|
CHI3L1
Chitinase-3-like protein 1 (CHI3L1), also known as YKL-40, is a secreted glycoprotein that is approximately 40k Da in size that in humans is encoded by the ''CHI3L1'' gene. The name YKL-40 is derived from the three N-terminal amino acids present on the secreted form and its molecular mass. YKL-40 is expressed and secreted by various cell-types including macrophages, chondrocytes, fibroblast-like synovial cells, vascular smooth muscle cells, and hepatic stellate cells. The biological function of YKL-40 is unclear. It is not known to have a specific receptor. Its pattern of expression is associated with pathogenic processes related to inflammation, extracellular tissue remodeling, fibrosis and solid carcinomas and asthma. Function Chitinases catalyze the hydrolysis of chitin, which is an abundant glycopolymer found in insect exoskeletons and fungal cell walls. The glycoside hydrolase 18 family of chitinases includes eight human family members. This gene encodes a glycoprotein me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitinase
Chitinases (EC 3.2.1.14, chitodextrinase, 1,4-β-poly-N-acetylglucosaminidase, poly-β-glucosaminidase, β-1,4-poly-N-acetyl glucosamidinase, poly ,4-(N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminide)glycanohydrolase, (1→4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-β-D-glucan glycanohydrolase; systematic name (1→4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-β-D-glucan glycanohydrolase) are hydrolytic enzymes that break down glycosidic bonds in chitin. They catalyse the following reaction: : Random endo-hydrolysis of ''N''-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminide (1→4)-β-linkages in chitin and chitodextrins As chitin is a component of the cell walls of fungi and exoskeletal elements of some animals (including mollusks and arthropods), chitinases are generally found in organisms that either need to reshape their own chitin or dissolve and digest the chitin of fungi or animals. Species distribution Chitinivorous organisms include many bacteria ( Aeromonads, ''Bacillus'', ''Vibrio'', among others), which may be pathogenic or detritivorous. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NFIX
Nuclear factor 1 X-type is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NFIX'' gene. NFI-X3, a splice variant of NFIX, regulates Glial fibrillary acidic protein and YKL-40 in astrocytes. Interactions Nfix has been shown to interact with SKI protein and it is also known to interact with AP-1. NFI-X3 has been shown to interact with STAT3. In embryonic cells, Nfix has been shown to regulate intermediate progenitor cell (IPC) generation by promoting the transcription of the protein inscuteable (INSC). INSC regulates spindle orientation to facilitate the division of radial glia cells into IPC's. Nfix is thought to be necessary for the commitment of glia progeny into the intermediate progenitors. Mutations may cause overproduction of radial glia, impaired and improperly timed IPC development, and underproduction of neurons. In adult development, the timing of neural differentiation is regulated by Nfix to promote ongoing growth of the hippocampus and proper memory function. Nf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitinase
Chitinases (EC 3.2.1.14, chitodextrinase, 1,4-β-poly-N-acetylglucosaminidase, poly-β-glucosaminidase, β-1,4-poly-N-acetyl glucosamidinase, poly ,4-(N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminide)glycanohydrolase, (1→4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-β-D-glucan glycanohydrolase; systematic name (1→4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-β-D-glucan glycanohydrolase) are hydrolytic enzymes that break down glycosidic bonds in chitin. They catalyse the following reaction: : Random endo-hydrolysis of ''N''-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminide (1→4)-β-linkages in chitin and chitodextrins As chitin is a component of the cell walls of fungi and exoskeletal elements of some animals (including mollusks and arthropods), chitinases are generally found in organisms that either need to reshape their own chitin or dissolve and digest the chitin of fungi or animals. Species distribution Chitinivorous organisms include many bacteria ( Aeromonads, ''Bacillus'', ''Vibrio'', among others), which may be pathogenic or detritivorous. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chitin are produced each year in the biosphere. It is a primary component of cell walls in fungi (especially basidiomycetes and filamentous fungi), the exoskeletons of arthropods such as crustaceans and insects, the radulae, cephalopod beaks and gladii of molluscs and in some nematodes and diatoms. It is also synthesised by at least some fish and lissamphibians. Commercially, chitin is extracted from the shells of crabs, shrimps, shellfishes and lobsters, which are major by-products of the seafood industry. The structure of chitin is comparable to cellulose, forming crystalline nanofibrils or whiskers. It is functionally comparable to the protein keratin. Chitin has proved useful for several medicinal, industrial and biotechnological purpos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
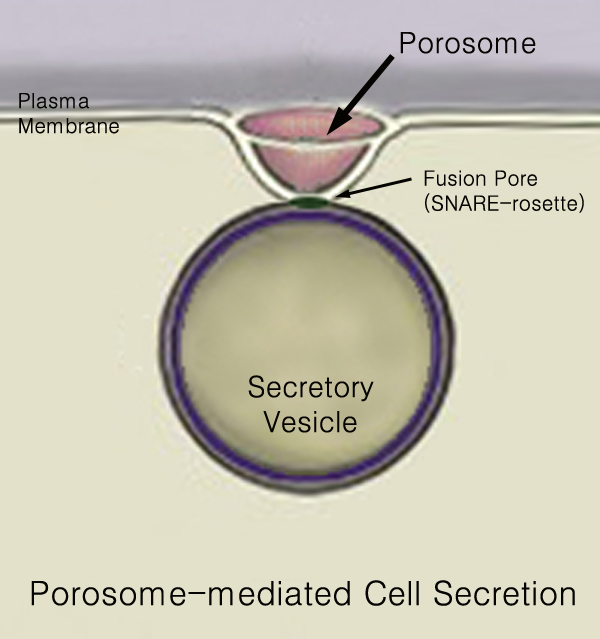
Secretion
440px Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. Secretion in bacterial species means the transport or translocation of effector molecules for example: proteins, enzymes or toxins (such as cholera toxin in pathogenic bacteria e.g. ''Vibrio cholerae'') from across the interior (cytoplasm or cytosol) of a bacterial cell to its exterior. Secretion is a very important mechanism in bacterial functioning and operation in their natural surrounding environment for adaptation and survival. In eukaryotic cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Killer Cell
Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells or large granular lymphocytes (LGL), are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system that belong to the rapidly expanding family of known innate lymphoid cells (ILC) and represent 5–20% of all circulating lymphocytes in humans. The role of NK cells is analogous to that of cytotoxic T cells in the vertebrate adaptive immune response. NK cells provide rapid responses to virus-infected cell and other intracellular pathogens acting at around 3 days after infection, and respond to tumor formation. Typically, immune cells detect the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) presented on infected cell surfaces, triggering cytokine release, causing the death of the infected cell by lysis or apoptosis. NK cells are unique, however, as they have the ability to recognize and kill stressed cells in the absence of antibodies and MHC, allowing for a much faster immune reaction. They were named "natural killers" because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IL13RA2
Interleukin-13 receptor subunit alpha-2 (IL-13Rα2), also known as CD213A2 (cluster of differentiation 213A2), is a membrane bound protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IL13RA2'' gene. Function IL-13Rα2 is closely related to IL-13Rα1, a subunit of the interleukin-13 receptor complex. This protein binds IL13 with high affinity, but lacks any significant cytoplasmic domain, and does not appear to function as a signal mediator. It is, however, able to regulate the effects of both IL-13 and IL-4, despite the fact it is unable to bind directly to the latter. It is also reported to play a role in the internalization of IL13. Clinical Significance IL-13Rα2 has been found to be over-expressed in a variety of cancers, including pancreatic, ovarian, melanomas, and malignant gliomas. See also * Interleukin-13 receptor The interleukin-13 receptor is a type I cytokine receptor, binding Interleukin-13. It consists of two subunits, encoded by IL13RA1 and IL4R, respec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NLRX1
NLRX1 or NLR family member X1, short for ''nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, leucine rich repeat containing X1'' is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NLRX1'' gene. It is also known as ''NOD-like receptor X1'', ''NLR family, X1'', NOD5, NOD9, and CLR11.3, and is a member of the NOD-like receptor family of pattern recognition receptors. Function NLRX1 is an intracellular protein that plays a role in the immune system. NLRX1 has been proposed to affect innate immunity to viruses by interfering with the mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein ( MAVS)/retinoic-acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) mitochondrial antiviral pathway., although this was recently questioned. NLRX1 also plays a role in host immunity during bacterial infections, such as ''Chlamydia trachomatis'' and ''Helicobacter pylori,'' by regulating bacterial burden and inflammation in mononuclear phagocytes. Mechanisms underlying the modulation of NLRX1 are not well characterized, however computational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SEMA7A
Semaphorin 7A, GPI membrane anchor (John Milton Hagen blood group) (SEMA7A) also known as CD108 (Cluster of Differentiation 108), is a human gene. SEMA7A is a membrane-bound semaphorin that associates with cell surfaces via a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) linkage. SEMA7A is also known as the John-Milton-Hagen (JMH) blood group antigen, an 80-kD glycoprotein expressed on activated lymphocytes and erythrocytes. upplied by OMIMref name="entrez"/> SEMA7A is expressed in various adult tissues such as adipose, colon, esophagus, heart, brain, spleen, testis, lung, ovary, and uterus. Development SEMA7A promotes axonal growth and is involved in mesoderm derived somite formation. Murine embryonic Sema7A expression is highest on day 7, which is indicative of its role on the differentiation of germ layer structure. Embryonic Sema7A expression is noticeable at all developmental stages as well as in the newborn and adult thymus, indicative of a development T-cell role. In wild type neuron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AP-1 Transcription Factor
Activator protein 1 (AP-1) is a transcription factor that regulates gene expression in response to a variety of stimuli, including cytokines, growth factors, stress, and bacterial and viral infections. AP-1 controls a number of cellular processes including differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. The structure of AP-1 is a heterodimer composed of proteins belonging to the c-Fos, c-Jun, ATF and JDP families. History AP-1 was first discovered as a TPA-activated transcription factor that bound to a cis-regulatory element of the human metallothionein IIa ( hMTIIa) promoter and SV40. The AP-1 binding site was identified as the 12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate ( TPA) response element (TRE) with the consensus sequence 5’-TGA G/C TCA-3’. The AP-1 subunit Jun was identified as a novel oncoprotein of avian sarcoma virus, and Fos-associated p39 protein was identified as the transcript of the cellular Jun gene. Fos was first isolated as the cellular homologue of two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STAT3
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is a transcription factor which in humans is encoded by the ''STAT3'' gene. It is a member of the STAT protein family. Function STAT3 is a member of the STAT protein family. In response to cytokines and growth factors, STAT3 is phosphorylated by receptor-associated Janus kinases (JAK), forms homo- or heterodimers, and translocates to the cell nucleus where it acts as a transcription activator. Specifically, STAT3 becomes activated after phosphorylation of tyrosine 705 in response to such ligands as interferons, epidermal growth factor (EGF), Interleukin (IL-)5 and IL-6. Additionally, activation of STAT3 may occur via phosphorylation of serine 727 by Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) and through c-src non-receptor tyrosine kinase. STAT3 mediates the expression of a variety of genes in response to cell stimuli, and thus plays a key role in many cellular processes such as cell growth and apoptosis. STAT3-deficien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |