|
CLIP-Seq
High-throughput sequencing of RNA isolated by crosslinking immunoprecipitation (HITS-CLIP, also known as CLIP-Seq) is a genome-wide means of mapping protein–RNA binding sites or RNA modification sites in vivo. HITS-CLIP was originally used to generate genome-wide protein-RNA interaction maps for the neuron-specific RNA-binding protein and splicing factor NOVA1 and NOVA2; since then a number of other splicing factor maps have been generated, including those for PTB, RbFox2, SFRS1, hnRNP C, and even N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) mRNA modifications. HITS-CLIP of the RNA-binding protein Argonaute has been performed for the identification of microRNA targets by decoding microRNA-mRNA and protein-RNA interaction maps in mouse brain, and subsequently in ''Caenorhabditis elegans'', embryonic stem cells and tissue culture cells. As a novel modification of HITS-CLIP, m6A-CLIP was developed to precisely map N6-Methyladenosine(m6A) locations in mRNA by UV-crosslinking m6A antibody to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PAR-CLIP
PAR-CLIP (photoactivatable ribonucleoside-enhanced crosslinking and immunoprecipitation) is a biochemical method for identifying the binding sites of cellular RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) and microRNA-containing ribonucleoprotein complexes (miRNPs). The method relies on the incorporation of ribonucleoside analogs that are photoreactive, such as 4-thiouridine (4-SU) and 6-thioguanosine (6-SG), into nascent RNA transcripts by living cells. Irradiation of the cells by ultraviolet light of 365 nm wavelength induces efficient crosslinking of photoreactive nucleoside– labeled cellular RNAs to interacting RBPs. Immunoprecipitation of the RBP of interest is followed by isolation of the crosslinked and coimmunoprecipitated RNA. The isolated RNA is converted into a cDNA library and is deep sequenced using next-generation sequencing technology. Recently, PAR-CLIP have been applied to determine the transcriptome-wide binding sites of several known RBPs and microRNA-containing ribonucle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CLIP-Seq
High-throughput sequencing of RNA isolated by crosslinking immunoprecipitation (HITS-CLIP, also known as CLIP-Seq) is a genome-wide means of mapping protein–RNA binding sites or RNA modification sites in vivo. HITS-CLIP was originally used to generate genome-wide protein-RNA interaction maps for the neuron-specific RNA-binding protein and splicing factor NOVA1 and NOVA2; since then a number of other splicing factor maps have been generated, including those for PTB, RbFox2, SFRS1, hnRNP C, and even N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) mRNA modifications. HITS-CLIP of the RNA-binding protein Argonaute has been performed for the identification of microRNA targets by decoding microRNA-mRNA and protein-RNA interaction maps in mouse brain, and subsequently in ''Caenorhabditis elegans'', embryonic stem cells and tissue culture cells. As a novel modification of HITS-CLIP, m6A-CLIP was developed to precisely map N6-Methyladenosine(m6A) locations in mRNA by UV-crosslinking m6A antibody to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA-binding Protein
RNA-binding proteins (often abbreviated as RBPs) are proteins that bind to the double or single stranded RNA in cells and participate in forming ribonucleoprotein complexes. RBPs contain various structural motifs, such as RNA recognition motif (RRM), dsRNA binding domain, zinc finger and others. They are cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins. However, since most mature RNA is exported from the nucleus relatively quickly, most RBPs in the nucleus exist as complexes of protein and pre-mRNA called heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein particles (hnRNPs). RBPs have crucial roles in various cellular processes such as: cellular function, transport and localization. They especially play a major role in post-transcriptional control of RNAs, such as: splicing, polyadenylation, mRNA stabilization, mRNA localization and translation. Eukaryotic cells express diverse RBPs with unique RNA-binding activity and protein–protein interaction. According to the Eukaryotic RBP Database (EuRBPDB), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argonaute
The Argonaute protein family, first discovered for its evolutionarily conserved stem cell function, plays a central role in RNA silencing processes as essential components of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). RISC is responsible for the gene silencing phenomenon known as RNA interference (RNAi). Argonaute proteins bind different classes of small non-coding RNAs, including microRNAs (miRNAs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs). Small RNAs guide Argonaute proteins to their specific targets through sequence complementarity (base pairing), which then leads to mRNA cleavage, translation inhibition, and/or the initiation of mRNA decay. The name of this protein family is derived from a mutant phenotype resulting from mutation of AGO1 in ''Arabidopsis thaliana'', which was likened by Bohmert et al. to the appearance of the pelagic octopus '' Argonauta argo''. RNA interference RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which the RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of 'junk' DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The International Human Genome Project reported the sequence of the genome for ''Homo sapiens'' in 200The Human Genome Project although the initial "finished" sequence was missing 8% of the genome consisting mostly of repetitive sequences. With advancements in technology that could handle seq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICLIP
iCLIP (individual-nucleotide resolution CrossLinking and ImmunoPrecipitation) is a variant of the original CLIP method used for identifying protein-RNA interactions, which uses UV light to covalently bind proteins and RNA molecules to identify RNA binding sites of proteins. This crosslinking step has generally less background than standard RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) protocols, because the covalent bond formed by UV light allows RNA to be fragmented, followed by stringent purification, and this also enables CLIP to identify the positions of protein-RNA interactions. As with all CLIP methods, iCLIP allows for a very stringent purification of the linked protein-RNA complexes by stringent washing during immunoprecipitation followed by SDS-PAGE and transfer to nitrocellulose. The labelled protein-RNA complexes are then visualised for quality control, excised from nitrocellulose, and treated with proteinase to release the RNA, leaving only a few amino acids at the crosslink site of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CeRNA
Cerna may refer to: Populated places * Cerna, Croatia, Vukovar-Syrmia County, Croatia * Černá (Žďár nad Sázavou District), Czech Republic * Černá, Semily District, Czech Republic * Cerna, Tulcea, Romania * A village in Vaideeni Commune, Vâlcea County, Romania Rivers Romania * Cerna (Mureș), a tributary of the Mureș in Hunedoara County * Cerna (Danube), a tributary of the Danube in southwestern Romania * Cerna (Olteț), a tributary of the Olteț in Vâlcea County * Cerna (Tulcea), a small tributary of the Danube in Tulcea County * Cerna (Crasna), a tributary of the Crasna in Maramureș and Satu Mare Counties * A tributary of the Mag river in Sibiu County Other rivers * Černá (river), a river in the Czech Republic and Germany People * Cerna (surname) * Černá (surname) Černá may refer to: * Černá, Semily District, a village near Lomnice nad Popelkou, Czech Republic * Černá (Žďár nad Sázavou District), a village in the Czech Republic * Černá v Po� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudogene
Pseudogenes are nonfunctional segments of DNA that resemble functional genes. Most arise as superfluous copies of functional genes, either directly by DNA duplication or indirectly by reverse transcription of an mRNA transcript. Pseudogenes are usually identified when genome sequence analysis finds gene-like sequences that lack regulatory sequences needed for transcription or translation, or whose coding sequences are obviously defective due to frameshifts or premature stop codons. Most non-bacterial genomes contain many pseudogenes, often as many as functional genes. This is not surprising, since various biological processes are expected to accidentally create pseudogenes, and there are no specialized mechanisms to remove them from genomes. Eventually pseudogenes may be deleted from their genomes by chance DNA replication or DNA repair errors, or they may accumulate so many mutational changes that they are no longer recognizable as former genes. Analysis of these degeneration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
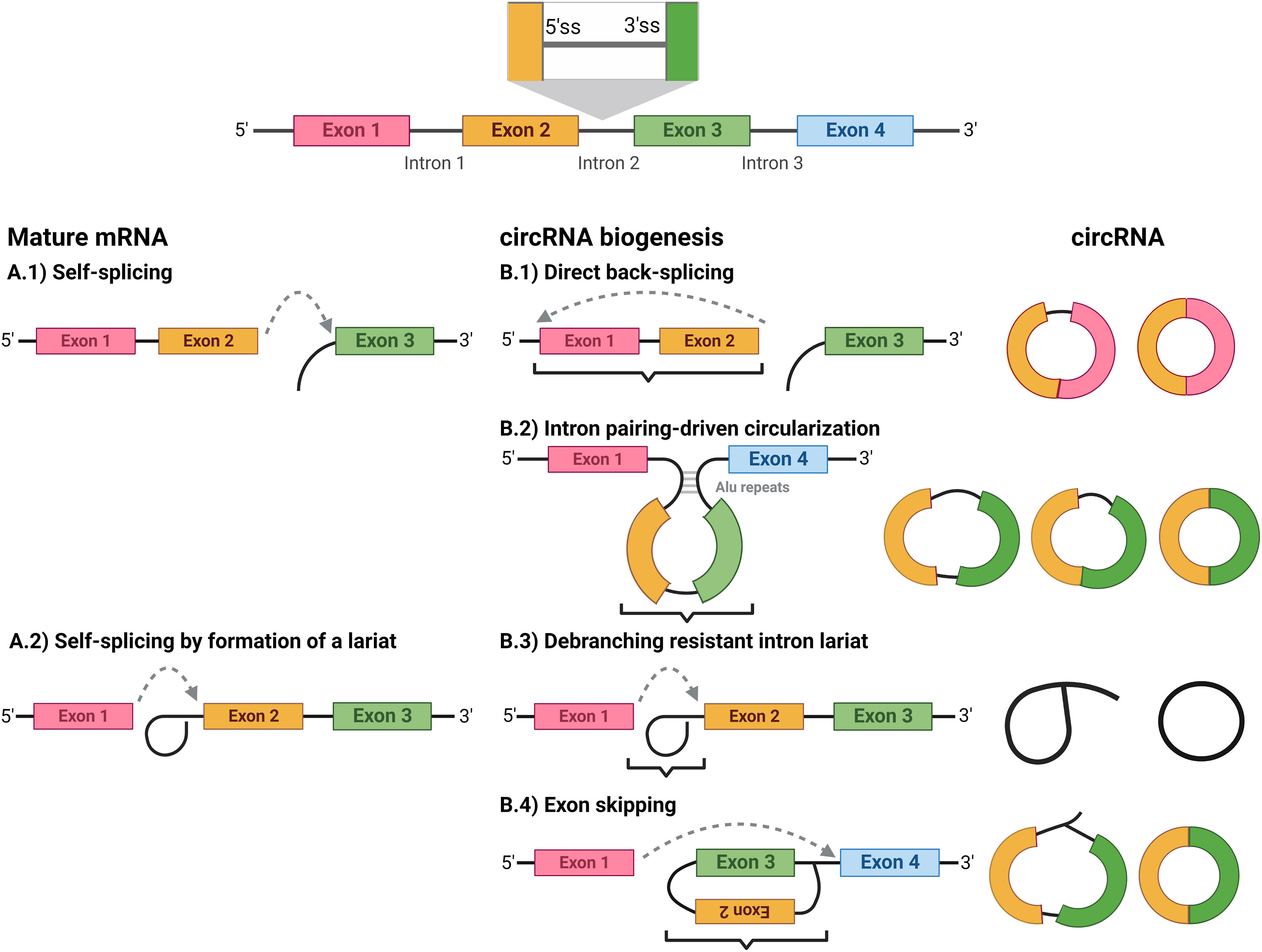
CircRNA
Circular RNA (or circRNA) is a type of single-stranded RNA which, unlike linear RNA, forms a covalently closed continuous loop. In circular RNA, the 3' and 5' ends normally present in an RNA molecule have been joined together. This feature confers numerous properties to circular RNA, many of which have only recently been identified. Many types of circular RNA arise from otherwise protein-coding genes. Some circular RNA has been shown to code for proteins. Some types of circular RNA have also recently shown potential as gene regulators. The biological function of most circular RNA is unclear. Because circular RNA does not have 5' or 3' ends, it is resistant to exonuclease-mediated degradation and is presumably more stable than most linear RNA in cells. Circular RNA has been linked to some diseases such as cancer. RNA splicing In contrast to genes in bacteria, eukaryotic genes are split by non-coding sequences called introns. In eukaryotes, as a gene is transcribed from DNA into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LncRNA
Long non-coding RNAs (long ncRNAs, lncRNA) are a type of RNA, generally defined as transcripts more than 200 nucleotides that are not translated into protein. This arbitrary limit distinguishes long ncRNAs from small non-coding RNAs, such as microRNAs (miRNAs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs), small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs), and other short RNAs. Long intervening/intergenic noncoding RNAs (lincRNAs) are sequences of lncRNA which do not overlap protein-coding genes. Long non-coding RNAs include intergenic lincRNAs, intronic ncRNAs, and sense and antisense lncRNAs, each type showing different genomic positions in relation to genes and exons. Abundance In 2007 a study found only one-fifth of transcription across the human genome is associated with protein-coding genes, indicating at least four times more long non-coding than coding RNA sequences. Large-scale complementary DNA (cDNA) sequencing projects such as FANTOM reveal the complexity of this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |