|
CASY Cell Counting Technology
CASY technology is an electric field multi-channel cell counting system. It was first marketed by Schärfe System GmbH in 1987 under the name CASY1. The first systems were sold with an ATARI computer and a rectangular chassis. In the 1990s the ATARI computer got replaced by a common PC and the chassis changed into cylinders. In 2006, Schärfe System was acquired by Innovatis AG, a company focused on cell culture analysis. CASY utilizes the techniques of electric current exclusion and pulse area analysis, the cells can be analyzed and counted in an efficient and precise manner. This technology can be applied for cell counting, cell culture analysis at a certain time interval, or even a period of time. Principle of CASY technology Cell viability can be assessed based on the integrity of plasma membrane: the living cells have intact plasma membranes whereas membranes of dead cells are broken. When a cell is exposed to a low voltage field, the electric current cannot go through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
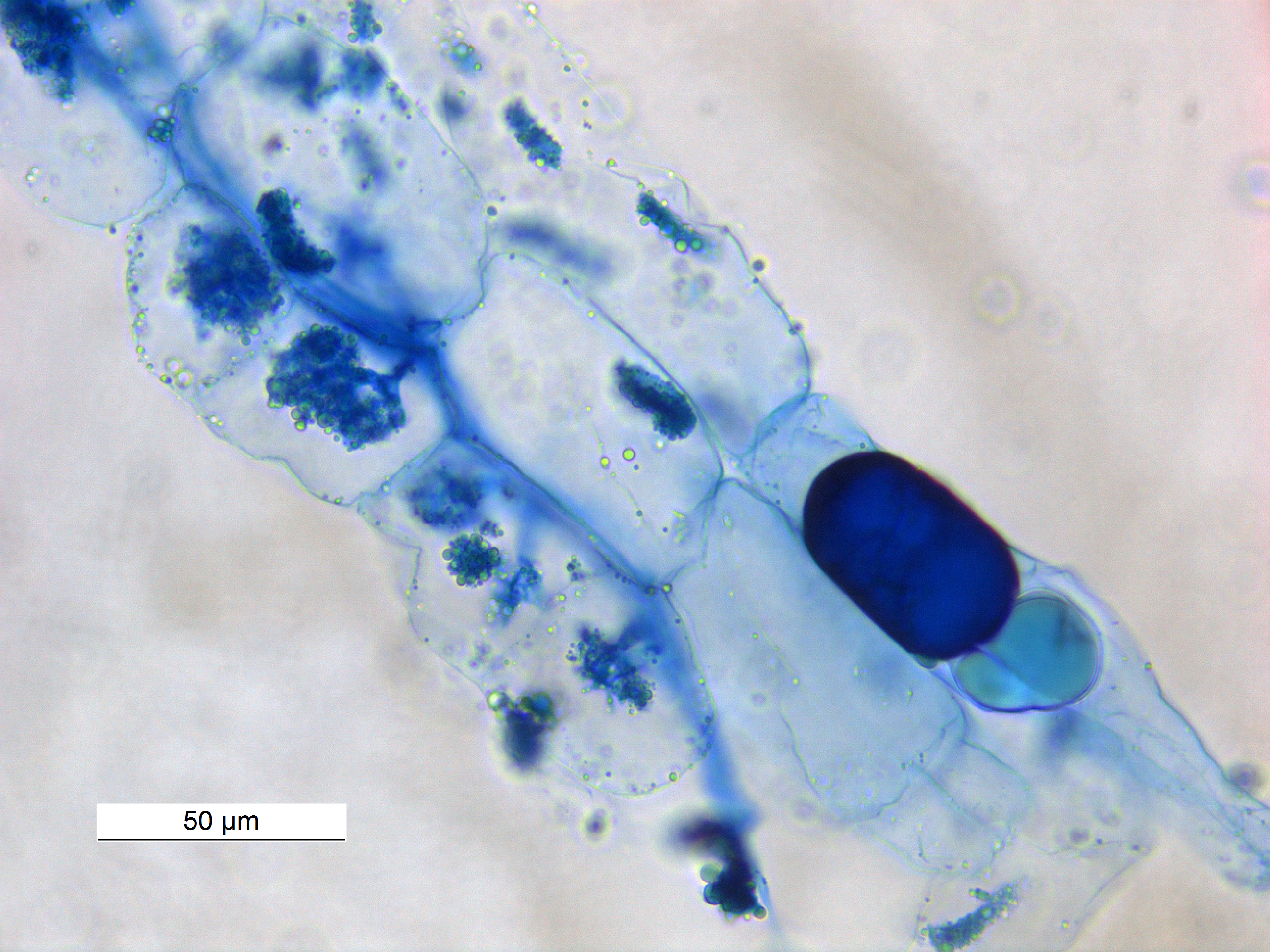
Cell Culture
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. The term "tissue culture" was coined by American pathologist Montrose Thomas Burrows. This technique is also called micropropagation. After the cells of interest have been isolated from living tissue, they can subsequently be maintained under carefully controlled conditions the need to be kept at body temperature (37 °C) in an incubator. These conditions vary for each cell type, but generally consist of a suitable vessel with a substrate or rich medium that supplies the essential nutrients (amino acids, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals), growth factors, hormones, and gases ( CO2, O2), and regulates the physio-chemical environment (pH buffer, osmotic pressure, temperature). Most cells require a surface or an artificial substrate to form an adherent culture as a monolayer (one single-cell thick), whereas others can be grown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Counting
Cell counting is any of various methods for the counting or similar quantification of cells in the life sciences, including medical diagnosis and treatment. It is an important subset of cytometry, with applications in research and clinical practice. For example, the complete blood count can help a physician to determine why a patient feels unwell and what to do to help. Cell counts within liquid media (such as blood, plasma, lymph, or laboratory rinsate) are usually expressed as a number of cells per unit of volume, thus expressing a concentration (for example, 5,000 cells per milliliter). Uses Numerous procedures in biology and medicine require the counting of cells. By the counting of cells in a known small volume, the concentration can be mediated. Examples of the need for cell counting include: * In medicine, the concentration of various blood cells, such as red blood cells and white blood cells, can give crucial information regarding the health situation of a person (see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles, being selectively permeable to ions an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Insulator
An electrical insulator is a material in which electric current does not flow freely. The atoms of the insulator have tightly bound electrons which cannot readily move. Other materials—semiconductors and conductors—conduct electric current more easily. The property that distinguishes an insulator is its resistivity; insulators have higher resistivity than semiconductors or conductors. The most common examples are non-metals. A perfect insulator does not exist because even insulators contain small numbers of mobile charges ( charge carriers) which can carry current. In addition, all insulators become electrically conductive when a sufficiently large voltage is applied that the electric field tears electrons away from the atoms. This is known as the breakdown voltage of an insulator. Some materials such as glass, paper and PTFE, which have high resistivity, are very good electrical insulators. A much larger class of materials, even though they may have lower bulk resistivit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrolyte
An electrolyte is a medium containing ions that is electrically conducting through the movement of those ions, but not conducting electrons. This includes most soluble salts, acids, and bases dissolved in a polar solvent, such as water. Upon dissolving, the substance separates into cations and anions, which disperse uniformly throughout the solvent. Solid-state electrolytes also exist. In medicine and sometimes in chemistry, the term electrolyte refers to the substance that is dissolved. Electrically, such a solution is neutral. If an electric potential is applied to such a solution, the cations of the solution are drawn to the electrode that has an abundance of electrons, while the anions are drawn to the electrode that has a deficit of electrons. The movement of anions and cations in opposite directions within the solution amounts to a current. Some gases, such as hydrogen chloride (HCl), under conditions of high temperature or low pressure can also function as electrolytes. El ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buffer
Buffer may refer to: Science * Buffer gas, an inert or nonflammable gas * Buffer solution, a solution used to prevent changes in pH * Buffering agent, the weak acid or base in a buffer solution * Lysis buffer, in cell biology * Metal ion buffer * Mineral redox buffer, in geology Technology and engineering * Buffer (GIS), a HASS zone around a map feature * Buffer (optical fiber), a GG component of a fiber optic cable * Buffer (rail transport), a device that cushions impacts between vehicles * Buffer amplifier, an isolating circuit used in electronics or telecommunications * Buffer stop, a device that keeps rail vehicles on tracks * Buffer wheel, a device used to smooth a workpiece's surface * Digital buffer, an electronic circuit used to isolate the input from the output * Floor buffer, an appliance used to polish hard floors * Optical buffer, a device that stores optically transmitted data * Recoil buffer, a firearm component * Seismic buffers, protect structures against the ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry (FC) is a technique used to detect and measure physical and chemical characteristics of a population of cells or particles. In this process, a sample containing cells or particles is suspended in a fluid and injected into the flow cytometer instrument. The sample is focused to ideally flow one cell at a time through a laser beam, where the light scattered is characteristic to the cells and their components. Cells are often labeled with fluorescent markers so light is absorbed and then emitted in a band of wavelengths. Tens of thousands of cells can be quickly examined and the data gathered are processed by a computer. Flow cytometry is routinely used in basic research, clinical practice, and clinical trials. Uses for flow cytometry include: * Cell counting * Cell sorting * Determining cell characteristics and function * Detecting microorganisms * Biomarker detection * Protein engineering detection * Diagnosis of health disorders such as blood cancers * Measuring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trypan Blue
Trypan blue is an azo dye. It is a direct dye for cotton textiles. In biosciences, it is used as a vital stain to selectively colour dead tissues or cells blue. Live cells or tissues with intact cell membranes are not coloured. Since cells are very selective in the compounds that pass through the membrane, in a viable cell trypan blue is not absorbed; however, it traverses the membrane in a dead cell. Hence, dead cells appear as a distinctive blue colour under a microscope. Since live cells are excluded from staining, this staining method is also described as a dye exclusion method. Background and chemistry Trypan blue is derived from toluidine, that is, any of several isomeric bases, C14H16N2, derived from toluene. Trypan blue is so-called because it can kill trypanosomes, the parasites that cause sleeping sickness. An analog of trypan blue, suramin, is used pharmacologically against trypanosomiasis. Trypan blue is also known as diamine blue and Niagara blue. The extinctio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propidium Iodide
Propidium iodide (or PI) is a fluorescent intercalating agent that can be used to stain cells and nucleic acids. PI binds to DNA by intercalating between the bases with little or no sequence preference. When in an aqueous solution, PI has a fluorescent excitation maximum of 493 nm (blue-green), and an emission maximum of 636 nm (red). After binding DNA, the quantum yield of PI is enhanced 20-30 fold, and the excitation/emission maximum of PI is shifted to 535 nm (green) / 617 nm (orange-red). Propidium iodide is used as a DNA stain in flow cytometry to evaluate cell viability or DNA content in cell cycle analysis, or in microscopy to visualize the nucleus and other DNA-containing organelles. Propidium Iodide is not membrane-permeable, making it useful to differentiate necrotic, apoptotic and healthy cells based on membrane integrity. PI also binds to RNA, necessitating treatment with nucleases to distinguish between RNA and DNA staining. PI is widely used in fluorescence stai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MTT Assay
The MTT assay is a colorimetric assay for assessing cell metabolic activity. NAD(P)H-dependent cellular oxidoreductase enzymes may, under defined conditions, reflect the number of viable cells present. These enzymes are capable of reducing the tetrazolium dye MTT, which is chemically 3-(4,5- di methyl thiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide, to its insoluble formazan, which has a purple color. Other closely related tetrazolium dyes including XTT, MTS and the WSTs, are used in conjunction with the intermediate electron acceptor, 1-methoxy phenazine methosulfate (PMS). With WST-1, which is cell-impermeable, reduction occurs outside the cell via plasma membrane electron transport. However, this traditionally assumed explanation is currently contended as proof has also been found of MTT reduction to formazan in lipidic cellular structures without apparent involvement of oxidoreductases. Tetrazolium dye assays can also be used to measure cytotoxicity (loss of viable cells) or cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coulter Counter
A Coulter counter is an apparatus for counting and sizing particles suspended in electrolytes. The Coulter counter is the commercial term for the technique known as resistive pulse sensing or electrical zone sensing, the apparatus is based on The Coulter principle named after its inventor, Wallace H. Coulter. A typical Coulter counter has one or more microchannels that separate two chambers containing electrolyte solutions. As fluid-containing particles or cells are drawn through each microchannel, each particle causes a brief change to the electrical resistance of the liquid. The counter detects these changes in the electrical resistance. Coulter principle The ''Coulter principle'' states that particles pulled through an orifice, concurrent with an electric current, produce a change in impedance that is proportional to the volume of the particle traversing the orifice. This pulse in impedance originates from the displacement of electrolyte caused by the particle. The princi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |