|
CIN3
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), also known as cervical dysplasia, is the abnormal growth of cells on the surface of the cervix that could potentially lead to cervical cancer. More specifically, CIN refers to the potentially Precancerous condition, precancerous transformation of cells of the cervix. CIN most commonly occurs at the Transformation zone, squamocolumnar junction of the cervix, a transitional area between the Squamous epithelial cell, squamous epithelium of the vagina and the columnar epithelium of the endocervix. It can also occur in vaginal walls and vulvar epithelium. CIN is graded on a 1–3 scale, with 3 being the most abnormal (see classification section below). Human papillomavirus (Human papillomavirus infection, HPV) infection is necessary for the development of CIN, but not all with this infection develop cervical cancer. Many women with HPV infection never develop CIN or cervical cancer. Typically, HPV resolves on its own. However, those with an HPV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is a cancer arising from the cervix or in any layer of the wall of the cervix. It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that can invade or spread to other parts of the body. Early on, typically no symptoms are seen. Later symptoms may include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain or pain during sexual intercourse. While bleeding after sex may not be serious, it may also indicate the presence of cervical cancer. Virtually all cervical cancer cases (99%) are linked to genital human papillomavirus infection (HPV); most who have had HPV infections, however, do not develop cervical cancer. HPV 16 and 18 strains are responsible for approximately 70% of cervical cancer cases globally and nearly 50% of high grade cervical pre-cancers. Minor risk factors include smoking, a weak immune system, birth control pills, starting sex at a young age, and having many sexual partners. Genetic factors also contribute to cervical cancer risk. Cervical cancer typically develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
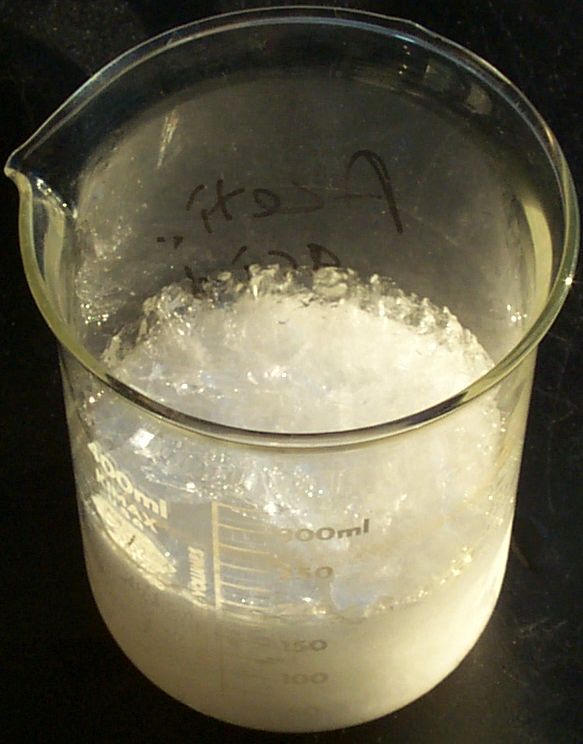
Acetic Acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water. Historically, vinegar was produced from the third century BC and was likely the first acid to be produced in large quantities. Acetic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid (after formic acid). It is an important Reagent, chemical reagent and industrial chemical across various fields, used primarily in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film, polyvinyl acetate for wood Adhesive, glue, and synthetic fibres and fabrics. In households, diluted acetic acid is often used in descaling agents. In the food industry, acetic acid is controlled by the E number, food additive code E260 as an acidity regulator and as a condiment. In biochemistry, the acetyl group, derived from acetic acid, is funda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelial Dysplasia
Epithelial dysplasia, a term becoming increasingly referred to as intraepithelial neoplasia, is the sum of various disturbances of epithelium, epithelial proliferation and differentiation as seen microscopically. Individual cellular features of dysplasia are called epithelial atypia. Examples of epithelial dysplasia include cervical intraepithelial neoplasia – a disorder commonly detected by an abnormal pap smear) consisting of an increased population of immature (basal-like) cells which are restricted to the mucosal surface, and have not invaded through the basement membrane to the deeper soft tissues. Analogous conditions include vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia and vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia. Metanephric dysplastic hematoma of the sacral region is a dysplastic overgrowth observed in infants. Screening Some tests which detect cancer could be called "screening for epithelial dysplasia". The principle behind these tests is that physicians expect dysplasia to occur at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LSIL (CIN 1), Cervical Biopsy (3776284166)
The Bethesda system (TBS), officially called The Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical Cytology, is a system for reporting cervical or vaginal cytologic diagnoses, used for reporting Pap smear results. It was introduced in 1988 and revised in 1991, 2001, and 2014. The name comes from the location (Bethesda, Maryland) of the conference, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, that established the system. Since 2010, there is also a Bethesda system used for cytopathology of thyroid nodules, which is called The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology (TBSRTC or BSRTC). Like TBS, it was the result of a conference sponsored by the NIH and is published in book editions (currently by Springer). Mentions of "the Bethesda system" without further specification usually refer to the cervical system, unless the thyroid context of a discussion is implicit. Cervix Abnormal results include: * Atypical squamous cells ** Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (AS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion
A squamous intraepithelial lesion (SIL) is an abnormal growth of squamous cells on the surface of the cervix; normal squamous cells make up the normal epithelium of the cervix. This lesion can progress to cervical cancer and can be diagnosed using a Pap smear or a colposcopy. It can be treated by using methods that remove the abnormal cells, allowing normal cells to grow in their place. In the Bethesda system, the cytology Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living an ... can be graded as LSIL (low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion) or HSIL (high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion). References Papillomavirus-associated diseases {{pathology-stub Cervical cancer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bethesda System
The Bethesda system (TBS), officially called The Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical Cytology, is a system for reporting cervical or vaginal cytologic diagnoses, used for reporting Pap smear results. It was introduced in 1988 and revised in 1991, 2001, and 2014. The name comes from the location (Bethesda, Maryland) of the conference, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, that established the system. Since 2010, there is also a Bethesda system used for cytopathology of thyroid nodules, which is called The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology (TBSRTC or BSRTC). Like TBS, it was the result of a conference sponsored by the NIH and is published in book editions (currently by Springer). Mentions of "the Bethesda system" without further specification usually refer to the cervical system, unless the thyroid context of a discussion is implicit. Cervix Abnormal results include: * Atypical squamous cells ** Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia (1) Normal Squamous Epithelium
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), also known as cervical dysplasia, is the abnormal growth of cells on the surface of the cervix that could potentially lead to cervical cancer. More specifically, CIN refers to the potentially precancerous transformation of cells of the cervix. CIN most commonly occurs at the squamocolumnar junction of the cervix, a transitional area between the squamous epithelium of the vagina and the columnar epithelium of the endocervix. It can also occur in vaginal walls and vulvar epithelium. CIN is graded on a 1–3 scale, with 3 being the most abnormal (see classification section below). Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is necessary for the development of CIN, but not all with this infection develop cervical cancer. Many women with HPV infection never develop CIN or cervical cancer. Typically, HPV resolves on its own. However, those with an HPV infection that lasts more than one or two years have a higher risk of developing a higher grade of CIN. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histology
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology that studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissue (biology), tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and ''cytology'', the study of cell (biology), cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous tumor of an ovary. It may originate from the ovary itself or more commonly from communicating nearby structures such as fallopian tubes or the inner lining of the abdomen. The ovary is made up of three different cell types including epithelial cells, germ cells, and stromal cells. When these cells become abnormal, they have the ability to divide and form tumors. These cells can also invade or spread to other parts of the body. When this process begins, there may be no or only vague symptoms. Symptoms become more noticeable as the cancer progresses. These symptoms may include bloating, vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, abdominal swelling, constipation, and loss of appetite, among others. Common areas to which the cancer may spread include the lining of the abdomen, lymph nodes, lungs, and liver. The risk of ovarian cancer increases with age. Most cases of ovarian cancer develop after menopause. It is also more common in women who have ovulated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterine Cancer
Uterine cancer, also known as womb cancer, includes two types of cancer that develop from the tissues of the uterus. Endometrial cancer forms from the lining of the uterus, and uterine sarcoma forms from the muscles or support tissue of the uterus. Endometrial cancer accounts for approximately 90% of all uterine cancers in the United States. Symptoms of endometrial cancer include changes in vaginal bleeding or pain in the pelvis. Symptoms of uterine sarcoma include unusual vaginal bleeding or a mass in the vagina. Risk factors for endometrial cancer include obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, taking pills that contain estrogen without progesterone, a history of tamoxifen use, late menopause, and a family history of the condition. Risk factors for uterine sarcoma include prior radiation therapy to the pelvis. Diagnosis of endometrial cancer is typically based on an endometrial biopsy. A diagnosis of uterine sarcoma may be suspected based on symptoms, a pelvic exam, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
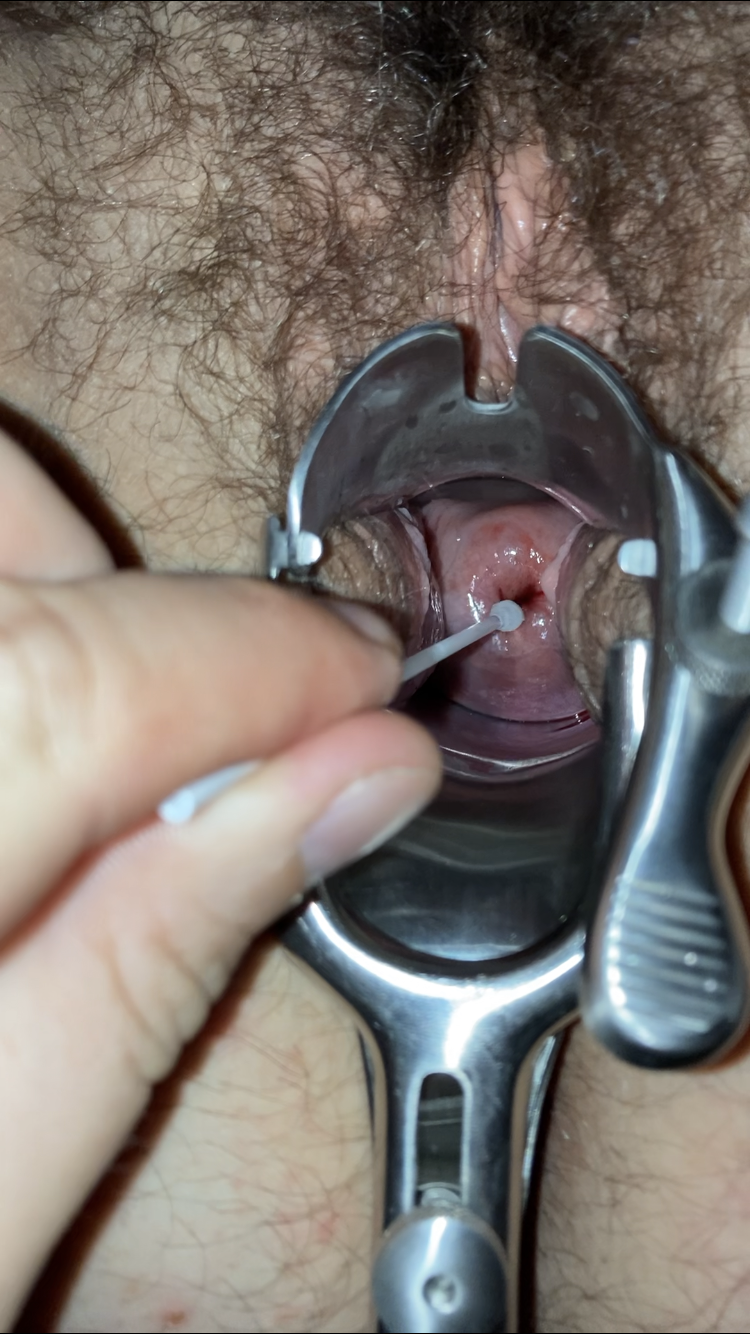
Colposcopy
Colposcopy ( + ''skopos'' 'look at') is a medical diagnostic procedure to visually examine the cervix as well as the vagina and vulva using a colposcope. The main goal of colposcopy is to prevent cervical cancer by detecting and treating precancerous lesions early. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a common infection and the underlying cause for most cervical cancers. Smoking also makes developing cervical abnormalities more likely. Other reasons for a patient to have a colposcopy include assessment of diethylstilbestrol (DES) exposure in utero, immunosuppression, abnormal appearance of the cervix or as a part of a sexual assault forensic examination. Colposcopy is done using a colposcope, which provides a magnified and illuminated view of the areas, allowing the colposcopist to visually distinguish normal from abnormal appearing tissue, such as damaged or abnormal changes in the tissue (lesions), and take directed biopsies for further pathological examination if needed. Colposc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pap Test
The Papanicolaou test (abbreviated as Pap test, also known as Pap smear (AE), cervical smear (BE), cervical screening (BE), or smear test (BE)) is a method of cervical screening used to detect potentially precancerous and cancerous processes in the cervix (opening of the uterus or womb) or, more rarely, anus (in both men and women). Abnormal findings are often followed up by more sensitive diagnostic procedures and, if warranted, interventions that aim to prevent progression to cervical cancer. The test was independently invented in the 1920s by the Greek physician Georgios Papanikolaou and named after him. A simplified version of the test was introduced by the Canadian obstetrician Anna Marion Hilliard in 1957. A Pap smear is performed by opening the vagina with a speculum and collecting cells at the outer opening of the cervix at the transformation zone (where the outer squamous cervical cells meet the inner glandular endocervical cells), using an Ayre spatula or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |