|
CO-OPN
The CO-OPN (Concurrent Object-Oriented Petri Nets) specification language is based on both algebraic specifications and algebraic Petri nets formalisms. The former formalism represent the data structures aspects, while the latter stands for the behavioral and concurrent aspects of systems. In order to deal with large specifications some structuring capabilities have been introduced. The object-oriented paradigm has been adopted, which means that a CO-OPN specification is a collection of objects which interact concurrently. Cooperation between the objects is achieved by means of a synchronization mechanism, i.e., each object event may request to be synchronized with some methods (parameterized events) of one or a group of partners by means of a synchronization expression. A CO-OPN specification consists of a collection of two different modules: the abstract data type modules and the object modules. The abstract data type modules concern the data structure component of the specifica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algebraic Petri Nets
An algebraic Petri net (APN) is an evolution of the well known Petri net in which elements of user defined data types (called algebraic abstract data types (AADT)) replace black tokens. This formalism can be compared to coloured Petri nets (CPN) in many aspects. However, in the APN case, the semantics of the data types is given by an axiomatization enabling proofs and computations on it. Algebraic Petri nets were invented by Jacques Vautherin in 1985 in his PhD thesis and later improved by Wolfang Reisig. The formalism has two aspects : * The control part which is handled by a Petri net. * The data part which is handled by one or many AADTs. AADT can be themselves split in two parts: * The ''signature'' (Sort and Ops in the example below) which gives the valid constants and operations of the term algebra. * The ''axiomatization'' (Axioms in the example below) which gives the semantics of the operations described in the signature part. The following picture describes an algebrai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specification Language
A specification language is a formal language in computer science used during systems analysis, requirements analysis, and systems design to describe a system at a much higher level than a programming language, which is used to produce the executable code for a system.Joseph Goguen "One, None, A Hundred Thousand Specification Languages" Invited Paper, IFIP Congress 1986 pp 995-1004 Overview Specification languages are generally not directly executed. They are meant to describe the ''what'', not the ''how''. Indeed, it is considered as an error if a requirement specification is cluttered with unnecessary implementation detail. A common fundamental assumption of many specification approaches is that programs are modelled as algebraic or model-theoretic structures that include a collection of sets of data values together with functions over those sets. This level of abstraction coincides with the view that the correctness of the input/output behaviour of a program takes precedence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
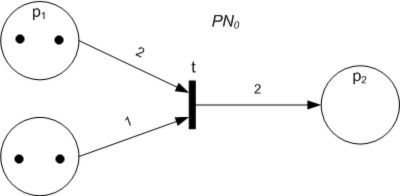
Petri Nets
A Petri net, also known as a place/transition (PT) net, is one of several mathematical modeling languages for the description of distributed systems. It is a class of discrete event dynamic system. A Petri net is a directed bipartite graph that has two types of elements, places and transitions. Place elements are depicted as white circles and transition elements are depicted as rectangles. A place can contain any number of tokens, depicted as black circles. A transition is enabled if all places connected to it as inputs contain at least one token. Some sources state that Petri nets were invented in August 1939 by Carl Adam Petri—at the age of 13—for the purpose of describing chemical processes. Like industry standards such as UML activity diagrams, Business Process Model and Notation, and event-driven process chains, Petri nets offer a graphical notation for stepwise processes that include choice, iteration, and concurrent execution. Unlike these standards, Petri nets ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Geneva
The University of Geneva (French: ''Université de Genève'') is a public research university located in Geneva, Switzerland. It was founded in 1559 by John Calvin as a theological seminary. It remained focused on theology until the 17th century, when it became a center for enlightenment scholarship. Today, it is the third largest university in Switzerland by number of students. In 1873, it dropped its religious affiliations and became officially secular. In 2009, the University of Geneva celebrated the 450th anniversary of its founding. Almost 40% of the students come from foreign countries. The university holds and actively pursues teaching, research, and community service as its primary objectives. In 2016, it was ranked 53rd worldwide by the Shanghai Academic Ranking of World Universities, 89th by the QS World University Rankings, and 131st in the Times Higher Education World University Ranking. UNIGE is a member of the League of European Research Universities (includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specification Languages
A specification often refers to a set of documented requirements to be satisfied by a material, design, product, or service. A specification is often a type of technical standard. There are different types of technical or engineering specifications (specs), and the term is used differently in different technical contexts. They often refer to particular documents, and/or particular information within them. The word ''specification'' is broadly defined as "to state explicitly or in detail" or "to be specific". A requirement specification is a documented requirement, or set of documented requirements, to be satisfied by a given material, design, product, service, etc. It is a common early part of engineering design and product development processes in many fields. A functional specification is a kind of requirement specification, and may show functional block diagrams. A design or product specification describes the features of the ''solutions'' for the Requirement Specification, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |