|
C1 Esterase Inhibitor Deficiency
Acquired C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency, also referred to as acquired angioedema (AAE), is a rare medical condition that presents as body swelling that can be life-threatening and manifests due to another underlying medical condition.. The acquired form of this disease can occur from a deficiency or abnormal function of the enzyme C1 esterase inhibitor (C1-INH). This disease is also abbreviated in medical literature as C1INH-AAE. This form of angioedema is considered acquired due to its association with lymphatic malignancies, immune system disorders, or infections. Typically, acquired angioedema presents later in adulthood, in contrast to hereditary angioedema which usually presents from early childhood and with similar symptoms. Acquired angioedema is usually found after recurrent episodes of swelling and can in some cases take several months to diagnose. Diagnosis usually consists of medical evaluation in addition to laboratory testing. Laboratory evaluation includes complement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angioedema Of The Face
Angioedema is an area of swelling (edema) of the dermis, lower layer of skin and subcutaneous tissue, tissue just under the skin or mucous membranes. The swelling may occur in the face, tongue, larynx, abdomen, or arms and legs. Often it is associated with hives, which are swelling within the upper skin. Onset is typically over minutes to hours. The underlying mechanism typically involves histamine or bradykinin. The version related to histamine is due to an allergic reaction to agents such as insect bites, foods, or medications. The version related to bradykinin may occur due to an heredity, inherited problem known as C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency, medications known as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, or a lymphoproliferative disorder. Treatment to protect the airway may include intubation or cricothyroidotomy. Histamine-related angioedema can be treated with antihistamines, corticosteroids, and epinephrine. In those with bradykinin-related disease a C1 esterase in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retrospective Cohort Study
A retrospective cohort study, also called a historic cohort study, is a longitudinal cohort study used in medical and psychological research. A cohort of individuals that share a common exposure factor is compared with another group of equivalent individuals not exposed to that factor, to determine the factor's influence on the incidence of a condition such as disease or death. Retrospective cohort studies have existed for approximately as long as prospective cohort studies. Design The retrospective cohort study compares groups of individuals who are alike in many ways but differ by a certain characteristic (for example, female nurses who smoke and ones who do not smoke) in terms of a particular outcome (such as lung cancer). Data on the relevant events for each individual (the form and time of exposure to a factor, the latent period, and the time of any subsequent occurrence of the outcome) are collected from existing records and can immediately be analyzed to determine the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperviscosity Syndrome
Hyperviscosity syndrome is a group of symptoms triggered by an increase in the viscosity of the blood. Symptoms of high blood viscosity include spontaneous bleeding from mucous membranes, visual disturbances due to retinopathy, and neurologic symptoms ranging from headache and vertigo to seizures and coma. Hyperviscosity occurs from pathologic changes of either cellular or protein fractions of the blood such as is found in polycythemias, multiple myeloma (particularly IgA and IgG3), leukemia, monoclonal gammopathies such as Waldenström macroglobulinemia, sickle cell anemia, and sepsis. Types of hyperviscosity syndromes vary by pathology; including serum hyperviscosity, which may cause neurologic or ocular disorders; polycythemic hyperviscosity, which results in reduced blood flow or capillary perfusion and increased organ congestion; and syndromes of hyperviscosity, caused by reduced deformability of red blood cells, often evident in sickle cell anemia. Cause High cell cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, the symptoms are often vague, such as tiredness, weakness, shortness of breath, headaches, and a reduced ability to exercise. When anemia is acute, symptoms may include confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out, loss of consciousness, and increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Symptoms of anemia depend on how quickly hemoglobin decreases. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause. Preoperative anemia can increase the risk of needing a blood transfusion following surgery. Anemia can be temporary or long term and can range from mild to severe. Anemia can be caused by blood loss, decreased red blood cell production, and increased red blood cell breakdown. Causes o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
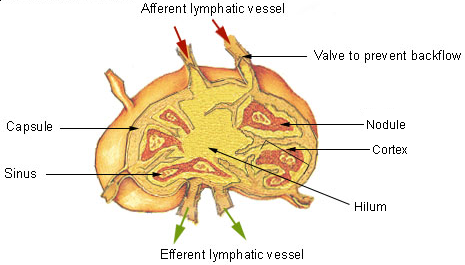
Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid organs, and lymphoid tissues. The vessels carry a clear fluid called lymph (the Latin word ''lympha'' refers to the deity of fresh water, "Lympha") back towards the heart, for re-circulation. Unlike the circulatory system that is a closed system, the lymphatic system is open. The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood per day through capillary filtration, which removes plasma from the blood. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered blood is reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining three litres are left in the interstitial fluid. One of the main functions of the lymphatic system is to provide an accessory return route to the blood for the surplus three litres. The other main function is that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-cell Malignancies
Lymphoid leukemias are a group of leukemias affecting circulating lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell. The lymphocytic leukemias are closely related to lymphomas of the lymphocytes, to the point that some of them are unitary disease entities that can be called by either name (for example, adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma). Such diseases are all lymphoproliferative disorders. Most lymphoid leukemias involve a particular subtype of lymphocytes, the B cells. Classification Historically, they have been most commonly divided by the stage of maturation at which the clonal (neoplastic) lymphoid population stopped maturing: * Acute lymphoblastic leukemia * Chronic lymphocytic leukemia However, the influential WHO Classification (published in 2001) emphasized a greater emphasis on cell lineage. To this end, lymphoid leukemias can also be divided by the type of cells affected: * B-cell leukemia * T-cell leukemia * NK-cell leukemia The most common type of lymphoid leukemia is B-cell ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Failure
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as either acute kidney failure, which develops rapidly and may resolve; and chronic kidney failure, which develops slowly and can often be irreversible. Symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications of acute and chronic failure include uremia, high blood potassium, and volume overload. Complications of chronic failure also include heart disease, high blood pressure, and anemia. Causes of acute kidney failure include low blood pressure, blockage of the urinary tract, certain medications, muscle breakdown, and hemolytic uremic syndrome. Causes of chronic kidney failure include diabetes, high blood pressure, nephrotic syndrome, and polycystic kidney disease. Diagnosis of acute failure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
End Organ Damage
End organ damage usually refers to damage occurring in major organs fed by the circulatory system (heart, kidneys, brain, eyes) which can sustain damage due to uncontrolled hypertension, hypotension, or hypovolemia. Evidence of hypertensive damage In the context of hypertension, features include: * Heart - evidence on electrocardiogram screening of the heart muscle thickening (but may also be seen on chest X-ray) suggesting left ventricular hypertrophy) or by echocardiography of less efficient function (left ventricular failure). * Brain- hypertensive encephalopathy, hemorrhagic stroke, subarachnoid hemorrhage, confusion, loss of consciousness, eclampsia, seizures, or transient ischemic attack. * Kidney - leakage of protein into the urine (albuminuria or proteinuria), or reduced renal function, hypertensive nephropathy, acute renal failure, or glomerulonephritis. * Eye - evidence upon fundoscopic examination of hypertensive retinopathy, retinal hemorrhage, papilledema and bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclonal Paraprotein
A myeloma protein is an abnormal antibody (immunoglobulin) or (more often) a fragment thereof, such as an immunoglobulin light chain, that is produced in excess by an abnormal monoclonal proliferation of plasma cells, typically in multiple myeloma or Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Other terms for such a protein are monoclonal protein, M protein, M component, M spike, spike protein, or paraprotein. This proliferation of the myeloma protein has several deleterious effects on the body, including impaired immune function, abnormally high blood viscosity ("thickness" of the blood), and kidney damage. History The concept and the term ''paraprotein'' were introduced by the Berlin pathologist Dr Kurt Apitz in 1940, then the senior physician of the pathological institute at the Charité hospital. Paraproteins allowed the detailed study of immunoglobulins, which eventually led to the production of monoclonal antibodies in 1975. Cause Myeloma is a malignancy of pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malignancy
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse. Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not self-limited in its growth, is capable of invading into adjacent tissues, and may be capable of spreading to distant tissues. A benign tumor has none of those properties. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis. Malignant tumors are also characterized by genome instability, so that cancers, as assessed by whole genome sequencing, frequently have between 10,000 and 100,000 mutations in their entire genomes. Cancers usually show tumour heterogeneity, containing multiple subclones. They also frequently have reduced expression of DNA repair enzymes due to epigenetic methylation of DNA repair genes or altered microRNAs that control DNA repair gene expression. Tumours can be detected through the visual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |