork is an area of tissue in the eye located around the base of the cornea, near the ciliary body, and is responsible for draining the aqueous humor from the eye via the anterior chamber (the chamber on the front of the eye covered by the cornea). The tissue is spongy and lined by trabeculocytes; it allows fluid to drain into a set of tubes called Schlemm's canal which is lined by endothelium with blood and lymphatic properties that allow aqueous humor to flow into the blood system. Structure The meshwork is divided up into three parts, with characteristically different ultrastructures: #''Inner uveal meshwork'' - Closest to the anterior chamber angle, contains thin cord-like trabeculae, orientated predominantly in a radial fashion, enclosing trabeculae spaces larger than the corneoscleral meshwork. #''Corneoscleral meshwork'' - Contains a large amount of elastin, arranged as a series of thin, flat, perforated sheets arranged in a laminar pattern; cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that result in damage to the optic nerve (or retina) and cause vision loss. The most common type is open-angle (wide angle, chronic simple) glaucoma, in which the drainage angle for fluid within the eye remains open, with less common types including closed-angle (narrow angle, acute congestive) glaucoma and normal-tension glaucoma. Open-angle glaucoma develops slowly over time and there is no pain. Peripheral vision may begin to decrease, followed by central vision, resulting in blindness if not treated. Closed-angle glaucoma can present gradually or suddenly. The sudden presentation may involve severe eye pain, blurred vision, mid-dilated pupil, redness of the eye, and nausea. Vision loss from glaucoma, once it has occurred, is permanent. Eyes affected by glaucoma are referred to as being glaucomatous. Risk factors for glaucoma include increasing age, high pressure in the eye, a family history of glaucoma, and use of steroid medication. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
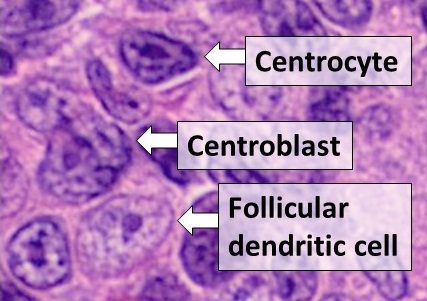
Follicular Dendritic Cells
Follicular dendritic cells (FDC) are cells of the immune system found in primary and secondary lymph follicles (lymph nodes) of the B cell areas of the lymphoid tissue. Unlike dendritic cells (DC), FDCs are not derived from the bone-marrow hematopoietic stem cell, but are of mesenchymal origin. Possible functions of FDC include: organizing lymphoid tissue's cells and microarchitecture, capturing antigen to support B cell, promoting debris removal from germinal centers, and protecting against autoimmunity. Disease processes that FDC may contribute include primary FDC-tumor, chronic inflammatory conditions, HIV-1 infection development, and neuroinvasive scrapie. Location and molecular markers Follicular DCs are a non-migratory population found in primary and secondary follicles of the B cell areas of lymph nodes, spleen, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). They form a stable network due to intercellular connections between FDCs processes and intimate interaction with f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |