|
CEP135
Centrosomal protein of 135 kDa is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CEP135'' gene. It is part of the centrosome throughout the cell cycle, being distributed in the pericentriolar material. CEP135 is required for the centriolar localization of CEP250 Centrosome-associated protein CEP250 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CEP250'' gene. This gene encodes a core centrosomal protein required for centriole-centriole cohesion during interphase of the cell cycle. The encoded protein di .... References External links * PDBe-KBprovides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human Centrosomal protein of 135 kDa Further reading * * * * * * {{gene-4-stub Centrosome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CEP250
Centrosome-associated protein CEP250 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CEP250'' gene. This gene encodes a core centrosomal protein required for centriole-centriole cohesion during interphase of the cell cycle. The encoded protein dissociates from the centrosomes when parental centrioles separate at the beginning of mitosis. The protein associates with and is phosphorylated by NIMA-related kinase 2, which is also associated with the centrosome. Furthermore, CEP135 Centrosomal protein of 135 kDa is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CEP135'' gene. It is part of the centrosome throughout the cell cycle, being distributed in the pericentriolar material Pericentriolar material (PCM, sometimes also cal ... is also required for the centriolar localization of CEP250. References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-20-stub Centrosome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrosome
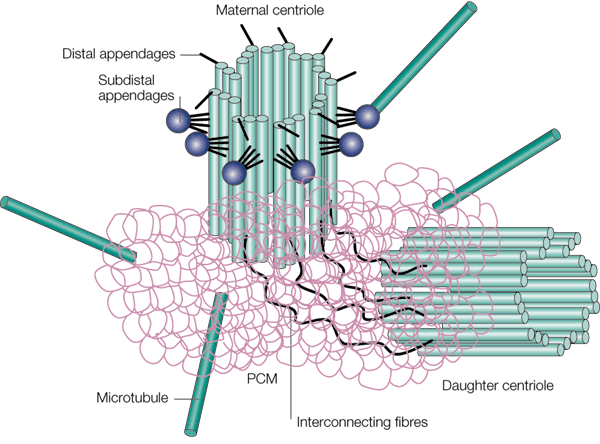
In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum 'center' + Greek sōma 'body') (archaically cytocentre) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center (MTOC) of the animal cell, as well as a regulator of cell-cycle progression. The centrosome provides structure for the cell. The centrosome is thought to have evolved only in the metazoan lineage of eukaryotic cells. Fungi and plants lack centrosomes and therefore use other structures to organize their microtubules. Although the centrosome has a key role in efficient mitosis in animal cells, it is not essential in certain fly and flatworm species. Centrosomes are composed of two centrioles arranged at right angles to each other, and surrounded by a dense, highly structured mass of protein termed the pericentriolar material (PCM). The PCM contains proteins responsible for microtubule nucleation and anchoring — including γ-tubulin, pericentrin and ninein. In general, each centriole of the centrosome is based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and subsequently the partitioning of its cytoplasm, chromosomes and other components into two daughter cells in a process called cell division. In cells with nuclei ( eukaryotes, i.e., animal, plant, fungal, and protist cells), the cell cycle is divided into two main stages: interphase and the mitotic (M) phase (including mitosis and cytokinesis). During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, and replicates its DNA and some of its organelles. During the mitotic phase, the replicated chromosomes, organelles, and cytoplasm separate into two new daughter cells. To ensure the proper replication of cellular components and division, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints after each of the key steps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericentriolar Material
Pericentriolar material (PCM, sometimes also called pericent matrix) is a highly structured, dense mass of protein which makes up the part of the animal centrosome that surrounds the two centrioles. The PCM contains proteins responsible for microtubule nucleation and anchoring including γ-tubulin, pericentrin and ninein. Although the PCM appears amorphous by electron microscopy, super-resolution microscopy finds that it is highly organized. The PCM have 9-fold symmetry that mimics the symmetry of the centriole. Some PCM proteins are organized such that one end of the protein is found near the centriole and the other end is farther away from the centriole. The PCM size is dynamic during the cell cycle. After cell division, the PCM size is reduced in a process named centrosome reduction.Atypical centrioles during sexual reproduction Tomer Avidor-Reiss*, Atul Khire, Emily L. Fishman and Kyoung H. Jo Curr Biol. 2015 Nov 16;25(22):2956-63. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.09.045. Epub 2015 Oct 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |