|
CHIP-8
CHIP-8 is an interpreted programming language, developed by Joseph Weisbecker made on his 1802 Microprocessor. It was initially used on the COSMAC VIP and Telmac 1800 8-bit microcomputers in the mid-1970s. CHIP-8 programs are run on a CHIP-8 virtual machine. It was made to allow video games to be more easily programmed for these computers. The simplicity of CHIP-8, and its long history and popularity, has ensured that CHIP-8 emulators and programs are still being made to this day. Roughly fifteen years after CHIP-8 was introduced, derived interpreters appeared for some models of graphing calculators (from the late 1980s onward, these handheld devices in many ways have more computing power than most mid-1970s microcomputers for hobbyists). An active community of users and developers existed in the late 1970s, beginning with ARESCO's "VIPer" newsletter whose first three issues revealed the machine code behind the CHIP-8 interpreter. CHIP-8 applications There are a number of cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
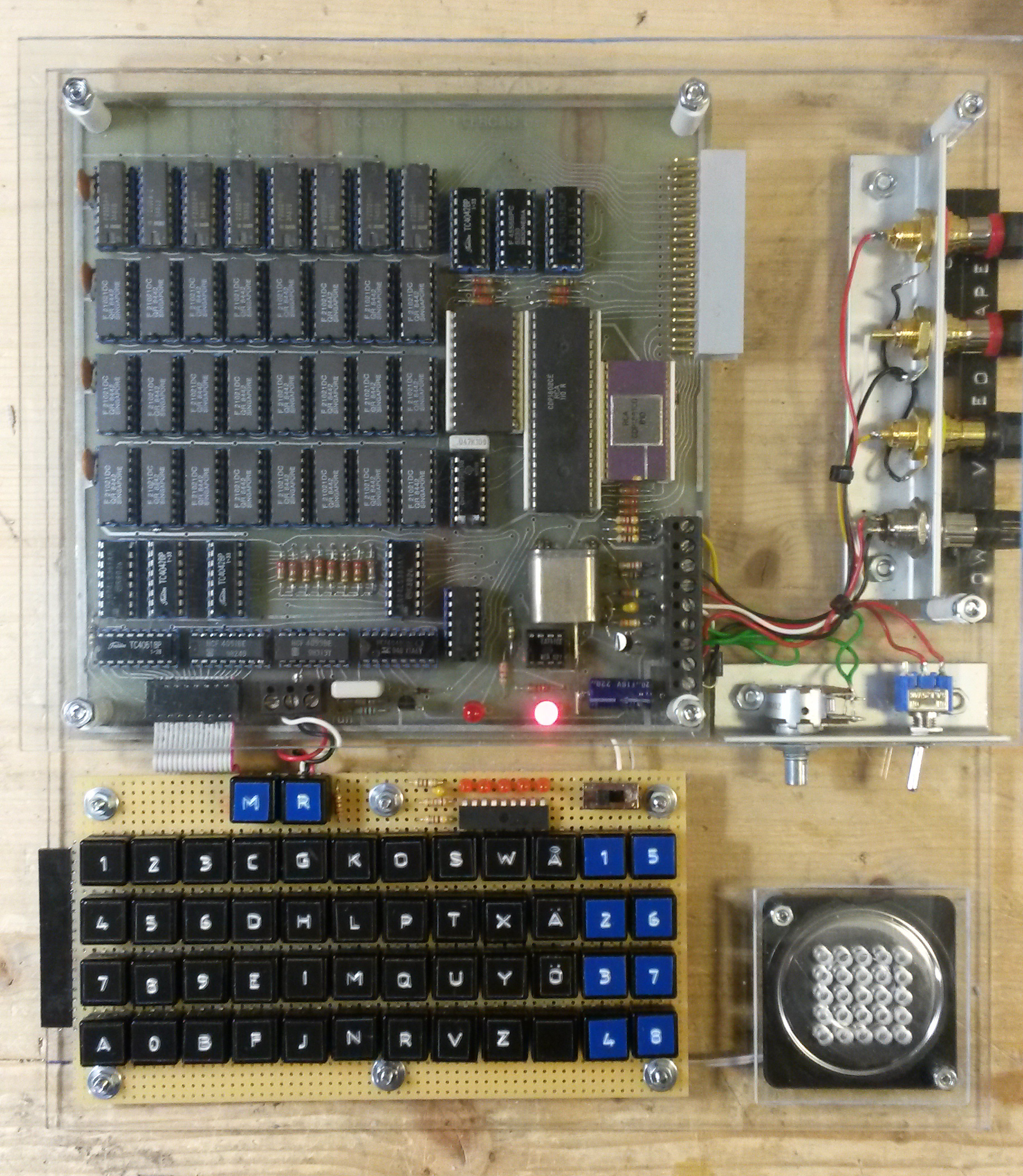
COSMAC VIP
The COSMAC VIP (1977) IP means Video Interface Processorwas an early microcomputer that was aimed at video games. Essentially, it was a COSMAC ELF with a supplementary CDP1861/CDP1864 video display chip. For a price of US$275, it could be purchased from RCA by mail order. It came in kit form, and had to be assembled. Its dimensions were 22 x 28 cm, and it had a RCA 1802 processor; along with a crystal clock operating at 1.76 MHz. It had 2 KB (2048 bytes) of RAM, which could be expanded to 4 KB on board, and 32 KB via an expansion slot. Its 5 V DC CDP18S023 power supply had an output of 600 mA. I/O ports could be added to connect to sensors, interface relays, an ASCII keyboard, or a printer. The machine connected to either a video monitor or to a TV with video input or by means of an external RF modulator. The VIP used a CDP1861/CDP1864 video display chip to generate the video output, and sound could be played using its integrated speaker. It had a 100 b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Weisbecker
Joseph A. Weisbecker (September 4, 1932 – November 15, 1990) was an early microprocessor and microcomputer researcher, as well as a gifted writer and designer of toys and games. He was a recipient of the David Sarnoff award for outstanding technical achievement, recipient of IEEE ''Computer'' magazine's "Best Paper" award, as well as several RCA lab awards for his work. His designs include the RCA 1800 and 1802 processors, the 1861 "Pixie" graphics chip, the RCA Microtutor, the COSMAC ELF, RCA Studio II, and COSMAC VIP computers. His daughter Joyce Weisbecker took to programming his prototypes, becoming the first female video game designer in the process, using his language called CHIP-8. Early career Professionally, Weisbecker began working with digital logic and computer systems in 1951. It was also his hobby, however, and even his early work is marked by designs that are intended for educational or hobbyist use. These include a hobby tic-tac-toe computer built from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RCA 1802
The COSMAC (Complementary Symmetry Monolithic Array Computer) is an 8-bit microprocessor family introduced by RCA. It is historically notable as the first CMOS microprocessor. The first production model was the two-chip CDP1801R and CDP1801U, which were later combined into the single-chip CDP1802. The 1802 represented the majority of COSMAC production, and today the entire line is known simply as the RCA 1802. The processor design traces its history to an experimental home computer designed by Joseph Weisbecker in the early 1970s, built at his home using TTL components. RCA began development of the CMOS version of the processor design in 1973, sampling it in 1974 with plans to move to a single-chip implementation immediately. Jerry Herzog led the design of the single-chip version, which sampled in 1975 and entered production in 1976. In contrast to most designs of the era, which were fabricated using the NMOS process, the COSMAC was implemented in CMOS form and used static ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telmac 1800
The Telmac 1800 was an early microcomputer delivered in kit form. It was introduced in 1977 by Telercas Oy, the Finnish importer of RCA microchips. Most of the 2,000 kits manufactured over four years were bought by electronics enthusiasts in Finland, Sweden and Norway. An expansion board, OSCOM, later became available, and included an alphanumeric video display, and up to of memory. A Tiny BASIC could be run on this configuration. The first-ever commercial video game to be developed in Finland, '' Chesmac'' ( fi), was developed by Raimo Suonio on a Telmac 1800 computer in 1979. The Telmac 1800 was followed by the Oscom Nano and the Telmac 2000. Major features * RCA 1802 (COSMAC) microprocessor CPU @ 1.75 MHz * Cassette tape interface * 2 kB RAM, expandable to 4 kB * RCA CDP1861 'Pixie' video chip, 64×128 pixels display resolution * Sound limited to a fixed frequency tone * Able to run a CHIP-8 interpreter References External linksRevival StudiosDeveloper of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PONG CHIP8
''Pong'' is a table tennis–themed twitch arcade sports video game, featuring simple two-dimensional graphics, manufactured by Atari and originally released in 1972. It was one of the earliest arcade video games; it was created by Allan Alcorn as a training exercise assigned to him by Atari co-founder Nolan Bushnell, but Bushnell and Atari co-founder Ted Dabney were surprised by the quality of Alcorn's work and decided to manufacture the game. Bushnell based the game's concept on an electronic ping-pong game included in the Magnavox Odyssey, the first home video game console. In response, Magnavox later sued Atari for patent infringement. ''Pong'' was the first commercially successful video game, and it helped to establish the video game industry along with the Magnavox Odyssey. Soon after its release, several companies began producing games that closely mimicked its gameplay. Eventually, Atari's competitors released new types of video games that deviated from ''Pong'''s orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emulator In computing, an emulator is hardware or software that enables one computer system (called the ''host'') to behave like another computer system (called the ''guest''). An emulator typically enables the host system to run software or use peripheral devices designed for the guest system. Emulation refers to the ability of a computer program in an electronic device to emulate (or imitate) another program or device. Many printers, for example, are designed to emulate HP LaserJet printers because so much software is written for HP printers. If a non-HP printer emulates an HP printer, any software written for a real HP printer will also run in the non-HP printer emulation and pro |