|
C9orf72
C9orf72 (chromosome 9 open reading frame 72) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the gene ''C9orf72''. The human ''C9orf72'' gene is located on the short (p) arm of chromosome 9 open reading frame 72, from base pair 27,546,546 to base pair 27,573,866 (GRCh38). Its cytogenetic location is at 9p21.2. The protein is found in many regions of the brain, in the cytoplasm of neurons as well as in presynaptic terminals. Disease-causing mutations in the gene were first discovered by two independent research teams, led by Rosa Rademakers of Mayo Clinic and Bryan Traynor of the National Institutes of Health, and were first reported in October 2011. The mutations in ''C9orf72'' are significant because it is the first pathogenic mechanism identified to be a genetic link between familial frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). It is the most common mutation identified that is associated with familial FTD and/or ALS. Gene location Cytogenetic Location ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or Lou Gehrig's disease, is a neurodegenerative disease that results in the progressive loss of motor neurons that control voluntary muscles. ALS is the most common type of motor neuron diseases. Early symptoms of ALS include stiff muscles, muscle twitches, and gradual increasing weakness and muscle wasting. ''Limb-onset ALS'' begins with weakness in the arms or legs, while ''bulbar-onset ALS'' begins with difficulty speaking or swallowing. Half of the people with ALS develop at least mild difficulties with thinking and behavior, and about 15% develop frontotemporal dementia. Most people experience pain. The affected muscles are responsible for chewing food, speaking, and walking. Motor neuron loss continues until the ability to eat, speak, move, and finally the ability to breathe is lost. ALS eventually causes paralysis and early death, usually from respiratory failure. Most cases of ALS (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Neuron Disease
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or Lou Gehrig's disease, is a neurodegenerative disease that results in the progressive loss of motor neurons that control voluntary muscles. ALS is the most common type of motor neuron diseases. Early symptoms of ALS include stiff muscles, muscle twitches, and gradual increasing weakness and muscle wasting. ''Limb-onset ALS'' begins with weakness in the arms or legs, while ''bulbar-onset ALS'' begins with difficulty speaking or swallowing. Half of the people with ALS develop at least mild difficulties with thinking and behavior, and about 15% develop frontotemporal dementia. Most people experience pain. The affected muscles are responsible for chewing food, speaking, and walking. Motor neuron loss continues until the ability to eat, speak, move, and finally the ability to breathe is lost. ALS eventually causes paralysis and early death, usually from respiratory failure. Most cases of ALS (abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAN Translation
Repeat Associated Non-AUG translation, or RAN translation, is an irregular mode of mRNA translation that can occur in eukaryotic cells. Mechanism For the majority of eukaryotic messenger RNAs (mRNAs), translation initiates from a methionine-encoding AUG start codon following the molecular processes of 'cap-binding' and 'scanning' by ribosomal pre-initiation complexes (PICs). In rare exceptions, such as translation by viral IRES-containing mRNAs, 'cap-binding' and/or 'scanning' are not required for initiation, although AUG is still typically used as the first codon. RAN translation is an exception to the canonical rules as it uses variable start site selection and initiates from a non-AUG codon, but may still depend on 'cap-binding' and 'scanning'. Disease RAN translation produces a variety of dipeptide repeat proteins by translation of expanded hexanucleotide repeats present in an intron of the C9orf72 gene. The expansion of the hexanucleotide repeats and thus accumulation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontotemporal Dementia
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD), or frontotemporal degeneration disease, or frontotemporal neurocognitive disorder, encompasses several types of dementia involving the progressive degeneration of frontal and temporal lobes. FTDs broadly present as behavioral or language disorders with gradual onsets. The three main subtypes or variant syndromes are a behavioral variant (bvFTD) previously known as ''Pick's disease'', and two variants of primary progressive aphasia – semantic variant (svPPA), and nonfluent variant (nfvPPA). Two rare distinct subtypes of FTD are neuronal intermediate filament inclusion disease (NIFID), and basophilic inclusion body disease. Other related disorders include corticobasal syndrome and FTD with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) ''FTD-ALS'' also called ''FTD- MND''. Frontotemporal dementias are mostly early-onset syndromes that are linked to frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD), which is characterized by progressive neuronal loss predominantl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinucleotide Repeat Disorder
Trinucleotide repeat disorders, also known as microsatellite expansion diseases, are a set of over 50 genetic disorders caused by trinucleotide repeat expansion, a kind of mutation in which repeats of three nucleotides ( trinucleotide repeats) increase in copy numbers until they cross a threshold above which they become unstable. Depending on its location, the unstable trinucleotide repeat may cause defects in a protein encoded by a gene; change the regulation of gene expression; produce a toxic RNA, or lead to chromosome instability. In general, the larger the expansion the faster the onset of disease, and the more severe the disease becomes. Trinucleotide repeats are a subset of a larger class of unstable microsatellite repeats that occur throughout all genomes. The first trinucleotide repeat disease to be identified was fragile X syndrome, which has since been mapped to the long arm of the X chromosome. Patients carry from 230 to 4000 CGG repeats in the gene that causes fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosa Rademakers
Rosa Rademakers, Ph.D., is a neurogeneticist and professor within the Department of Neuroscience at the Mayo Clinic. Her research centers on the genetic basis of neurodegenerative diseases, such as identifying causal genes and their function, exploring familial risk factors, and the mechanism of the degeneration. Her neurodegenerative diseases of focus include " Alzheimer's disease (AD), frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)." She received a Bachelor of Arts in Biology, a Master of Arts in Biochemistry, and a Ph.D. in Science, all from the University of Antwerp. Originally from the Netherlands, she came to the Mayo Clinic in 2005 for a post-doctoral fellowship, and in 2007 she was given a lab director position. Scientific research focus areas Rademakers has researched mutations within genetic regulators of progranulin (GRN), which can cause early-onset dementia. She worked to develop a test to identify carriers of this mutation. This blood test ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
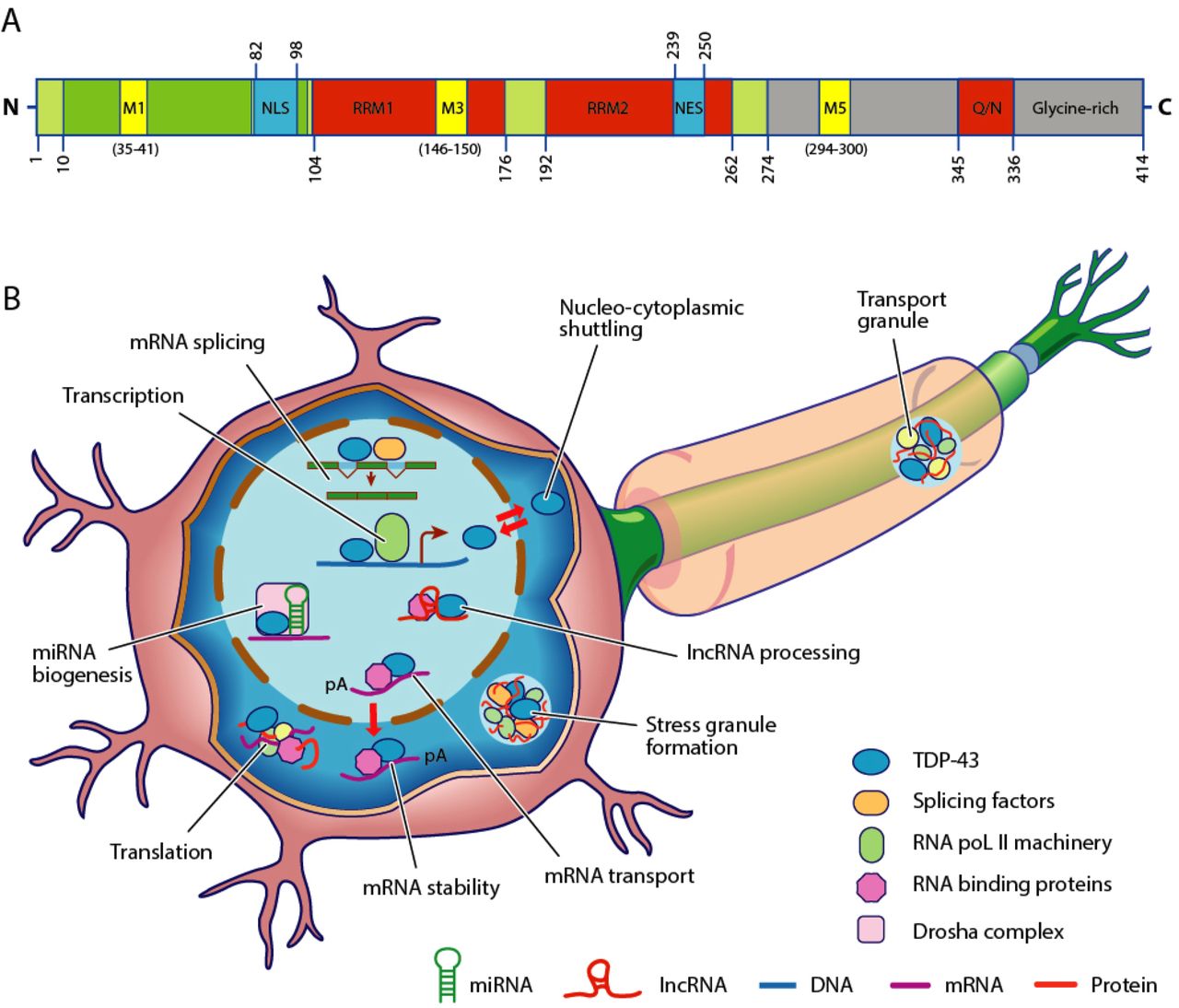
TDP-43
TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43, transactive response DNA binding protein 43 kDa) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TARDBP'' gene. Structure TDP-43 is 414 amino acid residues long. It consists of 4 domains: an N-terminal domain spanning residues 1-76 (NTD) with a well-defined fold that has been shown to form a dimer or oligomer; 2 highly conserved folded RNA recognition motifs spanning residues 106-176 (RRM1) and 191-259 (RRM2), respectively, required to bind target RNA and DNA; an unstructured C-terminal domain encompassing residues 274-414 (CTD), which contains a glycine-rich region, is involved in protein-protein interactions, and harbors most of the mutations associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. The entire protein devoid of large solubilising tags has been purified. The full-length protein is a dimer. The dimer is formed due to a self-interaction between two NTD domains, where the dimerisation can be propagated to form higher-order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor
Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are proteins or protein domains that activate monomeric GTPases by stimulating the release of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) to allow binding of guanosine triphosphate (GTP). A variety of unrelated structural domains have been shown to exhibit guanine nucleotide exchange activity. Some GEFs can activate multiple GTPases while others are specific to a single GTPase. Function Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are proteins or protein domains involved in the activation of small GTPases. Small GTPases act as molecular switches in intracellular signaling pathways and have many downstream targets. The most well-known GTPases comprise the Ras superfamily and are involved in essential cell processes such as cell differentiation and proliferation, cytoskeletal organization, vesicle trafficking, and nuclear transport. GTPases are active when bound to GTP and inactive when bound to GDP, allowing their activity to be regulated by GEFs and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small GTPase
Small GTPases (), also known as small G-proteins, are a family of hydrolase enzymes that can bind and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP). They are a type of G-protein found in the cytosol that are homologous to the alpha subunit of heterotrimeric G-proteins, but unlike the alpha subunit of G proteins, a small GTPase can function independently as a hydrolase enzyme to bind to and hydrolyze a guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to form guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The best-known members are the Ras GTPases and hence they are sometimes called Ras subfamily GTPases. A typical G-protein is active when bound to GTP and inactive when bound to GDP (i.e. when the GTP is hydrolyzed to GDP). The GDP can be then replaced by free GTP. Therefore, a G-protein can be switched on and off. GTP hydrolysis is accelerated by GTPase activating proteins (GAPs), while GTP exchange is catalyzed by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs). Activation of a GEF typically activates its cognate G-protein, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rab (G-protein)
The Rab family of proteins is a member of the Ras superfamily of small G proteins. Approximately 70 types of Rabs have now been identified in humans. Rab proteins generally possess a GTPase fold, which consists of a six-stranded beta sheet which is flanked by five alpha helices. Rab GTPases regulate many steps of membrane trafficking, including vesicle formation, vesicle movement along actin and tubulin networks, and membrane fusion. These processes make up the route through which cell surface proteins are trafficked from the Golgi to the plasma membrane and are recycled. Surface protein recycling returns proteins to the surface whose function involves carrying another protein or substance inside the cell, such as the transferrin receptor, or serves as a means of regulating the number of a certain type of protein molecules on the surface. Function Rab proteins are peripheral membrane proteins, anchored to a membrane via a lipid group covalently linked to an amino acid. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Founder Effect
In population genetics, the founder effect is the loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established by a very small number of individuals from a larger population. It was first fully outlined by Ernst Mayr in 1942, using existing theoretical work by those such as Sewall Wright. As a result of the loss of genetic variation, the new population may be distinctively different, both genotypically and phenotypically, from the parent population from which it is derived. In extreme cases, the founder effect is thought to lead to the speciation and subsequent evolution of new species. In the figure shown, the original population has nearly equal numbers of blue and red individuals. The three smaller founder populations show that one or the other color may predominate (founder effect), due to random sampling of the original population. A population bottleneck may also cause a founder effect, though it is not strictly a new population. The founder effect occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Anticipation
In genetics, anticipation is a phenomenon whereby as a genetic disorder is passed on to the next generation, the symptoms of the genetic disorder become apparent at an earlier age with each generation. In most cases, an increase in the severity of symptoms is also noted. Anticipation is common in trinucleotide repeat disorders, such as Huntington's disease and myotonic dystrophy, where a dynamic mutation in DNA occurs. All of these diseases have neurological symptoms. Prior to the understanding of the genetic mechanism for anticipation, it was debated whether anticipation was a true biological phenomenon or whether the earlier age of diagnosis was related to heightened awareness of disease symptoms within a family. Trinucleotide repeats and expansion Trinucleotide repeats are apparent in a number of loci in the human genome. They have been found in introns, exons and 5' or 3' UTR's. They consist of a pattern of three nucleotides (e.g. CGG) which is repeated a number of times. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |